
第8章蛋白质分选与膜泡运输 1. 蛋白质分选 2. 膜泡运输
第8章 蛋白质分选与膜泡运输 1. 蛋白质分选 2. 膜泡运输

8.1蛋白质的分选(定向转运) 真核细胞中核编码蛋白的分选概述 蛋白通过三种机制运入细胞器: >门控通道运输:通过核孔复合体运输。 >跨膜运输:内质网、线粒体、叶绿体、过氧化物酶 体蛋白运输。 >膜泡运输:内质网、高尔基体、质膜、溶酶体、胞 内体之间的蛋白运输。 蛋白质分选
8.1 蛋白质的分选(定向转运) 真核细胞中核编码蛋白的分选概述 ❖蛋白通过三种机制运入细胞器 : ➢门控通道运输: 通过核孔复合体运输。 ➢跨膜运输: 内质网、线粒体、叶绿体、过氧化物酶 体蛋白运输。 ➢膜泡运输: 内质网、高尔基体、质膜、溶酶体、胞 内体之间的蛋白运输。 蛋白质分选
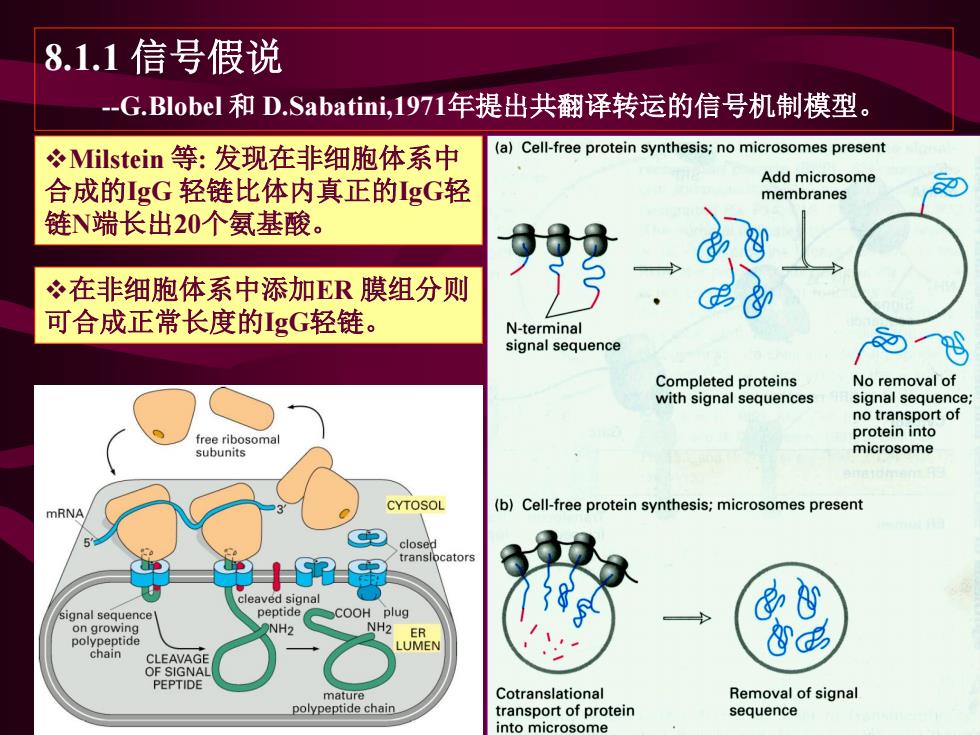
8.1.1信号假说 -G.Blobel和D.Sabatini,1971年提出共翻译转运的信号机制模型。 Milstein等:发现在非细胞体系中 (a)Cell-free protein synthesis;no microsomes present 合成的1gG轻链比体内真正的gG轻 Add microsome membranes 链N端长出20个氨基酸。 在非细胞体系中添加ER膜组分则 可合成正常长度的1gG轻链。 N-terminal signal sequence Completed proteins No removal of with signal sequences signal sequence; no transport of free ribosomal protein into subunits microsome CYTOSOL (b)Cell-free protein synthesis;microsomes present mRNA closed translocators leaved signal signal sequence peptide COOH plug on growing NH2 polypeptide NH2 ER LUMEN chain CLEAVAGE OF SIGNAL PEPTIDE mature Cotranslational Removal of signal polypeptide chain transport of protein sequence nto microsome
8.1.1 信号假说 --G.Blobel 和 D.Sabatini,1971年提出共翻译转运的信号机制模型。 ❖Milstein 等: 发现在非细胞体系中 合成的IgG 轻链比体内真正的IgG轻 链N端长出20个氨基酸。 ❖在非细胞体系中添加ER 膜组分则 可合成正常长度的IgG轻链

细胞内合成的蛋白质、,脂类等物质之所以能够定向的转运到特定的细胞 器取决于两个方面 其一是蛋白质中包含特殊的信号序列(signal seq心uence) 其二是细胞器上具特定的信号识别装置:(分选受体,sorting receptor)
• 细胞内合成的蛋白质、脂类等物质之所以能够定向的转运到特定的细胞 器取决于两个方面: – 其一是蛋白质中包含特殊的信号序列(signal sequence)。 – 其二是细胞器上具特定的信号识别装置(分选受体,sorting receptor)

冬蛋白分选:蛋白分子在蛋白内部的分选信号指导下从细 胞质运往各种目标细胞器或细胞表面。 TABLE 12-3 Some Typical Signal Sequences FUNCTION OF SIGNAL SEQUENCE EXAMPLE OF SIGNAL SEQUENCE Import into nucleus -Pro-Pro-Lys-Lys-Lys-Arg-Lys-Val- Export from nucleus -Leu-Ala-Leu-Lys-Leu-Ala-Gly-Leu-Asp-Ile- Import into mitochondria +HaN-Met-Leu-Ser-Leu-Arg-GIn-Ser-Ile-Arg-Phe-Phe-Lys-Pro-Ala-Thr-Arg-Thr- Leu-Cys-Ser-Ser-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Leu- Import into plastid +HaN-Met-Val-Ala-Met-Ala-Met-Ala-Ser-Leu-GIn-Ser-Ser-Met-Ser-Ser-Leu-Ser- Leu-Ser-Ser-Asn-Ser-Phe-Leu-Gly-GIn-Pro-Leu-Ser-Pro-lle-Thr-Leu-Ser-Pro- Phe-Leu-GIn-Glv- Import into peroxisomes -Ser-Lys-Leu-COO- Import into ER +H2N-Met-Met-Ser-Phe-Val-Ser-Leu-Leu-Leu-Val-Gly-Ile-Leu-Phe-Trp-Ala-Thr- Glu-Ala-Glu-GIn-Leu-Thr-Lys-Cys-Glu-Val-Phe-GIn- Return to ER -Lvs-Asp-Glu-Leu-COO Some characteristic features of the different classes of signal sequences are highlighted in color.Where they are known to be important for the function of the signal seqquence,positively charged amino acids are shown in red and negatively charged amino acids are shown in green.Similary,important hydrophobic arino acids are shown in yellow and hydroxylated amino acids are shown in blue.+H3N indicates the N-teminus of a protein;COO indicates the C-terminus. 冬没有任何信号肽(序列)的蛋白是细胞质基质驻留蛋白
❖蛋白分选: 蛋白分子在蛋白内部的分选信号指导下从细 胞质运往各种目标细胞器或细胞表面。 ❖没有任何信号肽(序列)的蛋白是细胞质基质驻留蛋白