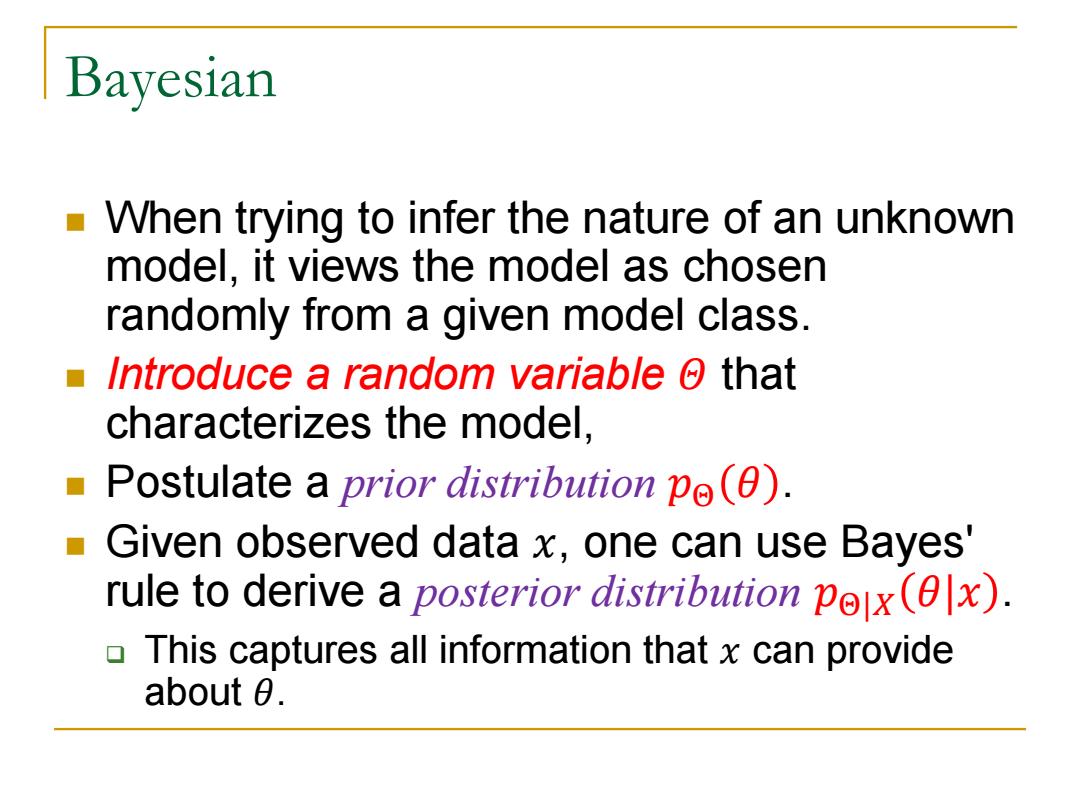
Bayesian When trying to infer the nature of an unknown model,it views the model as chosen randomly from a given model class. Introduce a random variable o that characterizes the model, Postulate a prior distribution pe(). ■ Given observed data x,one can use Bayes' rule to derive a posterior distribution pox(x). This captures all information that x can provide about 0
Bayesian When trying to infer the nature of an unknown model, it views the model as chosen randomly from a given model class. Introduce a random variable 𝛩 that characterizes the model, Postulate a prior distribution 𝑝Θ 𝜃 . Given observed data 𝑥, one can use Bayes' rule to derive a posterior distribution 𝑝Θ|𝑋 𝜃|𝑥 . This captures all information that 𝑥 can provide about 𝜃

Classical/frequentist -View the unknown quantity 0 as an unknown constant. ■ Strives to develop an estimate of 0. We are dealing with multiple candidate probabilistic models,one for each possible value of 0
Classical/frequentist View the unknown quantity 𝜃 as an unknown constant. Strives to develop an estimate of 𝜃. We are dealing with multiple candidate probabilistic models, one for each possible value of 𝜃
