
For example:binary digital communication s(t)has two hypotheses :x()=s(t)+v(t) Ho:S(t)-O H:S(t)=1 For example:radar detection target x(t)=s(t)+v(t) Ho:s(t)=0, without target H1:s(t)=A(t)cos(ot+φ),with target For example:radar target recognition missile,fighter, bomber;M=3. UESTC 11
UESTC 何子述等 s(t) has two hypotheses : H0 :S(t)=0 H1 :S(t)=1 11 For example: binary digital communication x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = + For example: radar detection target For example: radar target recognition :missile, fighter, bomber; M = 3. 0 1 0 H :s(t) 0, H :s(t) A(t)cos( t ), = = + without target with target x t s t v t ( ) ( ) ( ) = +
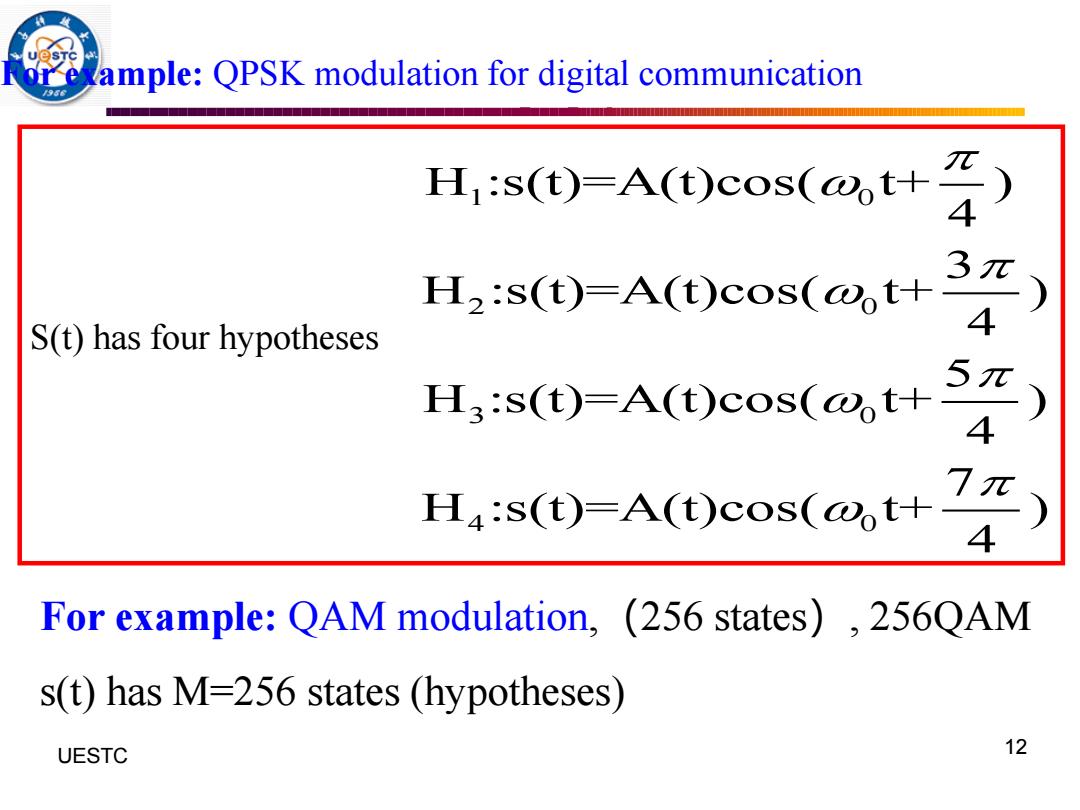
oreample:QPSK modulation for digital communication H:s(t)=A(t)cos(@ot+ 4 H2:s(t)-A(t)cos(@t+ 3x S(t)has four hypotheses H3:s(t)-A(t)cos(@t+ H4:s(t)-A(t)cos(@t+ 4 For example:QAM modulation,(256 states),256QAM s(t)has M-256 states (hypotheses) UESTC 12
UESTC 何子述等 12 For example: QPSK modulation for digital communication For example: QAM modulation,(256 states), 256QAM s(t) has M=256 states (hypotheses) 1 0 2 0 3 0 4 0 H :s(t)=A(t)cos( t+ ) 4 3 H :s(t)=A(t)cos( t+ ) 4 5 H :s(t)=A(t)cos( t+ ) 4 7 H :s(t)=A(t)cos( t+ ) 4 S(t) has four hypotheses

4.The concept of signal estimation According to the observing vector,to estimate the unknown parameters of s(t)on an optimum criterion XO Parameter a=Q(X),X=(X1,X2,…,Xw)月 Estimator a is a parameter of s(t) UESTC 13
UESTC 何子述等 13 4、The concept of signal estimation According to the observing vector, to estimate the unknown parameters of s(t) on an optimum criterion. Parameter Estimator x(t) T 1 2 (X);X (x , x , , x ) is a parameter of s(t) = = N

5 For example:radar target parameter estimation s(t)=A(t-z)cos 2z(fo+fa)(t-t)+ target distance (time delay) f Doppler frequency (target radial speed) electronic reconnaissance:the direction of signal source, signal frequency,etc. The c continuous estimation of parameters is called tracking. UESTC 14
UESTC 何子述等 14 For example: radar target parameter estimation The continuous estimation of parameters is called tracking. 0 d d s( ) A( )cos 2 (f +f )(t ) : f t t = − − + : target distance (time delay) Doppler frequency (target radial speed) electronic reconnaissance: the direction of signal source, signal frequency, etc

Comparison of detection and estimation In a dim night with some moonlight and strong wind (1)Is there a person in the street?(radar detection) (2)Is this person a man or a woman?(binary digital communication detection) (3)If there is a man,how old is he?his height,his weight?(parameter estimations) UESTC 15
UESTC 何子述等 15 Comparison of detection and estimation In a dim night with some moonlight and strong wind , (1) Is there a person in the street? (radar detection) (2) Is this person a man or a woman? (binary digital communication detection) (3) If there is a man, how old is he? his height, his weight? (parameter estimations)