
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Structure Name Acyl group 0 CH3CCO2H Pyruvic Pyruvoyl OH HOCH2CHCO2H Glyceric Glyceroyl OH HO2CCHCH2CO2H Malic Maloyl 0 HO2CCCH2CO2H Oxaloacetic Oxaloacetyl CO2H Benzoic Benzoyl CO2H Phthalic Phthaloyl CO2H
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles

Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Nitriles,RCEN Compounds containing -C=N functional group are called nitriles Named by adding -nitrile as a suffix to the alkane name Nitrile carbon numbered C1 CH3 CH3CHCH2CH2CN 4-Methylpentanenitrile 54321
Nitriles, RC≡N Compounds containing -C≡N functional group are called nitriles ▪ Named by adding –nitrile as a suffix to the alkane name ▪ Nitrile carbon numbered C1 Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
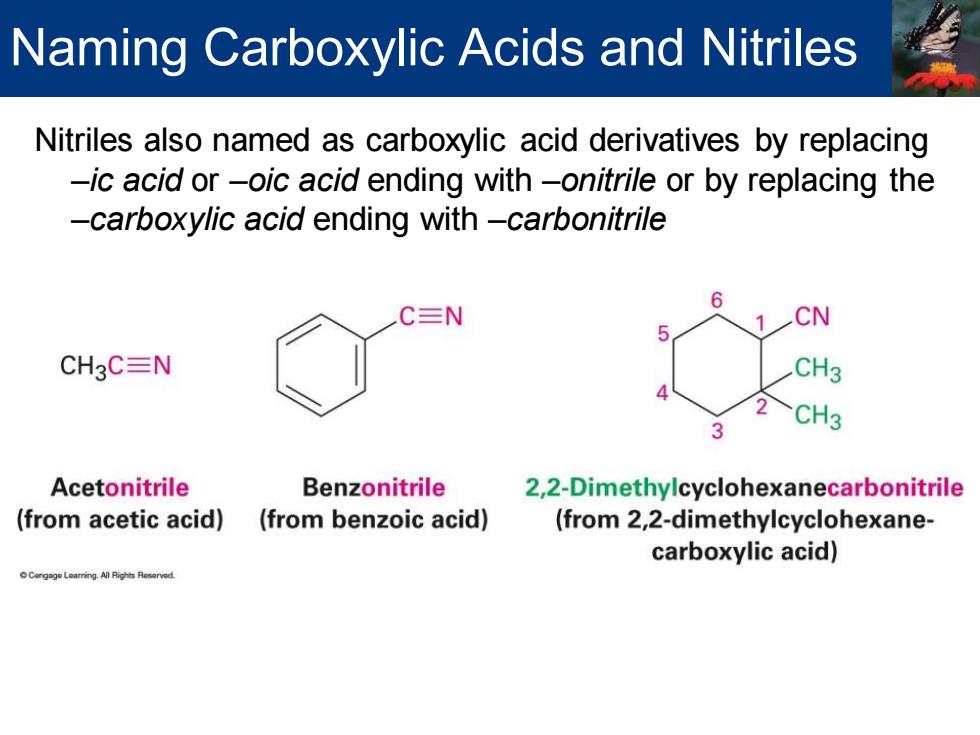
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Nitriles also named as carboxylic acid derivatives by replacing -ic acid or-oic acid ending with-onitrile or by replacing the -carboxylic acid ending with-carbonitrile C三N CN CH3C=N CH3 Acetonitrile Benzonitrile 2,2-Dimethylcyclohexanecarbonitrile (from acetic acid) (from benzoic acid) (from 2,2-dimethylcyclohexane- carboxylic acid)
