
2.Design Models for Underground Structures 2.2 Empirical model Rain enters here #1 (water must be pumped from water table) Flowing artesian well Pressure surface Resistance to flow limits rise of water #2 to this level Normal water table Aquiclude Aquifer Aquiclude 百年同濟17 TONGII UNIVERSITY
17 2.2 Empirical model 2. Design Models for Underground Structures
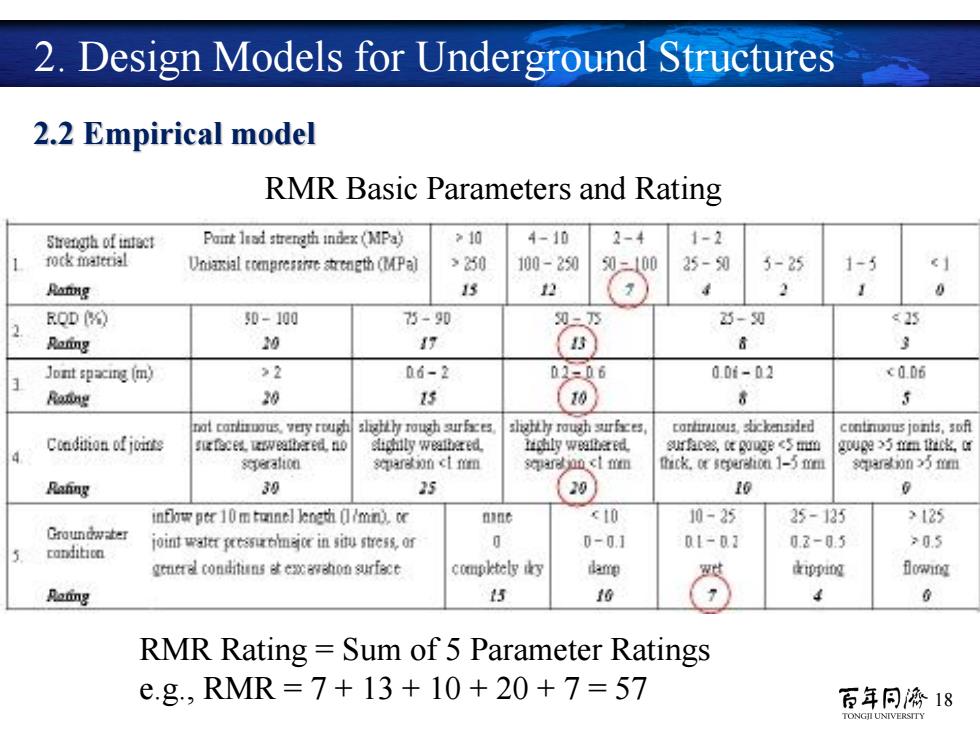
2.Design Models for Underground Structures 2.2 Empirical model RMR Basic Parameters and Rating Stength ofintact Pairt lad strength index (MPa) >10 4-10 2-4 1-2 rock matttal Uniaxial comnpree segth (MPal >250 100-20 50-100 25-0 5-25 1-5 Rating 13 12 1 ROD ( 0-100 75-90 0-下 25-0 ≤25 Raring 20 17 Jont spacing (m) >2 06-2 02-06 0.0i-02 c0.D6 Rating 20 15 10】 8 5 carliroous,very rou内 址ah如rf在巴 hho动r在s cartiruous.sbckensided contnoaus jonts,sof Condition ofjine 这企c继Wa6d10 c如ly weatbered tchly weatbered HA8Gtg的g9c50 gouge >5 mm thack,or speralion sg以0 ncl mm separdoo