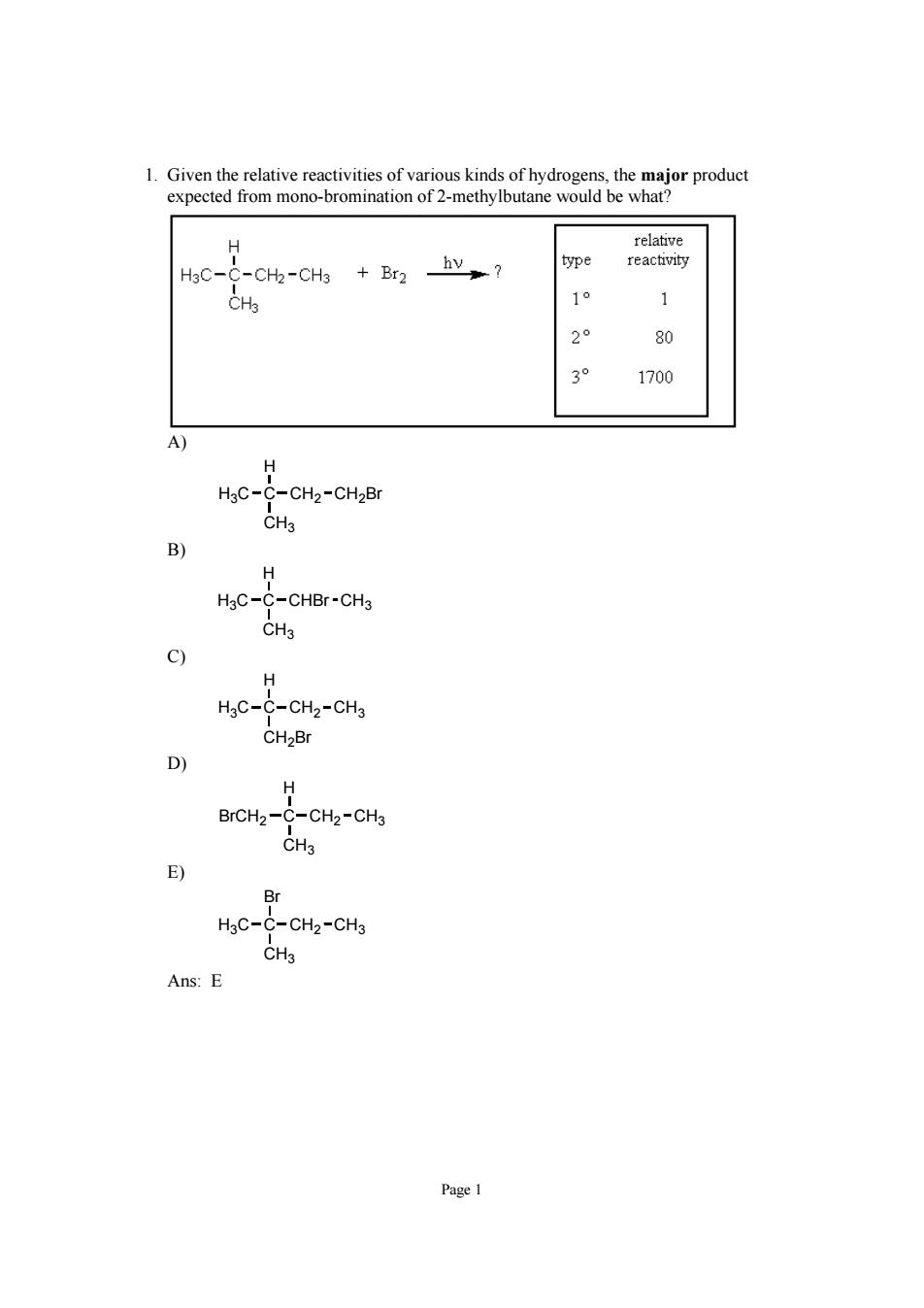
1.Given the relative reactivities of various kinds of hydrogens.the major product expected from mono-bromination of 2-methylbutane would be what H3C- -CH2-CH3 +Br2 hv? 1° 1 80 1700 -CH2-CH2Br CHa B) H HgC-C-CHBr-CH3 CH3 9 H HgC-C-CH2-CH3 CH2Br H BrCH2-C-CH2-CH3 E) Br HaC-C-CHz-CHj CH3 Ans:E
Page 1 1. Given the relative reactivities of various kinds of hydrogens, the major product expected from mono-bromination of 2-methylbutane would be what? A) H3C C CH3 H CH2 CH2Br B) H3C C CH3 H CHBr CH3 C) H3C C CH2Br H CH2 CH3 D) BrCH2 C CH3 H CH2 CH3 E) H3C C CH3 Br CH2 CH3 Ans: E

2.Which of the following is a propagation step in the free-radical bromination of B) Bra hy 2Br. C)CH3+Br2- CH;Br Br. D)CHy+CH: CH3CH3 E)Br?+Br? Br2 Ans:C 3.Which of the reactions below would you expect to have the largest positive A? A) CH:Br B) Br2 hy 2 Br. c) CH3 Br2- CH;Br Br. D) CH3CH3 →CH,CH3 E)Br?+Br? Br2 Ans:B 4.What reactant is needed to complete and balance the following reaction? +302spark 3CO +3H0 A)C3Hs B)C2H6 C)C:Ha D)C:H6 E)CH2 Ans:D 5hnenscsbdwnnomgeyawcomtpgti。 A)CH3 I?CHjl B) 2hv+2. C)CH+I- →CH,I+I D)CH+一 →CH?+HⅢ E)I?+I?- 12 Ans:D Page2