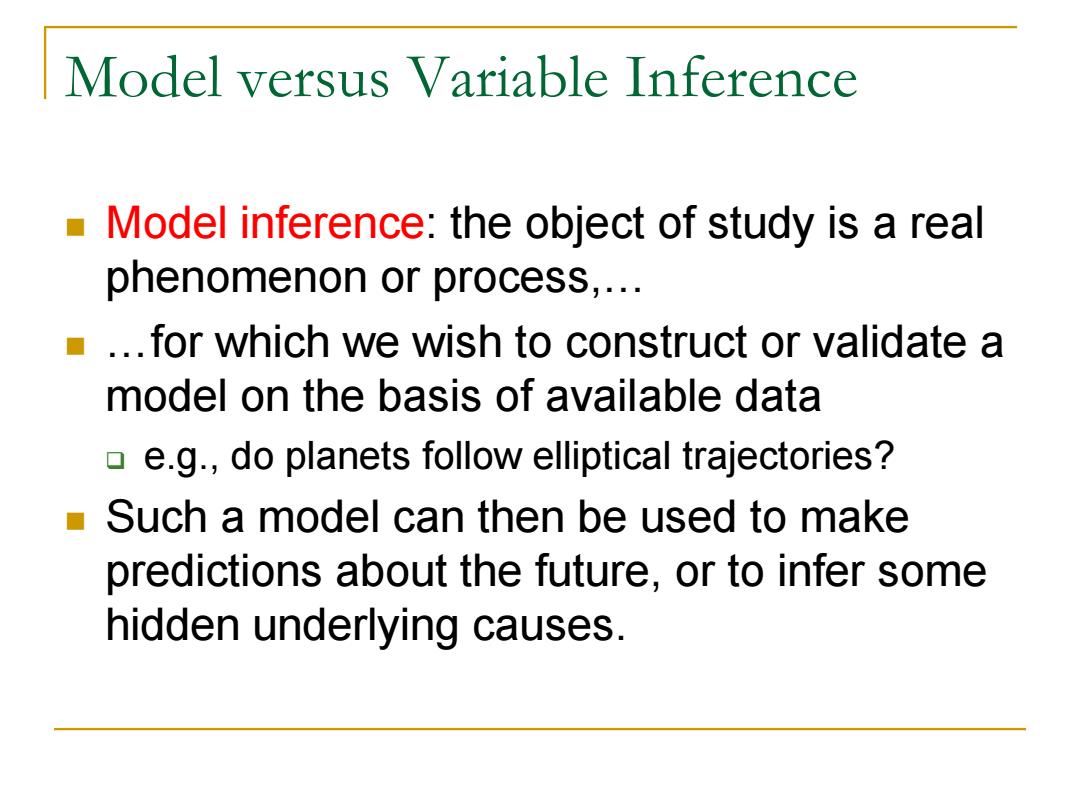
Model versus Variable Inference Model inference:the object of study is a real phenomenon or process,... ..for which we wish to construct or validate a model on the basis of available data e.g.,do planets follow elliptical trajectories? ■、 Such a model can then be used to make predictions about the future,or to infer some hidden underlying causes
Model versus Variable Inference Model inference: the object of study is a real phenomenon or process,… …for which we wish to construct or validate a model on the basis of available data e.g., do planets follow elliptical trajectories? Such a model can then be used to make predictions about the future, or to infer some hidden underlying causes
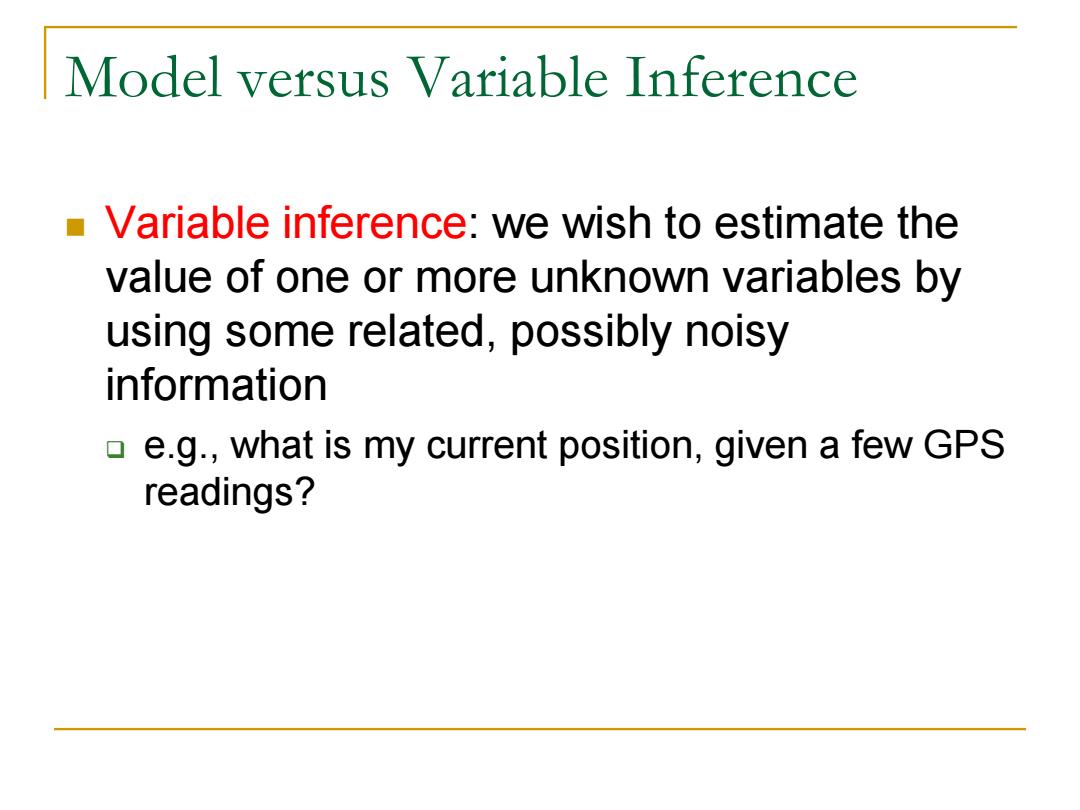
Model versus Variable Inference Variable inference:we wish to estimate the value of one or more unknown variables by using some related,possibly noisy information e.g.,what is my current position,given a few GPS readings?