cl mmn thick.ot sepertion 1-5 mm 9划00>5m Rafing 30 25 20 10 infkw per 10 m tunnel lngth (1/mn)ce ninc c10 10-25 25-125 >125 Groundwater joimatere5血ri诅i询cs系0时 0-01 01-07 02-0.5 >0.5 canditicn geer condituns surface compktelyy e kipping Blowing Batng 15 16 4 RMR Rating Sum of 5 Parameter Ratings e.g,RMR=7+13+10+20+7=57 百年同濟18 TONGILUNIVERSITY
18 RMR Rating = Sum of 5 Parameter Ratings e.g., RMR = 7 + 13 + 10 + 20 + 7 = 57 RMR Basic Parameters and Rating 2.2 Empirical model 2. Design Models for Underground Structures
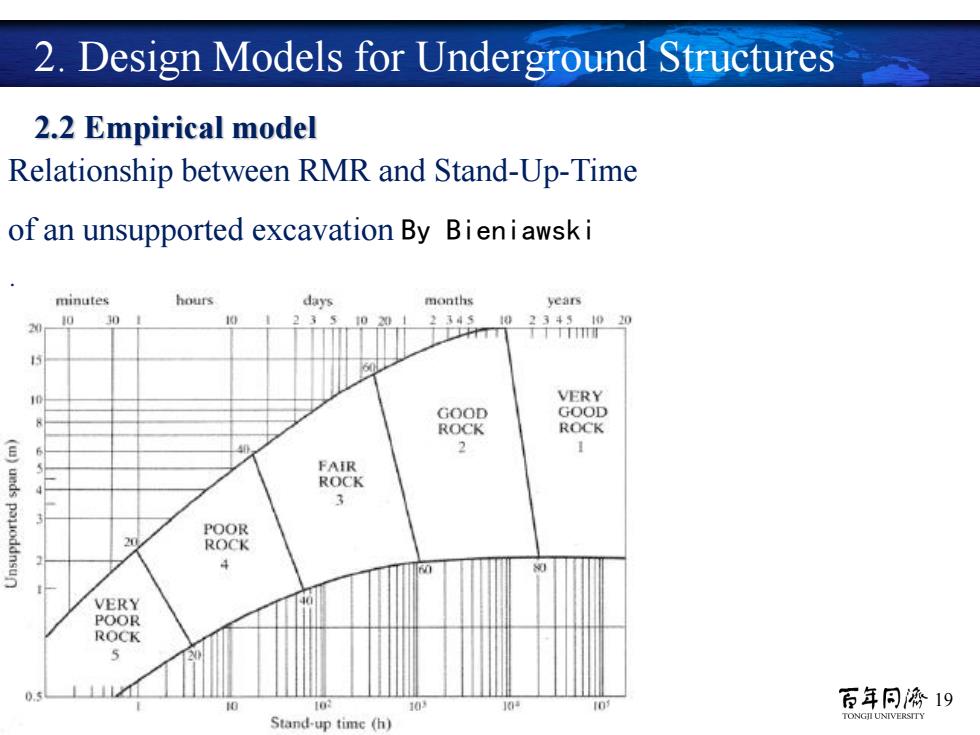
2.Design Models for Underground Structures 2.2 Empirical model Relationship between RMR and Stand-Up-Time of an unsupported excavation By Bieni awski minutes hours days months years 10 10 2345 1023451020 Tm VERY GOOD rH●●) ROCK ROCK ) FAIR ROCK 3 POOR ROCK VERY POOR ROCK 10 百年同濟19 Stand-up time (h)
19 Relationship between RMR and Stand-Up-Time of an unsupported excavation By Bieniawski : 2.2 Empirical model 2. Design Models for Underground Structures