Page 2 2. Which of the following is a propagation step in the free-radical bromination of methane? A) CH3• + Br? CH3Br B) Br2 2 Br • hν C) CH3• + Br2 CH3Br + Br• D) CH3• + CH3• CH3CH3 E) Br? + Br? Br2 Ans: C 3. Which of the reactions below would you expect to have the largest positive Δ? A) CH3• + Br? CH3Br B) Br2 2 Br • hν C) CH3• + Br2 CH3Br + Br• D) CH3• + CH3• CH3CH3 E) Br? + Br? Br2 Ans: B 4. What reactant is needed to complete and balance the following reaction? ? + 3 O2 3 CO + 3 H2O spark A) C3H8 B) C2H6 C) C3H4 D) C3H6 E) C6H12 Ans: D 5. Which one of the reactions below will not proceed and accounts for why iodine added to a free-radical chlorination or bromination will greatly slow or even stop the reaction? A) CH3• + I? CH3I B) hν I2 2 I• C) CH3 CH I + I• 3• + I2 D) CH4 + I• CH3? + HI E) I? + I? I2 Ans: D

6.Which of the following is not true of free-radical halogenation reactions? n chlorine in these reactions. s more s minations are faster emperatures to proceed These reactions are irreversible. Ans:D 7.Which of the following reaction types are typical of alkanes? on more than one of these is correct titution 8.Alkanes are noted for their(choose one) A)high reactivity with acids. D)lack of reactivity B)toxicity. E)water-solubility odor. Page3
Page 3 6. Which of the following is not true of free-radical halogenation reactions? A) Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine in these reactions. B) Bromine is more selective than chlorine. C) The reactions require either light or high temperatures to proceed. D) Brominations are faster than chlorinations. E) These reactions are irreversible. Ans: D 7. Which of the following reaction types are typical of alkanes? A) addition D) reduction B) elimination E) more than one of these is correct C) radical substitution Ans: C 8. Alkanes are noted for their (choose one) A) high reactivity with acids. D) lack of reactivity. B) toxicity. E) water-solubility. C) intense odor. Ans: D
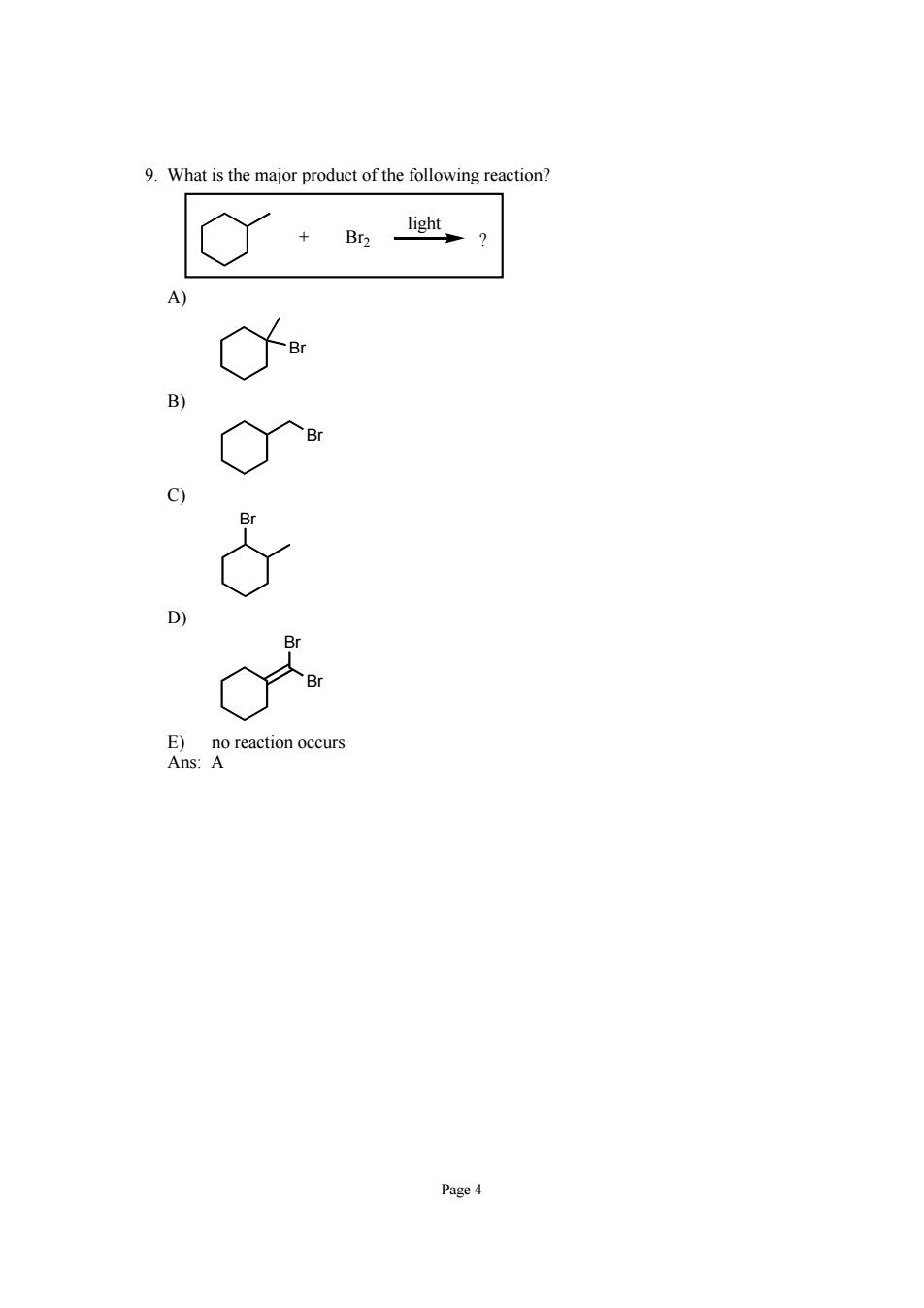
