
三营养物通过与细胞膜上载体蛋白(也称作透 过酶permease)的可逆性结合来加快其传递 速度 促进扩散 (facilitated diffusion/transport) Facilitated diffusion utilizes membrane protein channels to allow charged molecules (which otherwise could not diffuse across the cell membrane) to freely diffuse in a nd out of the cell. These channels comes into greatest use with small ions like K+, Na+, and Cl-. The speed of facilitated transport is limited by the number of protein channels available, whereas the speed of diffusion is dependent only on the concentration gradient
三营养物通过与细胞膜上载体蛋白(也称作透 过酶permease)的可逆性结合来加快其传递 速度 促进扩散 (facilitated diffusion/transport) Facilitated diffusion utilizes membrane protein channels to allow charged molecules (which otherwise could not diffuse across the cell membrane) to freely diffuse in a nd out of the cell. These channels comes into greatest use with small ions like K+, Na+, and Cl-. The speed of facilitated transport is limited by the number of protein channels available, whereas the speed of diffusion is dependent only on the concentration gradient

促进扩散(facilitated diffusion) 特点:在促进扩散过程中 ❖ 营养物质本身在分子结构上也不会发生变化 ❖ 不消耗代谢能量,故不能进行逆浓度运输 ❖ 运输的速率由胞内外该物质的浓度差决定 ❖需要细胞膜上的载体蛋白(透过酶)参与物质运输 ❖被运输的物质与载体蛋白有高度的特异性 ❖养料浓度过高时, 与载体蛋白出现饱和效应 促进扩散的运输方式多见于真核微生物中,例如通常在厌氧 生活的酵母菌中,某些物质的吸收和代谢产物的分泌是通过 这种方式完成的
促进扩散(facilitated diffusion) 特点:在促进扩散过程中 ❖ 营养物质本身在分子结构上也不会发生变化 ❖ 不消耗代谢能量,故不能进行逆浓度运输 ❖ 运输的速率由胞内外该物质的浓度差决定 ❖需要细胞膜上的载体蛋白(透过酶)参与物质运输 ❖被运输的物质与载体蛋白有高度的特异性 ❖养料浓度过高时, 与载体蛋白出现饱和效应 促进扩散的运输方式多见于真核微生物中,例如通常在厌氧 生活的酵母菌中,某些物质的吸收和代谢产物的分泌是通过 这种方式完成的

Embeded protein:
Embeded protein:
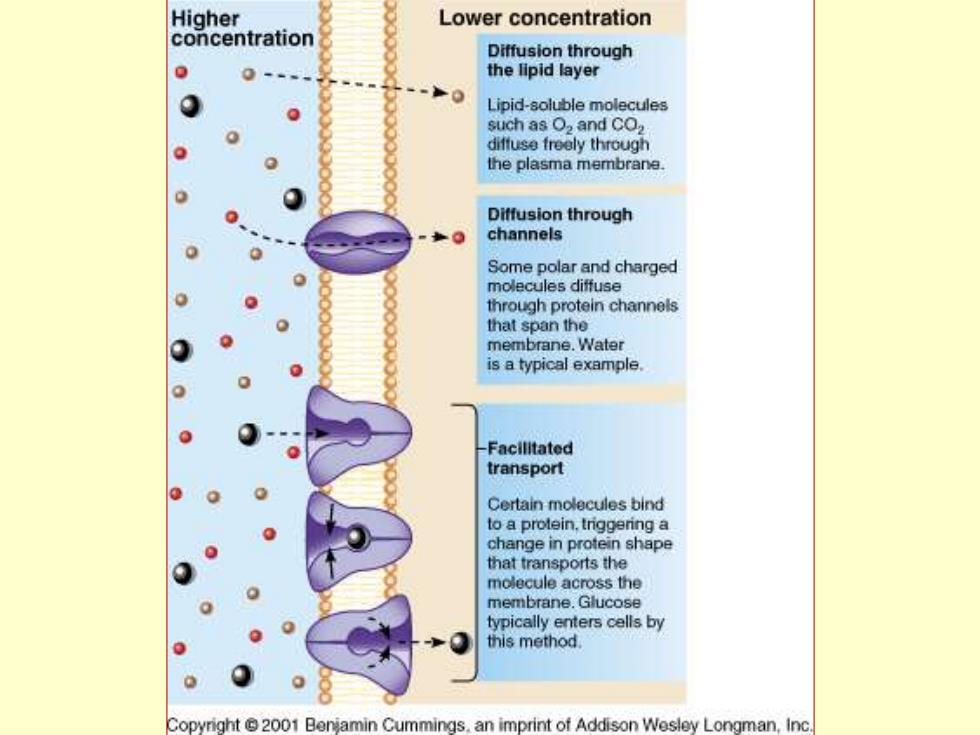
Higher Lower concentration concentration Diffusion through the lipid layer Lipid-soluble molecules such as O2 and CO2 diffuse freely through the plasma membrane. Diffusion through channels Some polar and charged molecules diffuse through protein channels that span the membrane.Water is a typical example Facilltated transport Certain molecules bind to a protein,triggering a change in protein shape that transports the molecule across the membrane.Glucose typically enters cells by this method. Copyright 2001 Benjamin Cummings.an imprint of Addison Wesley Longman,Inc