Model versus Variable Inference Variable inference: we wish to estimate the value of one or more unknown variables by using some related, possibly noisy information e.g., what is my current position, given a few GPS readings?
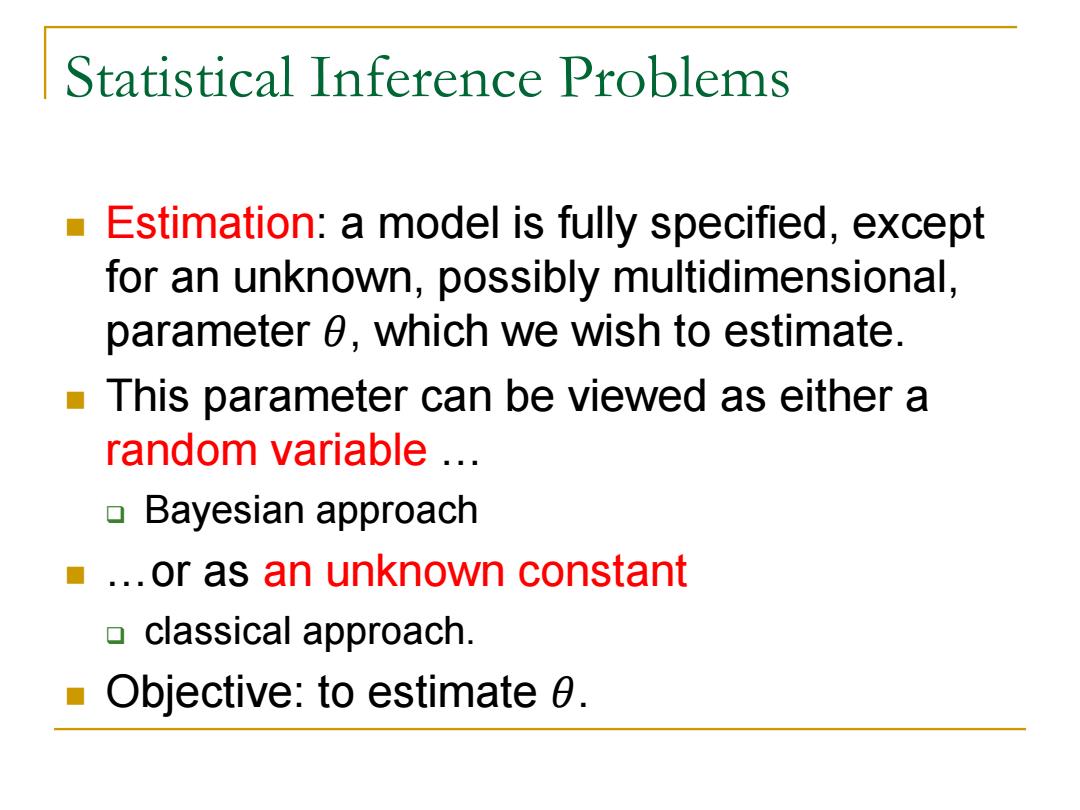
Statistical Inference Problems Estimation:a model is fully specified,except for an unknown,possibly multidimensional, parameter 0,which we wish to estimate. This parameter can be viewed as either a random variable .. Bayesian approach ..or as an unknown constant ▣classical approach. Objective:to estimate 0
Statistical Inference Problems Estimation: a model is fully specified, except for an unknown, possibly multidimensional, parameter 𝜃, which we wish to estimate. This parameter can be viewed as either a random variable … Bayesian approach …or as an unknown constant classical approach. Objective: to estimate 𝜃