9.What is the major product of the following reaction? C ) Page4
Page 4 9. What is the major product of the following reaction? + Br2 ? light A) Br B) Br C) Br D) Br Br E) no reaction occurs Ans: A
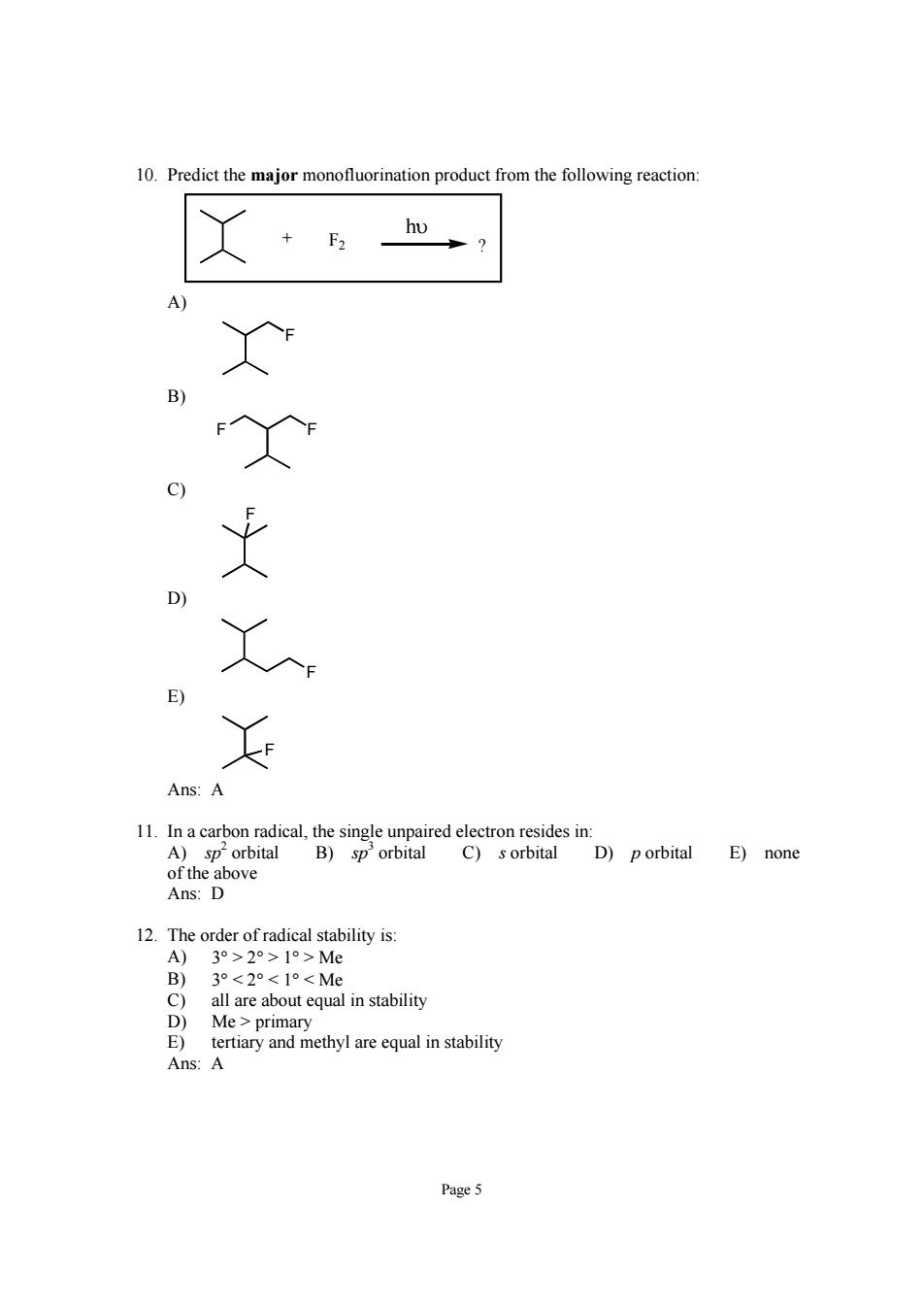
10.Predict the major monofluorination product from the following reaction: C) D) Ans:A 11.In a carbon radical,the single unpaired electron resides in: A)sp'orbital B)sp'orbital C)s orbital D)porbital E)none 12.The order of radical stability is: 3°>20>1>Me 3°<20<1°<Me Mepi all are about equal in stability E)tertiary and methyl are equal in stability Ans:A Page 5
Page 5 10. Predict the major monofluorination product from the following reaction: + ? hυ F2 A) F B) F F C) F D) F E) F Ans: A 11. In a carbon radical, the single unpaired electron resides in: A) sp 2 orbital B) sp 3 orbital C) s orbital D) p orbital E) none of the above Ans: D 12. The order of radical stability is: A) 3° > 2° > 1° > Me B) 3° < 2° < 1° < Me C) all are about equal in stability D) Me > primary E) tertiary and methyl are equal in stability Ans: A