
4 Requirements for Cluster Analysis(1) .Scalability .Ability to deal with different types of attributes Discovery of clusters with arbitrary shape Requirements for domain knowledge to determine input parameters 11 DATA Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 11 4 Requirements for Cluster Analysis(1) Scalability Ability to deal with different types of attributes Discovery of clusters with arbitrary shape Requirements for domain knowledge to determine input parameters
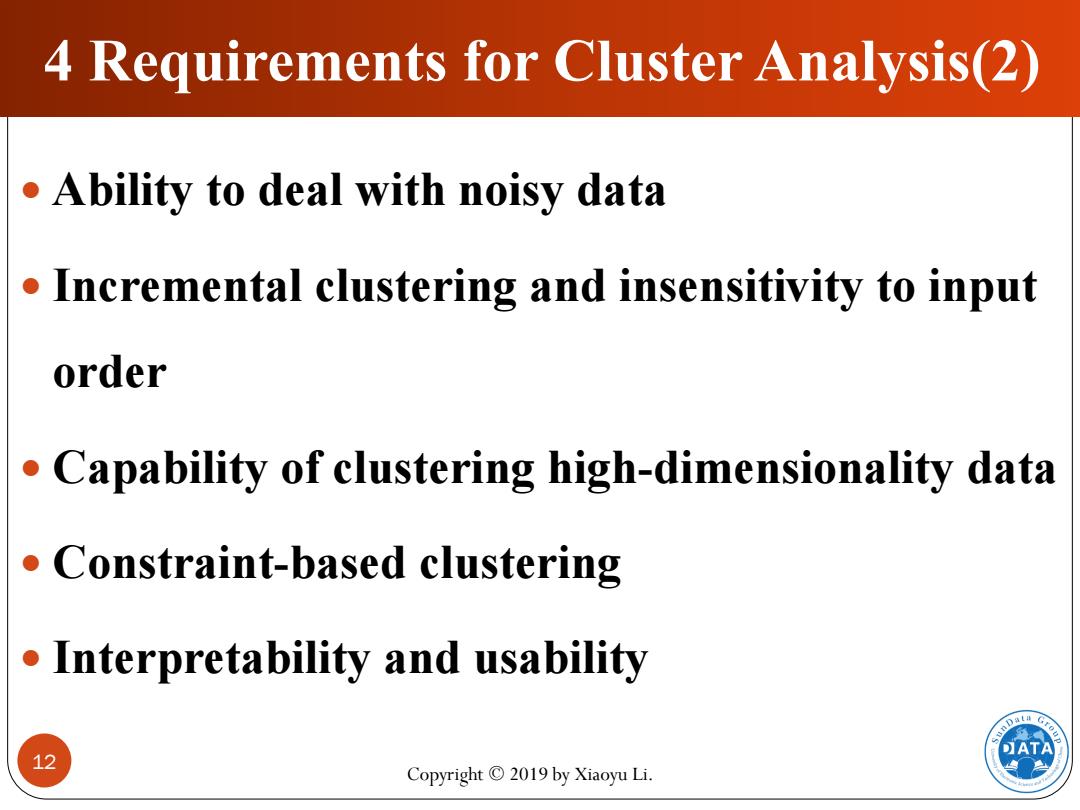
4 Requirements for Cluster Analysis(2) Ability to deal with noisy data Incremental clustering and insensitivity to input order Capability of clustering high-dimensionality data Constraint-based clustering Interpretability and usability DATA 12 Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 12 4 Requirements for Cluster Analysis(2) Ability to deal with noisy data Incremental clustering and insensitivity to input order Capability of clustering high-dimensionality data Constraint-based clustering Interpretability and usability

Similarity Calculation --Reference 1 Comparing Similarity Calculation Methods in Conversational CBR Mingyang Gu,Xin Tong,and Agnar Aamodt Department of Computer and Information Science,Norwegian University of Science and Technology,Sem Saelands vei 7-9,N-7491,Trondheim,Norway Email:mingyang,tongxin,agnar@idi.ntnu.no 13 DATA Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 13 Similarity Calculation --Reference 1

