
2.Digestion in the mouth esophagus ●Saliva&its function Nature Composition of saliva pH6.6~7.1,99%water Salivary amylase,lysozyme,salt,etc. Functions of saliva Moisten the cavity solve food;keep the mouth clean;anti-bacteria;digest starch Regulation of salivary secretion Pure neuroregulation Conditioned unconditioned reflex
§ 2. Digestion in the mouth & esophagus • Saliva & its function * Nature & Composition of saliva pH 6.6~7.1, 99% water Salivary amylase, lysozyme, salt, etc. * Functions of saliva Moisten the cavity & solve food; keep the mouth clean; anti-bacteria; digest starch * Regulation of salivary secretion Pure neuroregulation Conditioned & unconditioned reflex

Mastication or chewing its effects Definition Effects Break up large food particles;mixes the food with saliva;aid swallowing Deglutition or swallowing Definition *Process 1st,2nd 3rd phase Peristalsis lower esophageal sphincter
• Mastication or chewing & its effects * Definition * Effects Break up large food particles; mixes the food with saliva; aid swallowing • Deglutition or swallowing * Definition * Process 1st, 2nd & 3rd phase Peristalsis & lower esophageal sphincter
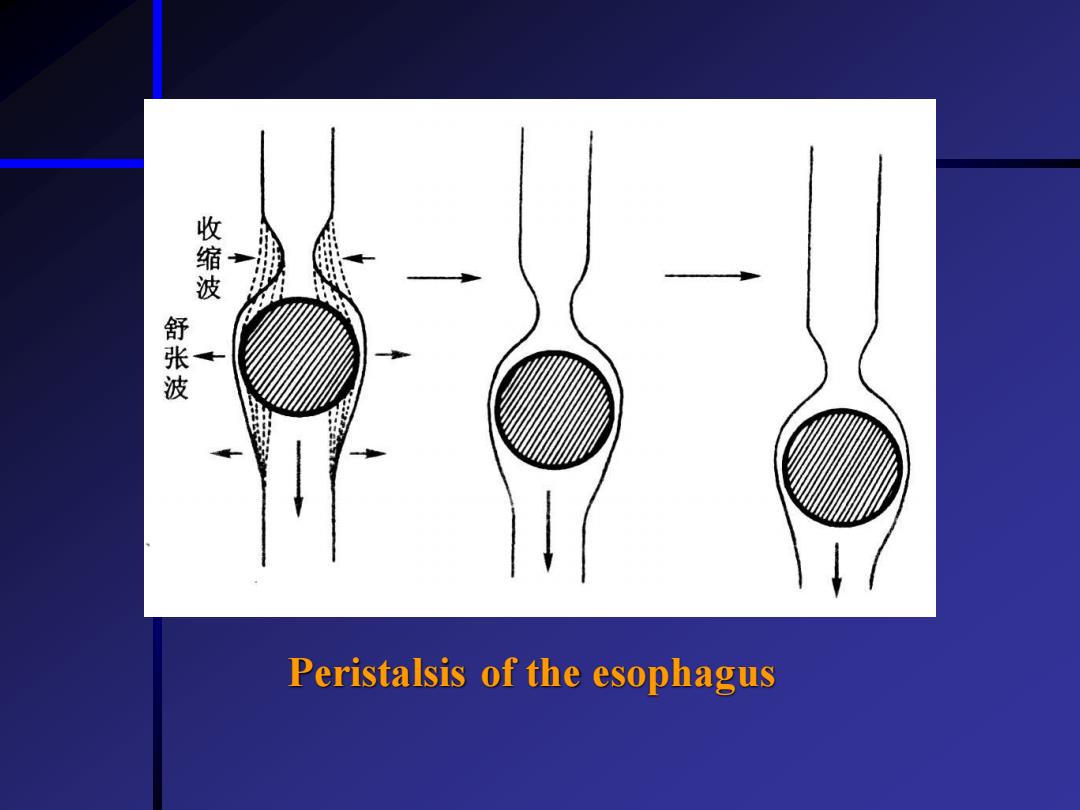
收缩波 舒张 Peristalsis of the esophagus
Peristalsis of the esophagus

3.Digestion in the stomach Gastric juice its secretion Nature,Compositions functions pH 0.9~1.5,colorless,1.5~2.5 L/day Hydrochloric acid (HCI) Secreted by parietal cells Basic secretion:0~5 mmol/h Max secretion:20~25 mmol/h Mechanism of HCI secretion Functions:see next page
§ 3. Digestion in the stomach • Gastric juice & its secretion * Nature, Compositions & functions pH 0.9~1.5, colorless, 1.5~2.5 L/day Hydrochloric acid (HCl) Secreted by parietal cells Basic secretion: 0~5 mmol/h Max secretion: 20~25 mmol/h Mechanism of HCl secretion Functions: see next page

60 0 30 10 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 壁细胞数(10细胞) Relationship between max volume of HCl secretion the number of parietal cells
Relationship between max volume of HCl secretion & the number of parietal cells