
2.4M文件 ■2.4.1M文件简介 在进行计算机仿真的过程中,有时需要编写很多的MATLAB程序代码来执行一个独立功能,其结构 相对较为复杂,每次调用也比较烦琐。为了简化程序的调用,MATLAB专门设置了M文件来解决这方面 的问题。 MATLAB的M文件分为脚本(Script)M文件和函数(Function)M文件两种。 脚本(Script)M文件是MATLAB程序按代码顺序组成的命令的集合,与MATLAB工作空间共享变 量空间,一般功能独立,其中包含很多诸如每个变量名称和类型的信息,每个数组的大小,以及对数据集 进行分析、运算、绘图等的命令,但不接受参数的输入与输出。运用MATLAB的脚本M文件,用户可以 把实现一个独立操作的所有程序代码都写在一个M文件中,每次只需在命令窗口直接键入该M文件名来 运行该M文件中的所有程序代码。 函数(Function)M文件是包含有函数功能的M文件,也是一个具有独立功能的程序块,但不同于上 面的脚本M文件,它的开头需要有一个函数名称,且运行于自己的独立工作空间,接受并处理输入参数列 表,并将处理后的结果传递到到输出参数列表。用户可以把一个抽象功能的MATLAB代码封装成一个输 入输出函数接口,在以后的应用中直接调用它。 MATLAB的脚本M文件和函数M文件相同之处在于它们都有一个扩展名为*.m的文本文件,在文本 编辑器中创建文件。但是,二者在语法和使用上略有不同。 ■2.4.2脚本(Script)文件 脚本是扩展名为.m的文件,可包含MATLAB的各种命令,类似于DOS系统中的批处理文件。在命 令窗口中直接键入此文件名,MATLAB可逐一执行文件内的所有命令。 脚本运行过程所产生的变量都是全局变量,都驻留在MATLAB工作空间内,只要不关闭MATLAB, 不使用清内存的clear命令,这些变量将一直保存。 ■脚本文件格式:通常为一连串指令,没有函数声明行,无输入和输出参数。 ■说明: (1)运行脚本文件时,只是简单地按顺序从文件中读取一条条命令,送到MATLAB命令窗口中去 执行: (2)脚本文件运行产生的变量都驻留在MATLAB的基本工作空间中,在命令窗口中运行的命令可 以使用这些变量: (3)脚本文件的命令可以访问工作空间的所有数据,因此要注意避免工作空间和脚本文件中的同名变 量相互覆盖,一般在M脚本文件的开头使用clear”命令清除工作空间的变量。 例2.4.1创建一个新的M脚本文件 (1)新建一个M脚本文件在MATLAB7.10.0(R2010a)环境下,选中File/New/Script菜单项,如 图2.4.1所示,或点击工具条上的新建M文件按钮口,可打开一个空的M文件编辑器,用于创建一个新的 M文件。 (2)在打开的文本编辑器中键入如下内容:如图2.4.2所示。 x=0:pi/100:2*pi yl=sin(2*x); y2=2*cos(2*x); plot(x,y1,'-k',x,y2,'b-); title ('Plot of f(x)=sin(2x)and its derivative'); xlabel('x'); 1
1 2.4 M 文件 ■ 2.4.1 M 文件简介 在进行计算机仿真的过程中,有时需要编写很多的 MATLAB 程序代码来执行一个独立功能,其结构 相对较为复杂,每次调用也比较烦琐。为了简化程序的调用,MATLAB 专门设置了 M 文件来解决这方面 的问题。 MATLAB 的 M 文件分为脚本(Script)M 文件和函数(Function)M 文件两种。 脚本(Script)M 文件是 MATLAB 程序按代码顺序组成的命令的集合,与 MATLAB 工作空间共享变 量空间,一般功能独立,其中包含很多诸如每个变量名称和类型的信息,每个数组的大小,以及对数据集 进行分析、运算、绘图等的命令,但不接受参数的输入与输出。运用 MATLAB 的脚本 M 文件,用户可以 把实现一个独立操作的所有程序代码都写在一个 M 文件中,每次只需在命令窗口直接键入该 M 文件名来 运行该 M 文件中的所有程序代码。 函数(Function)M 文件是包含有函数功能的 M 文件,也是一个具有独立功能的程序块,但不同于上 面的脚本 M 文件,它的开头需要有一个函数名称,且运行于自己的独立工作空间,接受并处理输入参数列 表,并将处理后的结果传递到到输出参数列表。用户可以把一个抽象功能的 MATLAB 代码封装成一个输 入/输出函数接口,在以后的应用中直接调用它。 MATLAB 的脚本 M 文件和函数 M 文件相同之处在于它们都有一个扩展名为*.m 的文本文件,在文本 编辑器中创建文件。但是,二者在语法和使用上略有不同。 ■ 2.4.2 脚本(Script)文件 脚本是扩展名为.m 的文件,可包含 MATLAB 的各种命令,类似于 DOS 系统中的批处理文件。在命 令窗口中直接键入此文件名,MATLAB 可逐一执行文件内的所有命令。 脚本运行过程所产生的变量都是全局变量,都驻留在 MATLAB 工作空间内,只要不关闭 MATLAB, 不使用清内存的 clear 命令,这些变量将一直保存。 脚本文件格式: 通常为一连串指令,没有函数声明行,无输入和输出参数。 