Nitriles also named as carboxylic acid derivatives by replacing –ic acid or –oic acid ending with –onitrile or by replacing the –carboxylic acid ending with –carbonitrile Naming Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
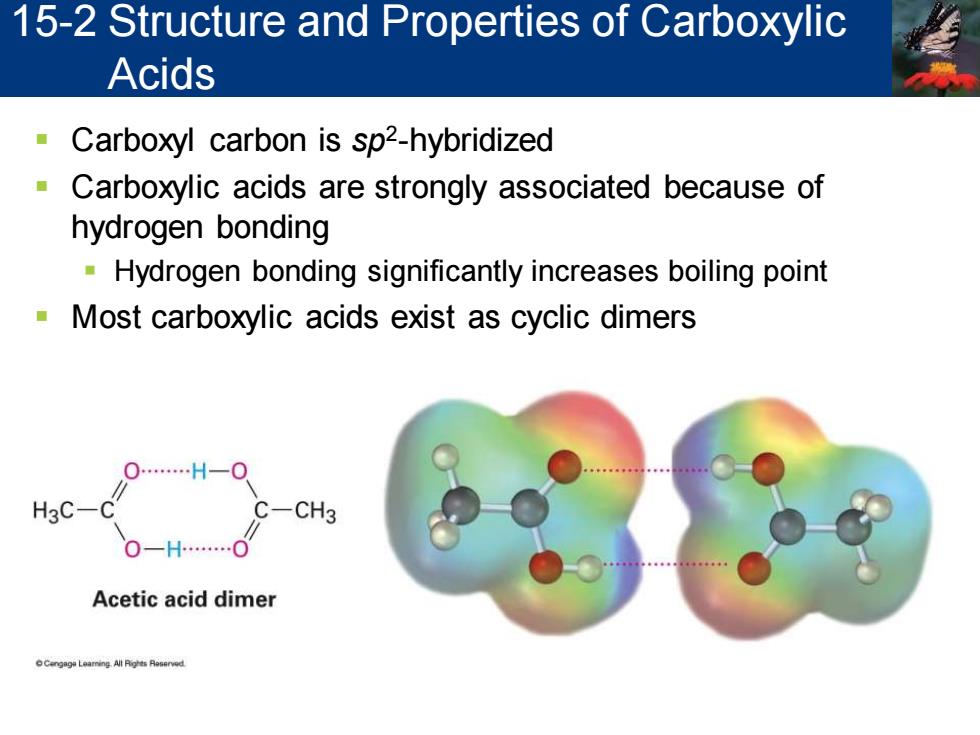
15-2 Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids Carboxyl carbon is sp2-hybridized a Carboxylic acids are strongly associated because of hydrogen bonding Hydrogen bonding significantly increases boiling point Most carboxylic acids exist as cyclic dimers O…H-O H3C-C C- CH3 Acetic acid dimer
▪ Carboxyl carbon is sp2 -hybridized ▪ Carboxylic acids are strongly associated because of hydrogen bonding ▪ Hydrogen bonding significantly increases boiling point ▪ Most carboxylic acids exist as cyclic dimers 15-2 Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids
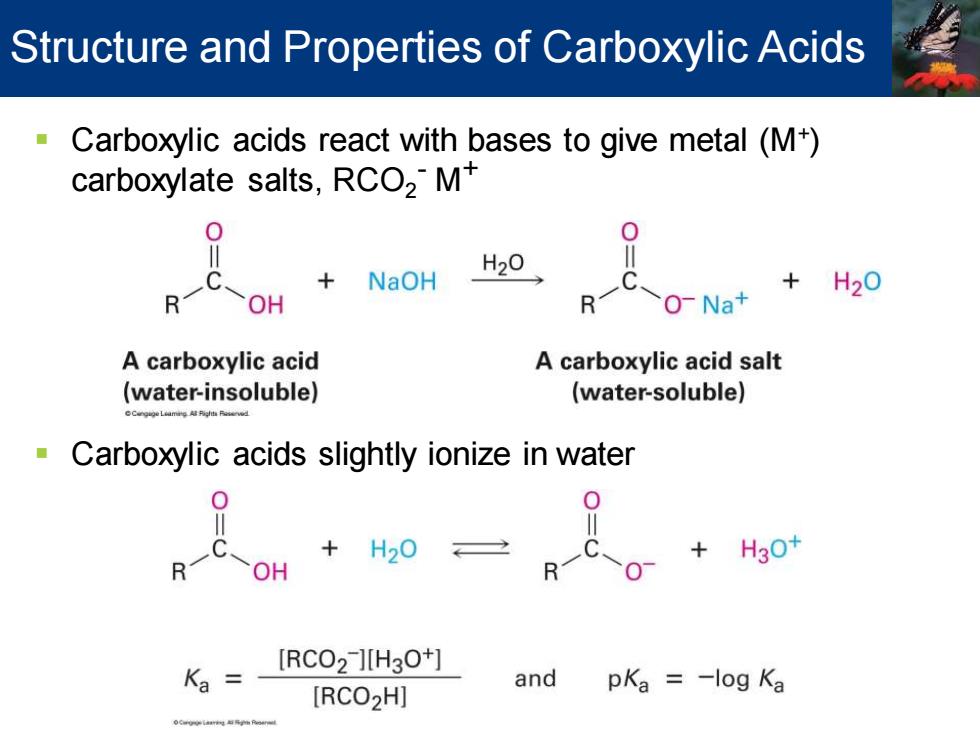
Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids react with bases to give metal(M+) carboxylate salts,RCO2M NaOH H20 +H20 OH R O-Na+ A carboxylic acid A carboxylic acid salt (water-insoluble) (water-soluble) Carboxylic acids slightly ionize in water R一 +H30 OH [RCO2 ][H3O+] Ka and pKa =-log Ka [RCO2H]
▪ Carboxylic acids react with bases to give metal (M+ ) carboxylate salts, RCO2 - M+ ▪ Carboxylic acids slightly ionize in water Structure and Properties of Carboxylic Acids