
全科医生的哲学方法 ■人的自然属性-生物学特征-疾病 ■人的社会属性-社会学特征-病人 ■整体观 ■人的各个组成部分之间: 口在结构上不可分割 口在病理上相互影响 口在功能上相互协同 ■人自身、人与环境之间统一性、完整性、关联性 ■体现医生的“全方位”或“立体性”思维方式 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

两个中心 专科医疗 以疾病为中心 disease-centered care 全科医疗 以人为中心 person-centered care This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

以病人为中心 ■病人是疾病的载体,但病人不仅仅是疾病的载 体,病人除了有疾病的生物学特征外,还具有人 的心理和社会学特征。 “了解你的病人是什么样的人,比了解他们患了 什么病重要得多” 希波克拉底 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information
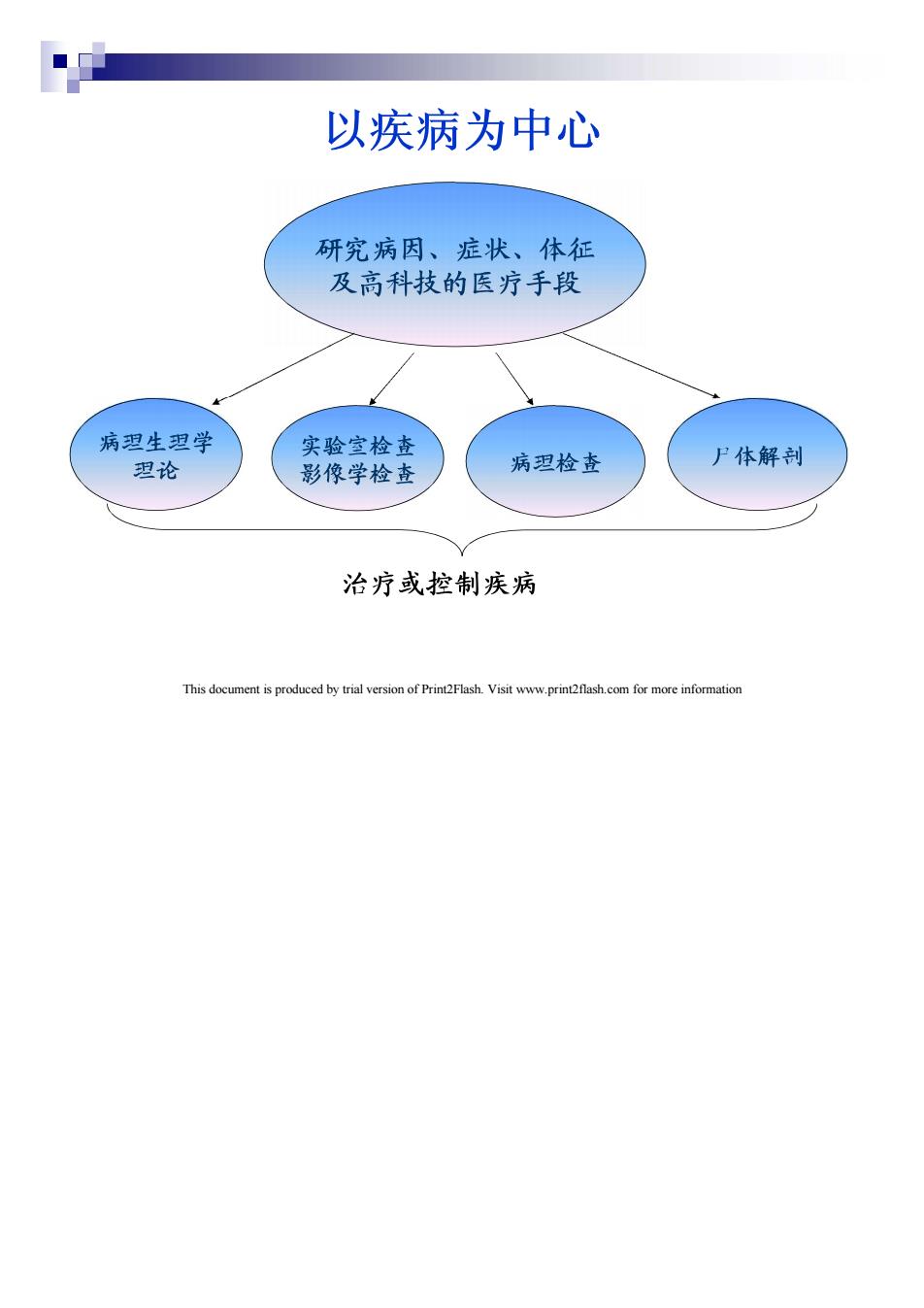
以疾病为中心 研究病因、症状、体征 及高科技的医疗手段 病塑生塑学 实验室检查 塑论 尸体解剖 影像学检查 病塑检查 治疗或控制疾病 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information

二、生物医学模式-以疾病为中心 biomedical model -disease centered ■模式:一词源于数学模型,是用于阐述 某种现象数量变化的。现泛指某种事物 的标准形象迫使人们照着做,学习做的 标准样式,从而构成我们观察、解决问 题的思维方式。 This document is produced by trial version of Print2Flash.Visit www.print2flash.com for more information