说明: (1)运行脚本文件时,只是简单地按顺序从文件中读取一条条命令,送到 MATLAB 命令窗口中去 执行; (2)脚本文件运行产生的变量都驻留在 MATLAB 的基本工作空间中,在命令窗口中运行的命令可 以使用这些变量; (3)脚本文件的命令可以访问工作空间的所有数据,因此要注意避免工作空间和脚本文件中的同名变 量相互覆盖,一般在 M 脚本文件的开头使用“clear”命令清除工作空间的变量。 例 2.4.1 创建一个新的 M 脚本文件 (1)新建一个 M 脚本文件 在 MATLAB 7.10.0(R2010a)环境下,选中 File/New/Script 菜单项,如 图 2.4.1 所示,或点击工具条上的新建 M 文件按钮 ,可打开一个空的 M 文件编辑器,用于创建一个新的 M 文件。 (2)在打开的文本编辑器中键入如下内容:如图 2.4.2 所示。 x=0:pi/100:2*pi; y1=sin(2*x); y2=2*cos(2*x); plot(x,y1,'-k',x,y2,'b--'); title ('Plot of f(x)=sin(2x) and its derivative'); xlabel('x');
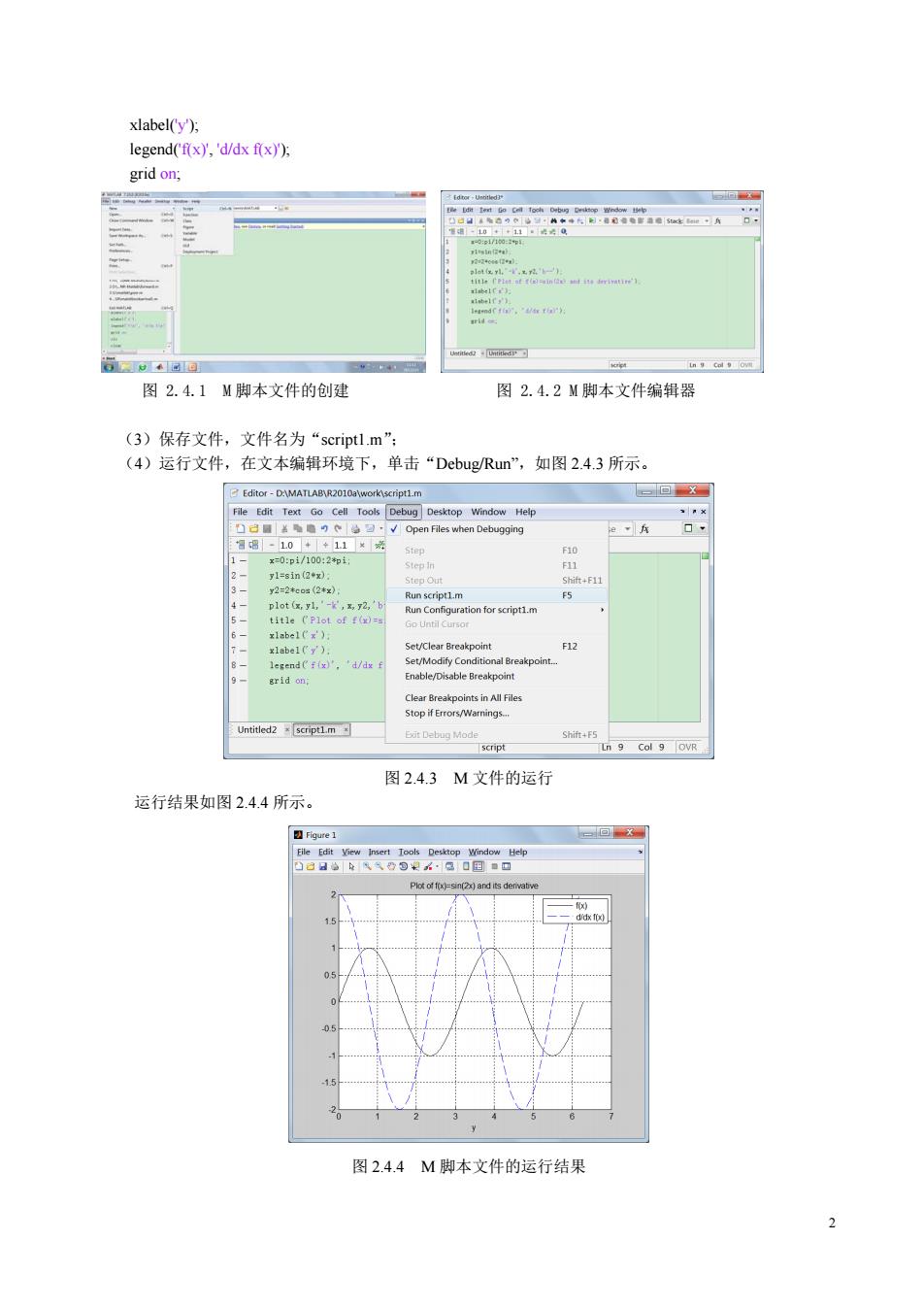
xlabel(y), legend('f(x)','d/dx f(x)); grid on; 回 通-10+11。2@ : st f((o s it derivatin') letendt fi.r th): 心@回团 图2.4.1M脚本文件的创建 图2.4.2M脚本文件编辑器 (3)保存文件,文件名为“scriptl.m”: (4)运行文件,在文本编辑环境下,单击“Debug/Run”,如图2.4.3所示。 Editor-D:\MATLAB\R2010a\work\script1.m 一回X File Edit Text Go Cell Tools Debug Desktop Window Help h己■盖●)c:√Open Files when Debugging 智8-10+◆11× Step F10 1 x=0:pi/100:2*和i Step in F11 y1=sin(2◆x) 3 Step Out Shift+F11 y2=2*cos(2*x) Run script1.m F5 4 plot (x,yl,'-k',x,y2,'bi Run Confguration for script1.m 5 title ('Plot of f(x)= Go Until Cursor 6 xlabel('x') 7 xlabel(y'). Set/Clear Breakpoint F12 8、 legend('f(x)','d/dx f Set/Modify Conditional Breakpoint. 9 grid on; Enable/Disable Breakpoint Clear Breakpoints in All Files Stop if Errors/Warnings.. Untitled2 script1.m Eit Debug Mode Shift+F5 script Ln 9 Col 9 OVR 图2.4.3M文件的运行 运行结果如图2.4.4所示。 Figure 1 回 File Edit View Insert Tools Desktop Window Help 凸8日始从线设包公·感口国■▣ Plot of f(x)=sin(2x)and its denvative -fix) 、d倒 图2.4.4M脚本文件的运行结果 2
2 xlabel('y'); legend('f(x)', 'd/dx f(x)'); grid on; 图 2.4.1 M 脚本文件的创建 图 2.4.2 M 脚本文件编辑器 (3)保存文件,文件名为“script1.m”; (4)运行文件,在文本编辑环境下,单击“Debug/Run”,如图 2.4.3 所示。 图 2.4.3 M 文件的运行 运行结果如图 2.4.4 所示。 图 2.4.4 M 脚本文件的运行结果

2.4.2 Evaluating a Function of Two Variables Write a MATLAB program to evaluate a function fx.y)for any two user-specified values x and y.The function fx.y)is defined as follows. x+yx≥0 and y≥0 x+y2x≥0 and y<0 f(x,y)= x2+y x<0 and y≥0 x2+y2x<0 and y<o The function f(xy)is evaluated differently depending on the signs of the two independent variables x and y To determine the proper equation to apply,it will be necessary to check for the signs of the x and y values supplied by the user. 1.State the problem Evaluate the function f.y)for any user-supplied values of x and y. 2.Define the inputs and outputs. The inputs required by this program are the values of the independent variables x and y.The output from the program will be the value of the function f(x,y). 