1 Data Types(1) Based on memory clustering algorithms use the following two data structures: Data matrix Dissimilarity matrix x11 x1f x1p 0 … d2,) 0 Xil … d3,I) d(3,2) 0 xnf d(n,1) d(n,2) .0 DATA 14 Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 14 1 Data Types(1) Based on memory clustering algorithms use the following two data structures: Data matrix & Dissimilarity matrix np ... x nf ... x n1 x ... ... ... ... ... ip ... x if ... x i1 x ... ... ... ... ... 1p ... x 1f ... x 11 x ( ,1) ( ,2) ... 0 : : : ) (3,2) d n d n ... d(3,1 d 0 d(2,1) 0 0
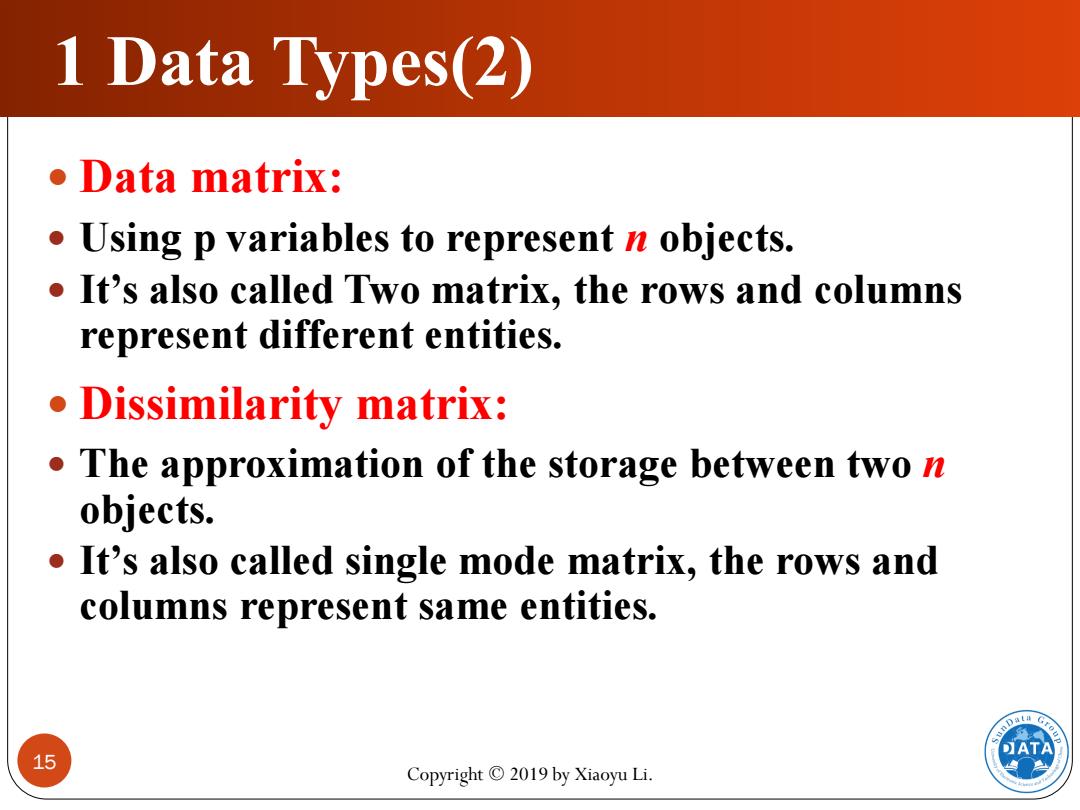
1 Data Types(2) ●Data matrix: Using p variables to represent n objects. It's also called Two matrix,the rows and columns represent different entities. Dissimilarity matrix: ● The approximation of the storage between two n objects. ● It's also called single mode matrix,the rows and columns represent same entities. 15 DATA Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 15 1 Data Types(2) Data matrix: Using p variables to represent n objects. It’s also called Two matrix, the rows and columns represent different entities. Dissimilarity matrix: The approximation of the storage between two n objects. It’s also called single mode matrix, the rows and columns represent same entities