
How to describe heat transfer inside human tissue? 。For in vitro tissue 。For in vivo tissue The existence of blood flow and metabolic rate of in living tissue when in vivo
How to describe heat transfer inside human tissue? • For in vitro tissue • For in vivo tissue The existence of blood flow and metabolic rate of in living tissue when in vivo
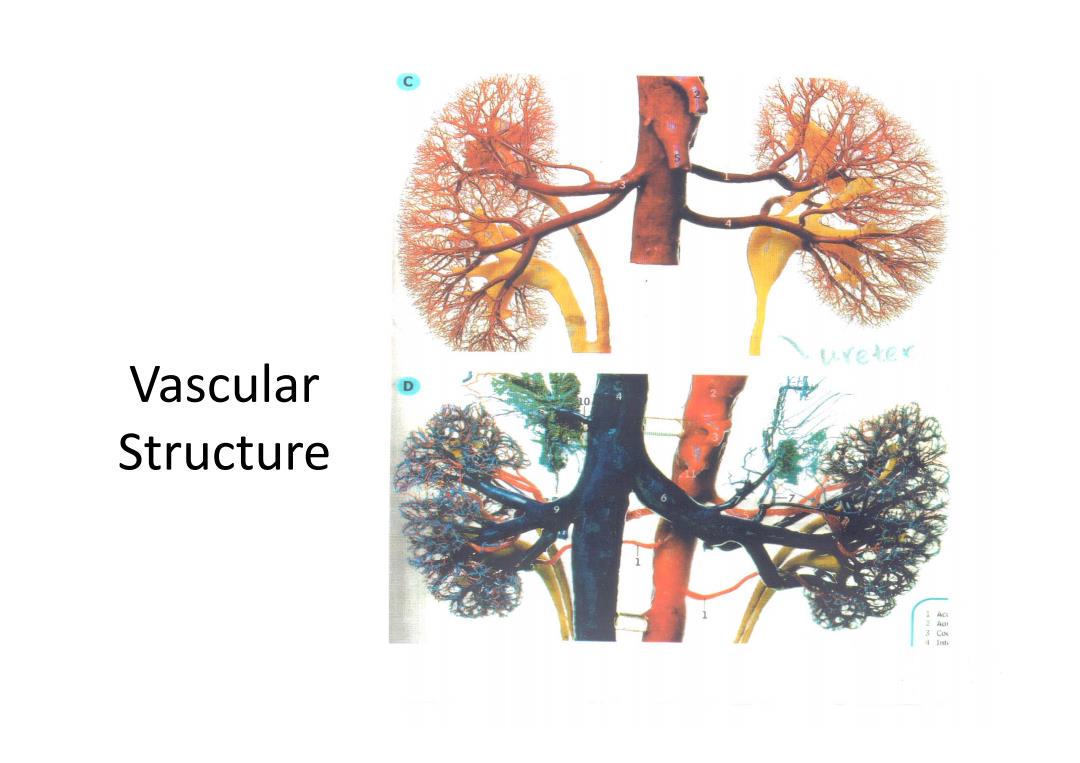
ee¥ Vascular D Structure +2家
Vascular Structure
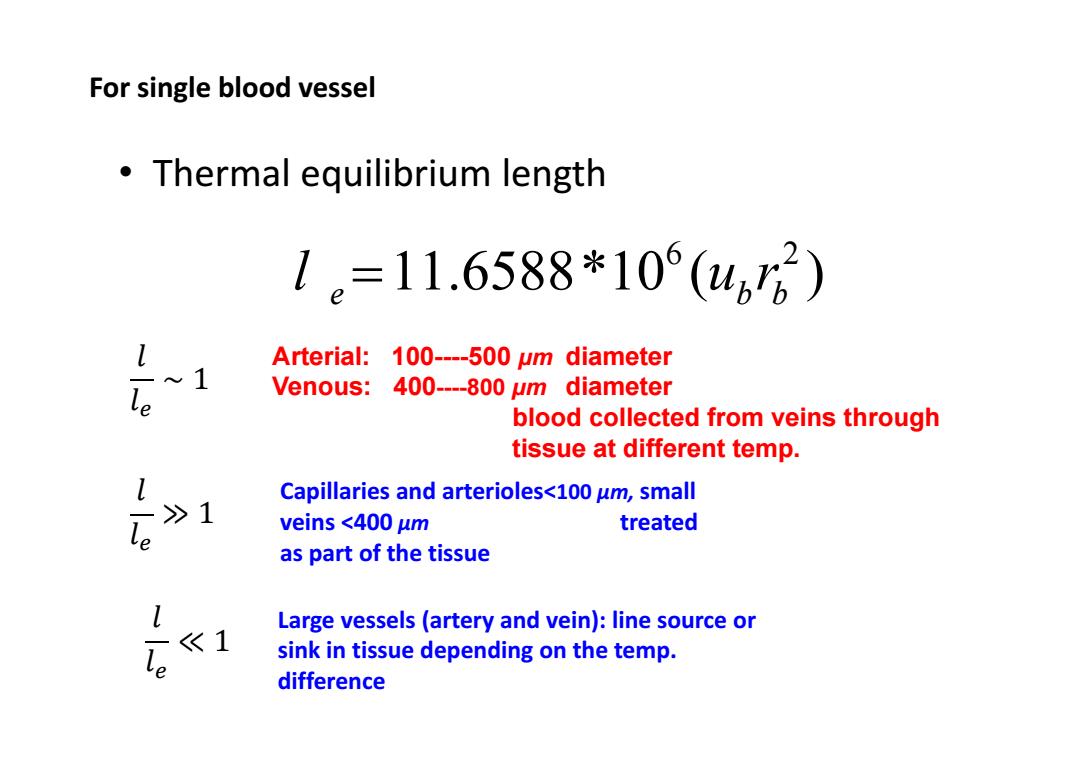
For single blood vessel Thermal equilibrium length 1e=11.6588*10(416) Arterial:100----500 um diameter 1 le Venous:400----800 um diameter blood collected from veins through tissue at different temp. Capillaries and arterioles<100 um,small >1 veins <400 um treated as part of the tissue Large vessels (artery and vein):line source or <1 le sink in tissue depending on the temp. difference
• Thermal equilibrium length 6 2 11.6588*10 ( ) e bb l ur For single blood vessel Arterial: 100----500 μm diameter Venous: 400----800 μm diameter blood collected from veins through tissue at different temp. ݈ ݈ ∼ 1 ݈ ݈ ≫ 1 ݈ ݈ ≪ 1 Large vessels (artery and vein): line source or sink in tissue depending on the temp. difference Capillaries and arterioles<100 μm, small veins <400 μm treated as part of the tissue

Bio-heat Transfer Equations
Bio‐heat Transfer Equations
The Pennes Equation a)Experimental study-Temp mapping in the Human Forearm Subjects:Bare forearms of normotensive males (Neurological Institute) Environmental conditions: Room Temperature 25-27C Relative Humidity:=62% Air:Free convection Measurement: T-type thermocouples J.A.P Vol.1No.2p.93-122,1948 H.H.Pennes Surface temp. Blood temp
The Pennes Equation a) Experimental study‐Temp mapping in the Human Forearm Subjects: Bare forearms of normotensive males (Neurological Institute) Environmental conditions: Room Temperature 25‐27℃ Relative Humidity: Air: Free convection Measurement: T‐type thermocouples J.A.P Vol. 1 No.2 p.93‐122, 1948 H.H.Pennes Surface temp. Blood temp. 62%