3.Design the algorithm. Prompt the user for the values x and y. Readx andy if x>0 and y>0 funx+y elseif x>0 andy<0 im←-x+y^2 elseif x<0 andy>0 fium←-x2+y else fim←x2+y2 end Write out f,以 Turn the algorithm into MATLAB statements. The final MATLAB code follows. Script file:funxy.m Purpose: This program solves the function f(x,y)for a user-specified x and y,where f(x,y)is defined as: % x+y x>=0 and y>=0 % X+y^2 x>=0andy<0 % f(x,y)=x2+y x<0andy>=0 % x^2+y2 x<0 andy>0 % % Record of revisions: % Date Programmer Description of change 3
3 例 2.4.2 Evaluating a Function of Two Variables Write a MATLAB program to evaluate a function f(x.y) for any two user-specified values x and y. The function f(x,y) is defined as follows. The function f (x,y) is evaluated differently depending on the signs of the two independent variables x and y To determine the proper equation to apply, it will be necessary to check for the signs of the x and y values supplied by the user. 1. State the problem. Evaluate the function f(x,y) for any user-supplied values of x and y. 2. Define the inputs and outputs. The inputs required by this program are the values of the independent variables x and y. The output from the program will be the value of the function f(x,y). 3. Design the algorithm. Prompt the user for the values x and y. Read x and y if x > 0 and y > 0 fun← x + y elseif x > 0 and y < 0 fun← x + y^2 elseif x < 0 and y >_ 0 fun ← x^2 + y else fun ← x^2 + y^2 end Write out f(x,y) Turn the algorithm into MATLAB statements. % The final MATLAB code follows. % Script file: funxy.m % Purpose: % This program solves the function f(x,y) for a % user-specified x and y, where f(x,y) is defined as: % x + y x >= 0 and y >= 0 % x + y^2 x >= 0 and y < 0 % f (x, y)= x^2 + y x < 0 and y >= 0 % x^2 + y^2 x < 0 and y > 0 % % Record of revisions: % Date Programmer Description of change ⎪ ⎪ ⎩ ⎪ ⎪ ⎨ ⎧ + < < + < ≥ + ≥ < + ≥ ≥ = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ( , ) 2 2 2 2 x y x and y x y x and y x y x and y x y x and y f x y

