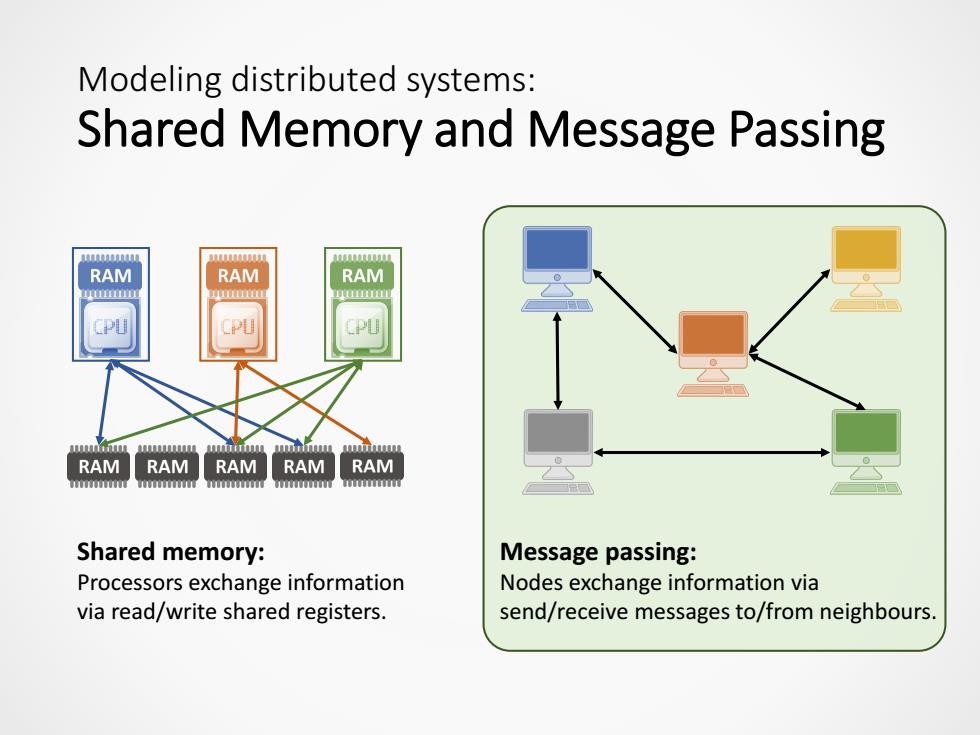
Modeling distributed systems: Shared Memory and Message Passing RAM RAM RAM M RAM RAM RAM RAM RAM 1 Shared memory: Message passing: Processors exchange information Nodes exchange information via via read/write shared registers. send/receive messages to/from neighbours
Modeling distributed systems: Shared Memory and Message Passing Shared memory: Processors exchange information via read/write shared registers. Message passing: Nodes exchange information via send/receive messages to/from neighbours
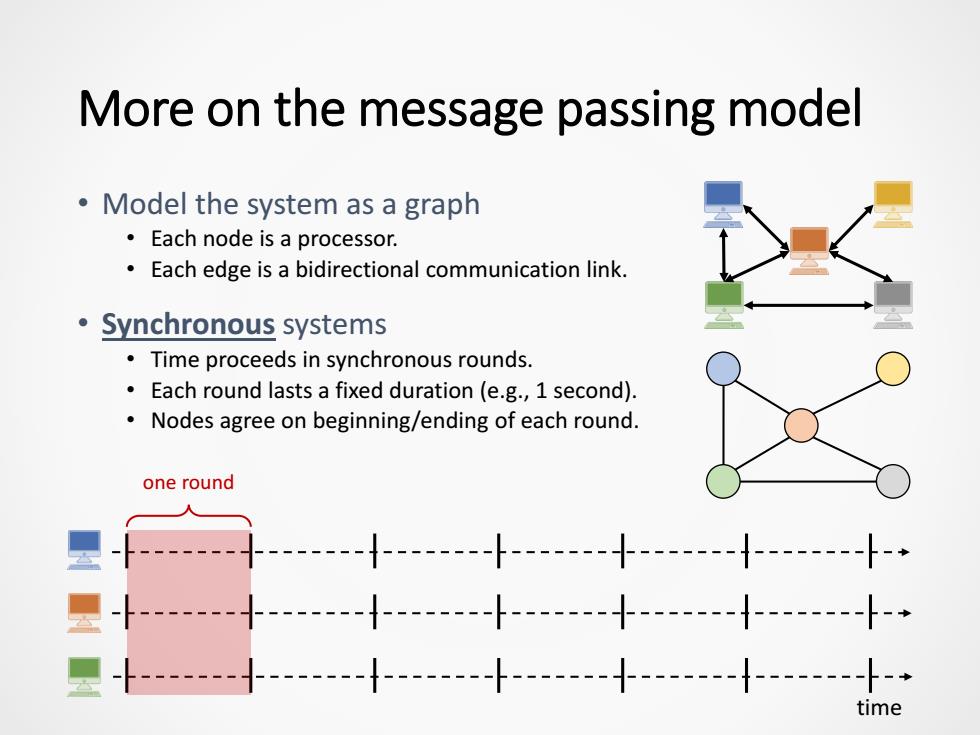
More on the message passing model Model the system as a graph Each node is a processor. Each edge is a bidirectional communication link. ·Synchronous systems Time proceeds in synchronous rounds. Each round lasts a fixed duration (e.g.,1 second). Nodes agree on beginning/ending of each round. one round ----十--- im
More on the message passing model • Model the system as a graph • Each node is a processor. • Each edge is a bidirectional communication link. • Synchronous systems • Time proceeds in synchronous rounds. • Each round lasts a fixed duration (e.g., 1 second). • Nodes agree on beginning/ending of each round. time one round

More on sync message passing model Nodes'behavior in each round: 1.Read messages from last round (if any).[Instantly done.] 2.Do local computation.[Instantly done.] 3.Send messages to neighbors (if any). Messages sent in round i guaranteed to arrive at destination by the beginning of round i+1. 里☆小十l 2{-☒----- 里☆-十--- time
More on sync message passing model • Nodes’ behavior in each round: 1. Read messages from last round (if any). [Instantly done.] 2. Do local computation. [Instantly done.] 3. Send messages to neighbors (if any). • Messages sent in round 𝑖 guaranteed to arrive at destination by the beginning of round 𝑖 + 1. time

More on async message passing model 。Message delays are“arbitrary but finite", Different messages can take(very)different time to deliver. Each message will be delivered eventually. We do not know the maximum message delay. Algorithms for asynchronous systems are "event-based". Typical async algorithm:"upon receiving message...,do..." Typical sync algorithm:"for each round,do..." ☒ ☒ ☒ time
More on async message passing model • Message delays are “arbitrary but finite”. • Different messages can take (very) different time to deliver. • Each message will be delivered eventually. • We do not know the maximum message delay. • Algorithms for asynchronous systems are “event-based”. • Typical async algorithm: “upon receiving message …, do …” • Typical sync algorithm: “for each round, do …” time

Complexity measure Time complexity:number of rounds needed to accomplish the task in the worst case.(How about async systems?) Message complexity:number of messages/bits needed to transmit to accomplish the task in the worst case. Space complexity:size of local/total memory needed to accomplish the task in the worst case. Feasibility:can the given task be accomplished at all
Complexity measure • Time complexity: number of rounds needed to accomplish the task in the worst case. (How about async systems?) • Message complexity: number of messages/bits needed to transmit to accomplish the task in the worst case. • Space complexity: size of local/total memory needed to accomplish the task in the worst case. • Feasibility: can the given task be accomplished at all