
Major Uses of Alkanes C-C2:gases(natural gas) C3-C4:liquified petroleum(LPG) ■Cs-Cg:gasoline C-C16:diesel,kerosene,jet fuel C17-up:lubricating oils,heating oil Origin:petroleum refining
Major Uses of Alkanes ◼C1 -C2 : gases (natural gas) ◼C3 -C4 : liquified petroleum (LPG) ◼C5 -C8 : gasoline ◼C9 -C16: diesel, kerosene, jet fuel ◼C17-up: lubricating oils, heating oil ◼Origin: petroleum refining
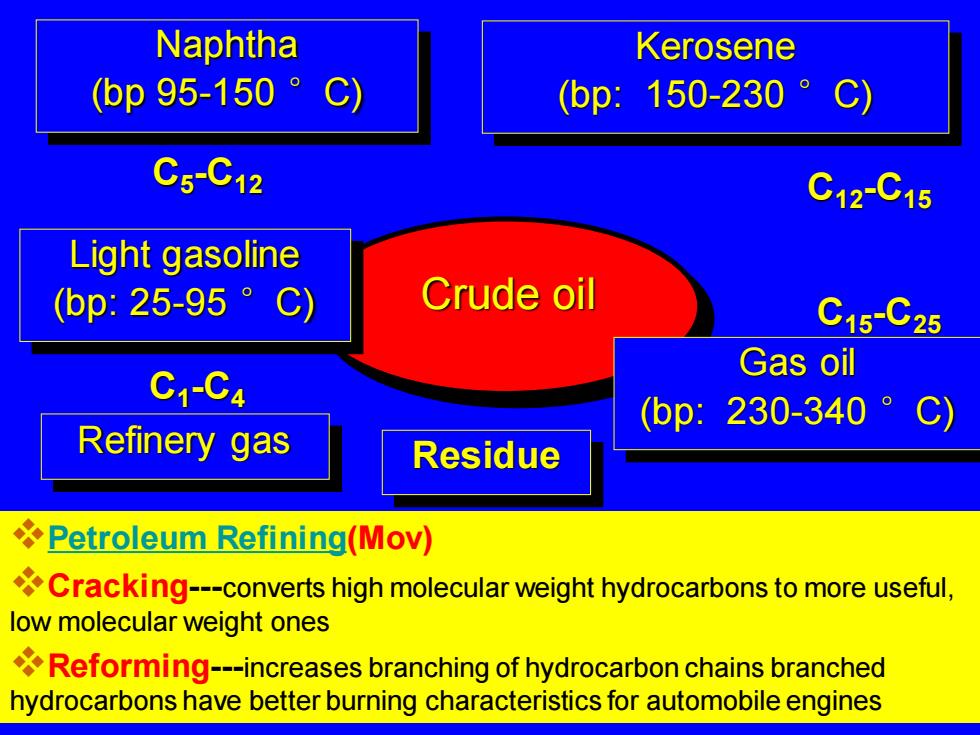
Naphtha Kerosene (bp95-150 C) (bp:150-230 C5-C12 C12C15 Light gasoline (bp:25-95°C) Crude oil C15-C25 C1-C4 Gas oil (bp:230-340°C) Refinery gas Residue Petroleum Refining(Mov) Cracking---converts high molecular weight hydrocarbons to more useful, low molecular weight ones Reforming---increases branching of hydrocarbon chains branched hydrocarbons have better burning characteristics for automobile engines
Crude oil Refinery gas C1 -C4 Light gasoline (bp: 25-95 °C) C5 -C12 Naphtha (bp 95-150 °C) Kerosene (bp: 150-230 °C) C12-C15 Gas oil (bp: 230-340 °C) C15-C25 Residue ❖Petroleum Refining(Mov) ❖Cracking---converts high molecular weight hydrocarbons to more useful, low molecular weight ones ❖Reforming---increases branching of hydrocarbon chains branched hydrocarbons have better burning characteristics for automobile engines
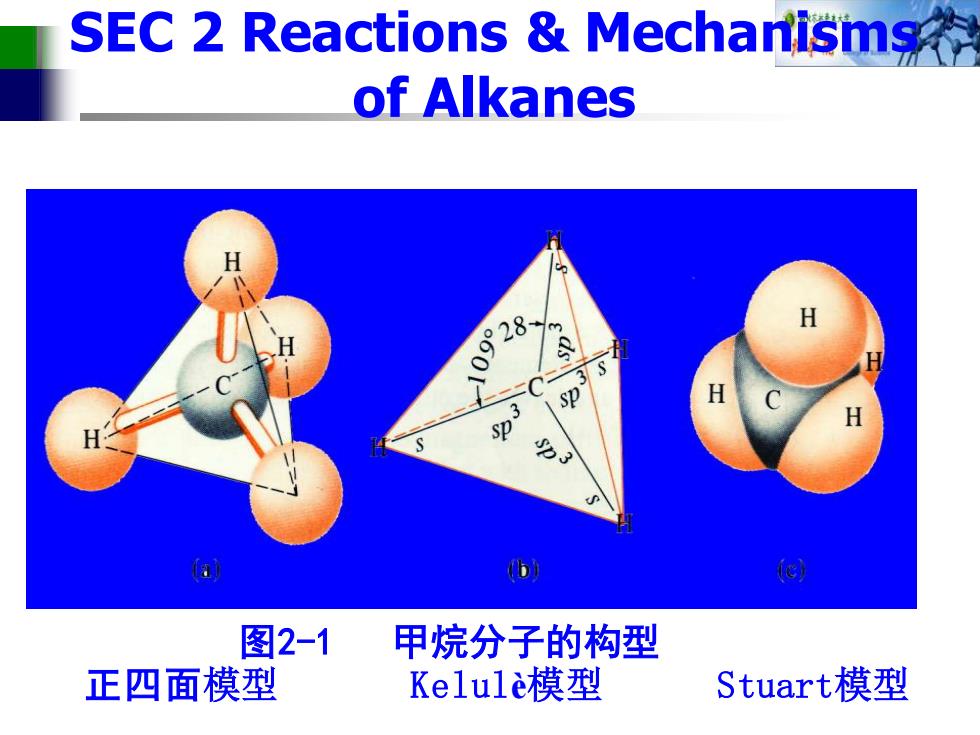
SEC 2 Reactions Mechanismg of Alkanes 0928 H sp %3 a 图2-1 甲烷分子的构型 正四面模型 Kelulè模型 Stuart模型
图2-1 甲烷分子的构型 正四面模型 Kelulè模型 Stuart模型 SEC 2 Reactions & Mechanisms of Alkanes

0秋精对 Structure 批中院 Alkane:single bonds,sp3 carbons Cycloalkane:carbons form a ring 结构特征 ■ CH3-CH3 ■SP杂化碳原子四面体碳原子 ■σ键相连 ■键合原子可绕σ键轴“自由”旋转 1874 J.H.Van't Hoff Utrecht Univ
Alkane: single bonds, sp3 carbons Cycloalkane: carbons form a ring ◼结构特征 CH3-CH3 ◼ SP3杂化碳原子 四面体碳原子 ◼ 键相连 ◼ 键合原子可绕键轴“自由”旋转 ❖1874 J.H.Van’t Hoff ❖ Utrecht Univ Structure

自秋不大中 Reactivity of alkanes Chemical stability:C-H;C-C ■不与强酸、强碱、氧化剂反应 ■自由基反应hv
Reactivity of alkanes ◼Chemical stability:C-H; C-C ◼不与强酸、强碱、氧化剂反应 ◼自由基反应 hv