12/05/98 S.J.Chapman Original code % Define variables: % x--First independent variable % y--Second independent variable % fun--Resulting function 的 Prompt the user for the values x and y x=input ('Enter the x coefficient:) y input ('Enter the y coefficient:) Calculate the function f(x,y)based upon the signs of x and y. ifx>=0&y>=0 fun=x+y; elseif x>=0&y<0 fun=x+y2; elseifx<0&y>=0 fun=x 2+y; else fun=x 2+y2; end Write the value of the function. disp ([The value of the function is'num2str(fun))); fprintf(The value of the function is %fn'fun): Test the program. >>funxy Enter the x coefficient:2 Enter the y coefficient:3 The value of the function is 5 >>funxy Enter the x coefficient:2 Enter the y coefficient:-3 The value of the function is 11 >>funxy Enter the x coefficient:-2 Enter the y coefficient:3 The value of the function is 7 >>funxy Enter the x coefficient:-2 Enter the y coefficient:-3 The value of the function is 13 ■2.4.3函数(Function) MATALB中许多常用的函数都是函数式M文件。函数被调用时,通过获取外部参数进行运算,并向 4
4 % 12/05/98 S. J. Chapman Original code % Define variables: % x -- First independent variable % y -- Second independent variable % fun -- Resulting function % Prompt the user for the values x and y x = input ('Enter the x coefficient:'); y = input ('Enter the y coefficient:'); % Calculate the function f(x,y) based upon % the signs of x and y. if x >= 0 & y >= 0 fun = x + y; elseif x >= 0 & y < 0 fun = x + y^2; elseif x < 0 & y >= 0 fun = x^2 + y; else fun = x^2 + y^2; end % Write the value of the function. % disp (['The value of the function is ' num2str(fun)]); fprintf(‘The value of the function is %f\n‘,fun); Test the program. >>funxy Enter the x coefficient: 2 Enter the y coefficient: 3 The value of the function is 5 >>funxy Enter the x coefficient: 2 Enter the y coefficient: -3 The value of the function is 11 >>funxy Enter the x coefficient: -2 Enter the y coefficient: 3 The value of the function is 7 >>funxy Enter the x coefficient: -2 Enter the y coefficient: -3 The value of the function is 13 ■ 2.4.3 函数(Function) MATALB 中许多常用的函数都是函数式 M 文件。函数被调用时,通过获取外部参数进行运算,并向

