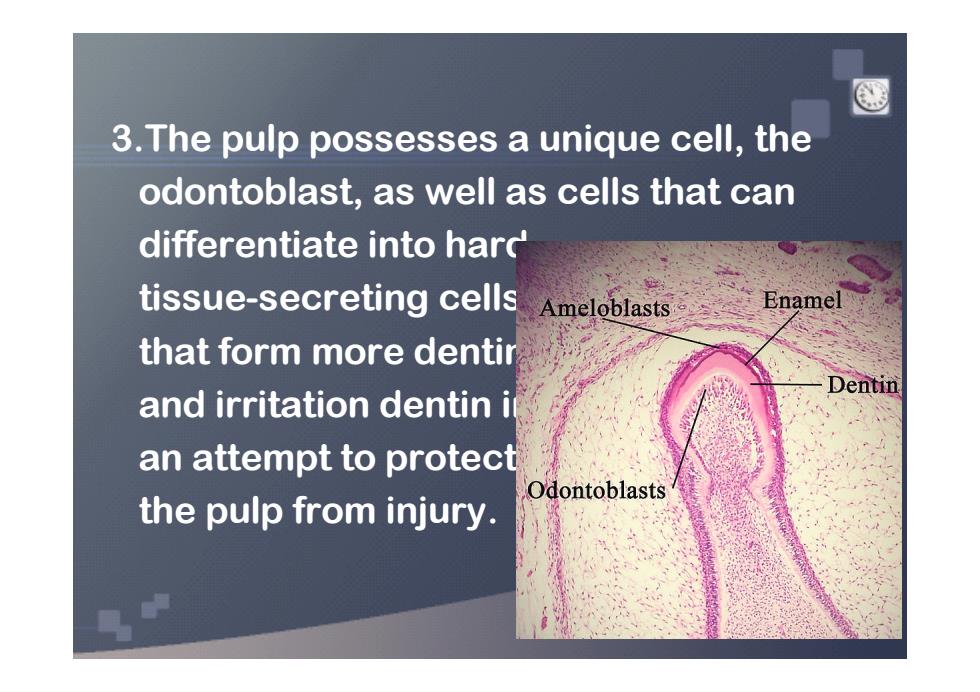
3.The pulp possesses a unique cell,the odontoblast,as well as cells that can differentiate into hard tissue-secreting cells Ameloblasts Enamel that form more dentir Dentin and irritation dentin i an attempt to protect Odontoblasts the pulp from injury
3.The pulp possesses a unique cell, the odontoblast, as well as cells that can differentiate into hard tissue-secreting cells that form more dentin and irritation dentin in an attempt to protect the pulp from injury

The central region of the coronal and radicular pulp contains large nerve trunks and blood vessels. This area is lined peripherally by a specialized odontogenic area which has four lavers
• The central region of the coronal and radicular pulp contains large nerve trunks and blood vessels. • This area is lined peripherally by a specialized odontogenic area which has four layers
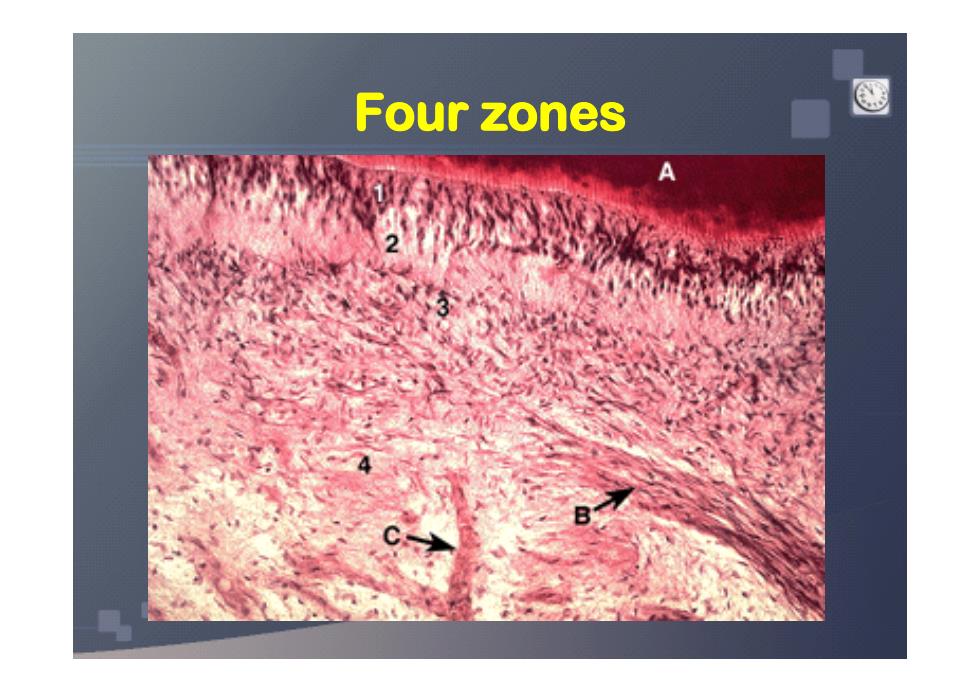
Four zones A
Four zones Four zones Four zones Four zones
Structural elements Odontoblasts Fibroblasts Cells- Reserve cells Defense cells Pulp Fibers Extracellular Ground substance Intercellular fluid
Pulp Cells Extracellular Odontoblasts Fibroblasts Reserve cells Defense cells Fibers Ground substance Intercellular fluid Structural elements Structural elements Structural elements Structural elements

Odontoblasts -The odontoblasts are highly specialized connective tissue cells of the dental pulp.They play the unique role in both dentin an Dentin Tubules Secretion of dentin Formation of dentinal tubules odontoblasts-
Odontoblasts ——The odontoblasts are highly specialized connective tissue cells of the dental pulp. They play the unique role in both dentin and pulp function. • Secretion of dentin • Formation of dentinal tubules