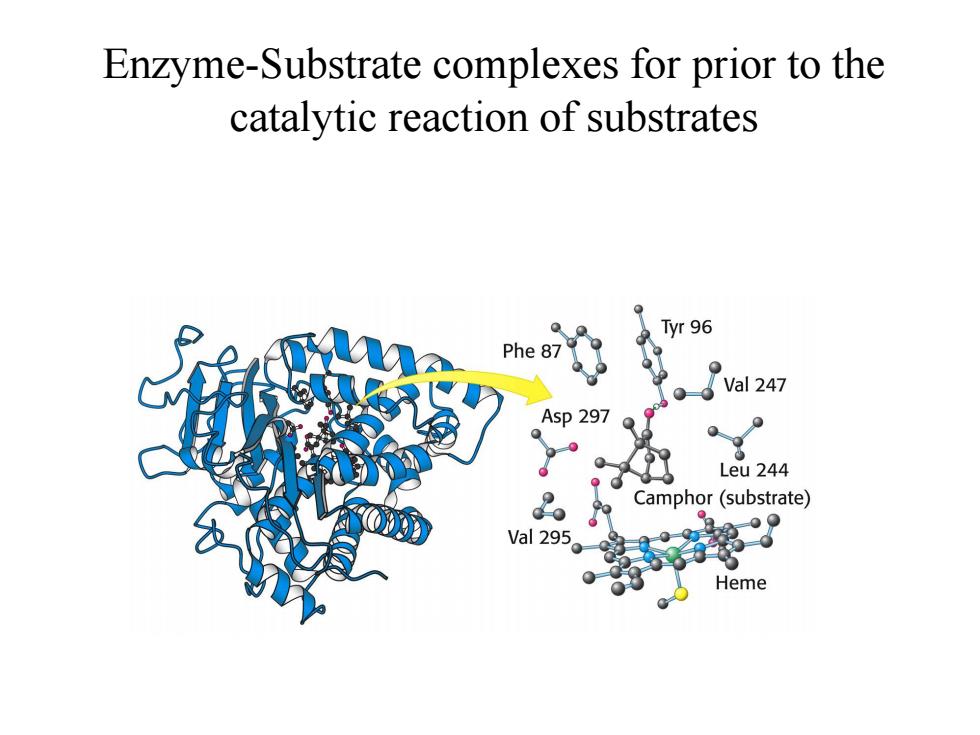
Enzyme-Substrate complexes for prior to the catalytic reaction of substrates Tyr 96 Phe 87 Val 247 Asp 297 Leu 244 Camphor(substrate) val295。% Heme
Enzyme-Substrate complexes for prior to the catalytic reaction of substrates
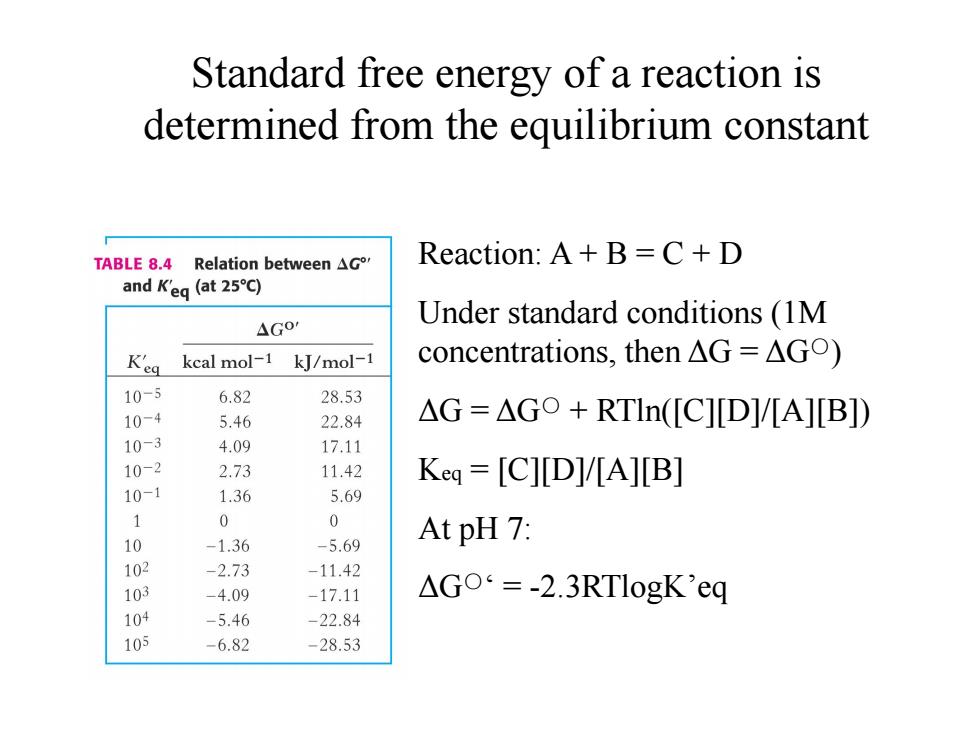
Standard free energy of a reaction is determined from the equilibrium constant TABLE 8.4 Relation between AG Reaction:A+B=C+D and K'eg (at 25C) 4G0 Under standard conditions (1M K'eg kcal mol-1 kJ/mol-1 concentrations,then△G=△Go) 10-5 6.82 28.53 10-4 5.46 22.84 △G=△Go+RTln([C][D]V[A][B]) 10-3 4.09 17.11 10-2 2.73 11.42 Keq=[C][D]/[A][B] 10-1 1.36 5.69 0 0 10 -1.36 -5.69 At pH 7: 102 -2.73 -11.42 103 -4.09 -17.11 △Go=-2.3 RTlogK'eq 104 -5.46 -22.84 105 -6.82 -28.53
Reaction: A + B = C + D Under standard conditions (1M concentrations, then ΔG = ΔG○) ΔG = ΔG○ + RTln([C][D]/[A][B]) Keq = [C][D]/[A][B] At pH 7: ΔG○‘ = -2.3RTlogK’eq Standard free energy of a reaction is determined from the equilibrium constant

10.2·Enzymes Provide Enormous Rate Accelerations Enzymes are powerful catalysts. Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are typically 107 to 1014 times faster than their uncatalyzed counterparts
10.2 • Enzymes Provide Enormous Rate Accelerations Enzymes are powerful catalysts. Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are typically 107 to 1014 times faster than their uncatalyzed counterparts