外部返回运算结果。函数内部的变量都是隐含的,或者说都是局部变量(除特别声明外),存放在函数本 身的工作空间内。这些变量不能被外部使用,也不会与外部的变量相互覆盖。对用户来说,函数可以看做 一个黑盒,提供输入,得到输出。因此易于使程序模块化,适合于大型程序代码编制。 例2.4.3创建一个新的M函数文件 (1)新建一个M函数文件在MATLAB7.10.0(R2010a)环境下,选中“File/New/Function”菜单 项,如图2.4.5所示。打开函数文本编辑器如图2.4.6所示。 本MATLAB7100R2010a Editor-Untitled 一回X rile fdit Debug Parallel Desktop Window Help New CtrleN nentsMATLAl Ele Edit Iext Go Cel Tools Debug Desktop Window Help Cut-c 刀司日h自9个2·4年中为日·看幻自时通增sa比以一年口 import Data see Demos,or 日国-1.0++11x塔话0 Save Workspace At. Set Path. Model i可function【otputas】:Untite5(iut.ars IITD Sumr of this fuctioo sos here Page Setup.. Detalled exlmnatlos goes here 101-010aworkvecript1.m end EMATLAB Ctl-Q 1 cendC《=)”,”d/ere cle ©☑国 Untitied5 Ln 1 Col 1 CVR 图2.4.5M函数文件的创建 图2.4.6M函数文件的编辑窗口 (2)在函数文本编辑器中键入如下内容: function distance dist2(x1,y1,x2,y2) DIST2 Calculate the distance between two points Function DIST2 calculates the distance between two points (x1,yl)and (x2.y2)in a Cartesian coordinate system. Calling sequence: res dist2(xl,yl,x2.y2) Define variables: x1--x-position ofpoint I yl--y-position of point I x2--x-position of point 2 y2--y-position of point 2 distance--Distance between points Record of revisions: Date Programmer Description of change 12/15/98 S.J.Chapman Original code Calculate distance. distance sqrt((x2-x1).2+(y2-y1).^2); (3)保存文件。在函数文本编辑器选中“File/Save As..”菜单项,显示如图2.4.7所示界面,函数文 件名自动显示,点击“保存”按钮就可以了。 5
5 外部返回运算结果。函数内部的变量都是隐含的,或者说都是局部变量(除特别声明外),存放在函数本 身的工作空间内。这些变量不能被外部使用,也不会与外部的变量相互覆盖。对用户来说,函数可以看做 一个黑盒,提供输入,得到输出。因此易于使程序模块化,适合于大型程序代码编制。 例 2.4.3 创建一个新的 M 函数文件 (1)新建一个 M 函数文件 在 MATLAB 7.10.0(R2010a)环境下,选中“File/New/Function”菜单 项,如图 2.4.5 所示。 打开函数文本编辑器如图 2.4.6 所示。 图 2.4.5 M 函数文件的创建 图 2.4.6 M 函数文件的编辑窗口 (2)在函数文本编辑器中键入如下内容: function distance = dist2 (x1, y1, x2, y2) % DIST2 Calculate the distance between two points % Function DIST2 calculates the distance between % two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) in a Cartesian coordinate system. % % Calling sequence: % res = dist2(xl, y1, x2, y2) % Define variables: % x1 -- x-position of point 1 % y1 -- y-position of point 1 % x2 -- x-position of point 2 % y2 -- y-position of point 2 % distance -- Distance between points % Record of revisions: % Date Programmer Description of change % 12/15/98 S. J. Chapman Original code % Calculate distance. distance = sqrt((x2-x1).^2 + (y2-y1).^2); (3)保存文件。在函数文本编辑器选中“File/Save As... ”菜单项,显示如图 2.4.7 所示界面,函数文 件名自动显示,点击“保存”按钮就可以了