
问题4: 什么是representative? 讨论数学与讨论数据结构 时它有什么差别?
representative

问题5: 讨论的不是一个算法, 而是一个数据结构. 所谓“时间复杂性分析 究竟是什么意思呢?
问题5: 讨论的不是一个算法, 而是一个数据结构. 所谓“时间复杂性分析” 究竟是什么意思呢?

Running times of disjoint-set Throughout this chapter,we shall analyze the running times of disjoint-set data structures in terms of two parameters n,the number of MAKE-SET operations, and m,the total number of MAKE-SET,UNION,and FIND-SET operations.Since the sets are disjoint,each UNION operation reduces the number of sets by one. After n-1 UNION operations,therefore,only one set remains.The number of UNION operations is thus at most n-1.Note also that since the MAKE-SET operations are included in the total number of operations m,we have m >n.We assume that the n MAKE-SET operations are the first n operations performed
Running times of disjoint-set
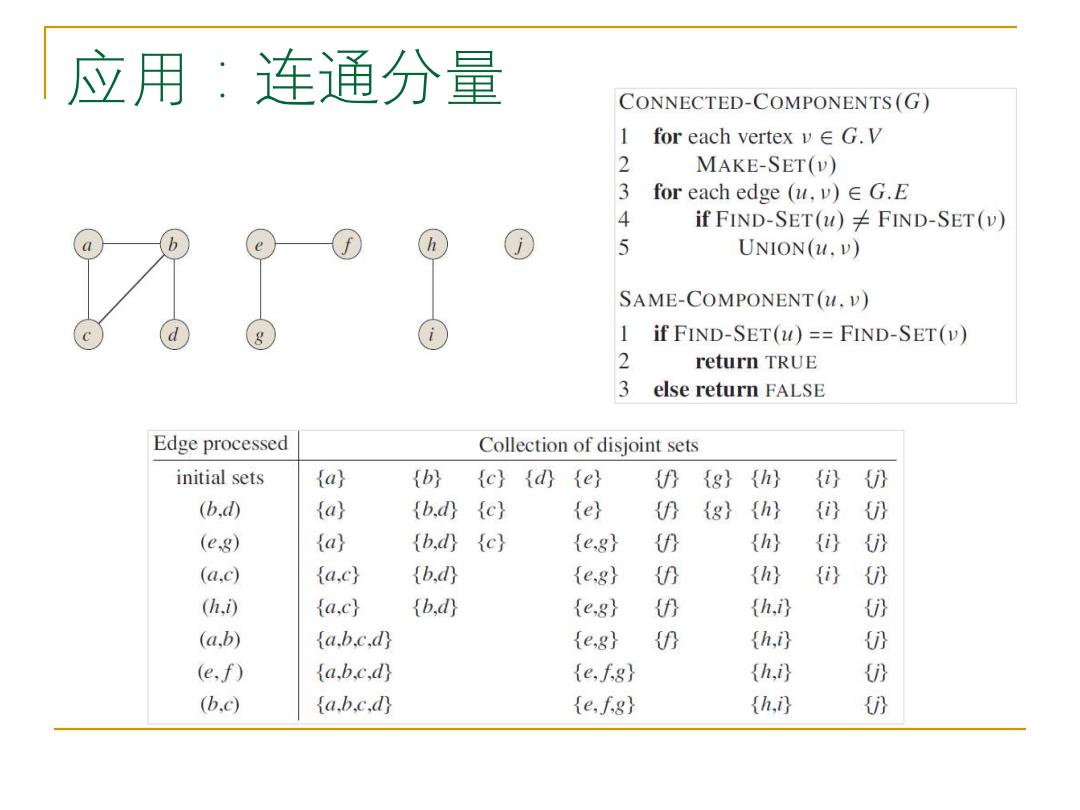
应用:连通分量 CONNECTED-COMPONENTS(G) 1 for each vertex v∈G.V 2 MAKE-SET(v) 3 for each edge (u,v)E G.E 4 if FIND-SET(u)FIND-SET(v) b ① 5 UNION(.V) SAME-COMPONENT(u.V) 1 if FIND-SET(u)==FIND-SET(v) 2 return TRUE 3 else return FALSE Edge processed Collection of disjoint sets initial sets La) {b) {c} Ad) {e} 价 {8} { 话 } (b,d0 La) {b,d) {c} {e} 仍 {g} (h) (0) 0 (eg) La) {b,d) {c} {e,8} 仍 th) {i) 仍 (a,c) {a,c} {b,d) {e,8} (h) (d} 仍 (h,i0 {a,c} (b,d) {e,8} 仍 {h,} } (a,b) a.b.c.dy {e,8} (h.i (e,f) a.b.c.dy e.fg) {h,i} 仍 (b,c) a.bc.dy {e,f8} (h,i }
应用:连通分量

Kruskal算法 7 d (a) 14 e (b) d (c) d e】 9 (g) (h) 10 Figure 23.4 The execution of Kruskal's algorithm on the graph from Figure 23.1.Shaded edges
Kruskal 算法