
哈佛光谱分类 Harvard大学天文台的天文学家在1890-1910年首 先提出的恒星光谱分类法。 PLATE 8.The Harvard College Observatory was known in the 1890s for the many women it employed to classify stellar spectra.Among those shown here in 1892 are Henrietta S.Leavitt (third from left).Williamina P.Fleming (standing),and Annie Jump Cannon (far right).(New England Magazine.n.s.6 [1892]:166.) (Edward)Pickering's Women Annie Jump Cannon
哈佛光谱分类 n Harvard大学天文台的天文学家在1890-1910年首 先提出的恒星光谱分类法。 (Edward) Pickering’s Women Annie Jump Cannon

The Harvard spectral classification Developed by Annie J.Cannon at Harvard Observatory and adopted in 1910 as the international standard Initially based upon the strengths of the hydrogen Balmer absorption lines (ABC...with A having the strongest Balmer lines,and P the weakest) a Some letters were dropped and the ordering was changed according to a sequence of decreasing temperatures. OBAFGKM The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system,such as class D for white dwarfs and classes S and C for carbon stars
The Harvard spectral classification n Developed by Annie J. Cannon at Harvard Observatory and adopted in 1910 as the international standard n Initially based upon the strengths of the hydrogen Balmer absorption lines (ABC… with A having the strongest Balmer lines, and P the weakest) n Some letters were dropped and the ordering was changed according to a sequence of decreasing temperatures. n O B A F G K M The sequence has been expanded with classes for other stars and star-like objects that do not fit in the classical system, such as class D for white dwarfs and classes S and C for carbon stars
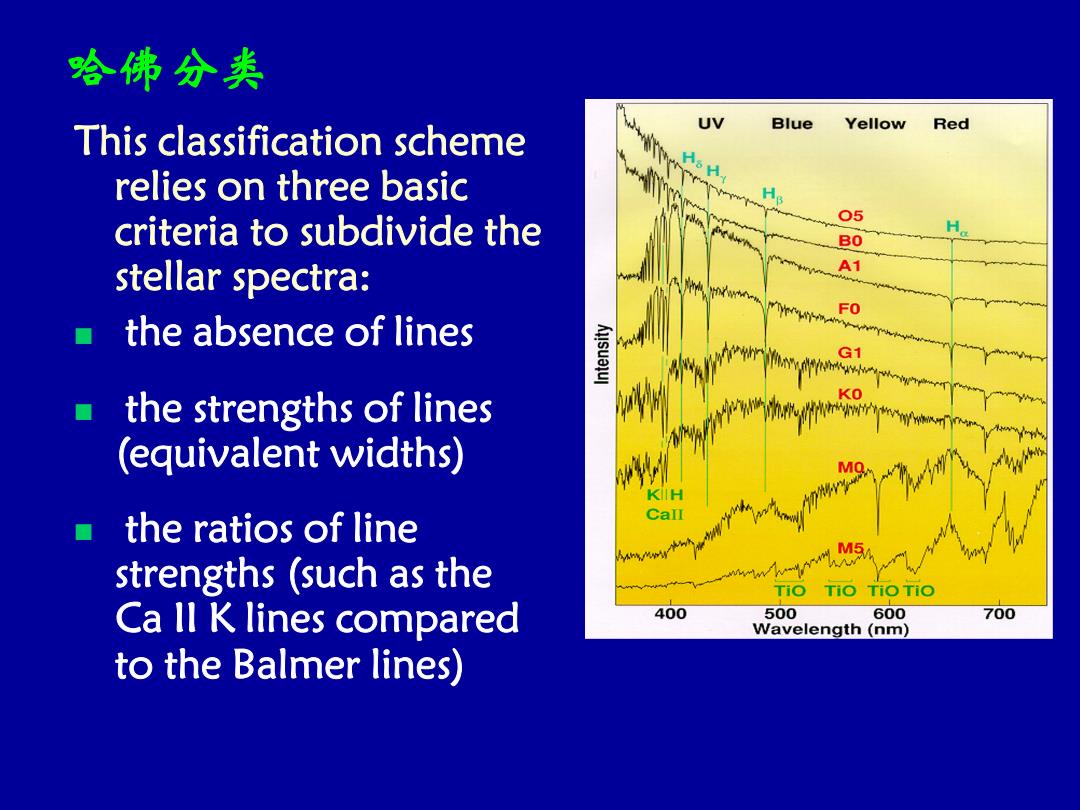
哈佛分类 UV Blue Yellow This classification scheme Red relies on three basic criteria to subdivide the O5 H BO stellar spectra: A1 FO the absence of lines the strengths of lines (equivalent widths) the ratios of line Call M5 strengths (such as the wwwh-pwh TiO TiO TiOTiO Ca ll K lines compared 400 500 600 700 Wavelength (nm) to the Balmer lines)
哈佛分类 This classification scheme relies on three basic criteria to subdivide the stellar spectra: n the absence of lines n the strengths of lines (equivalent widths) n the ratios of line strengths (such as the Ca II K lines compared to the Balmer lines)

S O-B一A-F一G一K-H R—N O stars are the hottest stars,M stars are the coolest O,B,and A stars are also called early-type stars;K and M stars are called late-type stars Each spectral type is divided into ten parts from O (early)to 9(late);for example ..F8 F9 GO G1 G2 G3..G9K0.. The Sun is spectral type G2 右端的S、R和N等分支反映化学组成的差别,都 属于AGB星的亚类,R、N是碳星,S是中问类型 ,M型AGB星又称为富氧AGB星
n O stars are the hottest stars, M stars are the coolest n O,B, and A stars are also called early-type stars; K and M stars are called late-type stars n Each spectral type is divided into ten parts from 0 (early) to 9 (late); for example … F8 F9 G0 G1 G2 G3 … G9 K0 … n The Sun is spectral type G2 n 右端的S、R和N等分支反映化学组成的差别,都 属于AGB星的亚类,R、N是碳星,S是中间类型 ,M型AGB星又称为富氧AGB星
Stellar Spectral Classification 4 Spectral types 4.1 "Early"and "late"nomenclature 4.2 Class O 4.3 Class B 4.4 Class A 4.5 Class F 4.6 Class G 4.7 Class K 4.8 Class M 5 Extended spectral types 5.1 Hot blue emission star classes 5.1.1 Class W:Wolf-Rayet 5.1.2 The "Slash"stars 5.2 Cool red and brown dwarf classes 5.2.1 Class L 5.2.2 Class T:methane dwarfs 5.2.3 Class Y 5.3 Late giant carbon-star classes 5.3.1 Class C:carbon stars 5.3.2 Class S 5.3.3 Classes MS and SC:intermediary carbon-related classes 5.4 White dwarf classifications
Stellar Spectral Classification