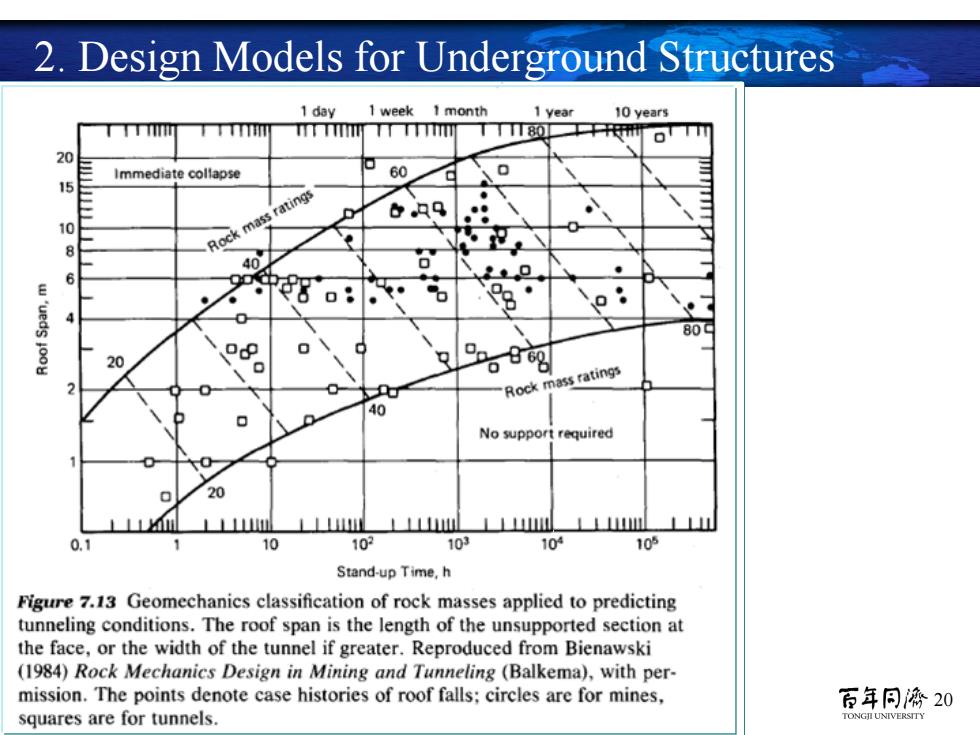
2.Design Models for Underground Structures 1 day 1 week I month 1 year 10 years Tm 20 Immediate collapse 60 15 tings 6只q。 8 Rock mass 6 28 o: 4 809 20 o.p Rock mass ratings 40 No support required 20 Lm⊥⊥⊥ML⊥mL 0.1 10 10 103 10 10的 Stand-up Time,h Figure 7.13 Geomechanics classification of rock masses applied to predicting tunneling conditions.The roof span is the length of the unsupported section at the face,or the width of the tunnel if greater.Reproduced from Bienawski (1984)Rock Mechanics Design in Mining and Tunneling (Balkema),with per- mission.The points denote case histories of roof falls:circles are for mines, 百年同海20 squares are for tunnels. TONGJI UNIVERSITY
20 2. Design Models for Underground Structures
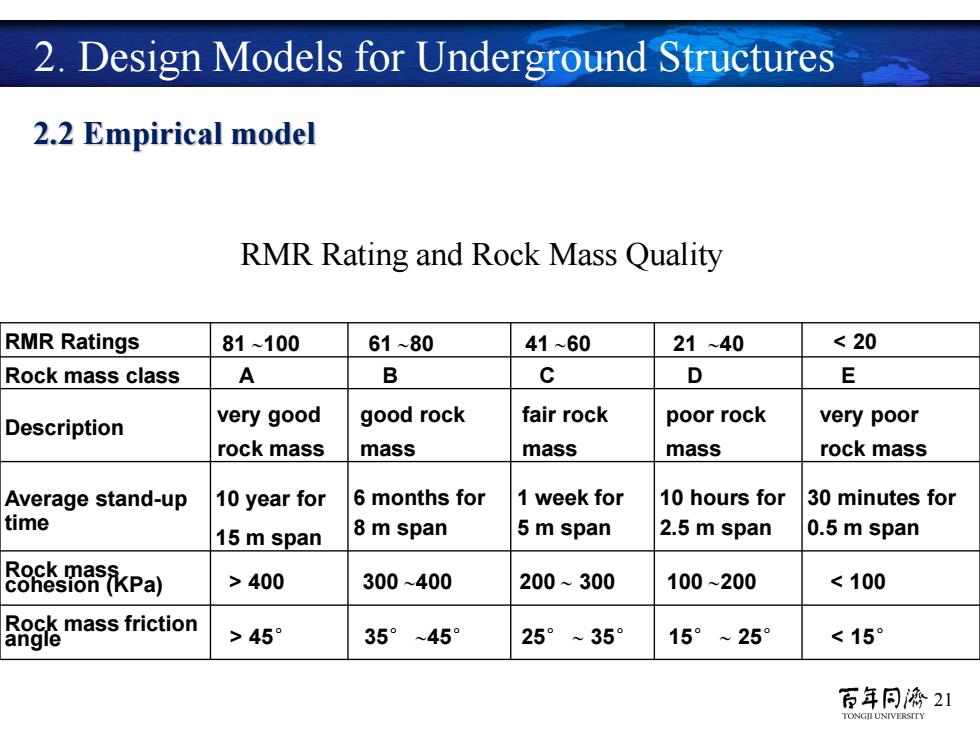
2.Design Models for Underground Structures 2.2 Empirical model RMR Rating and Rock Mass Quality RMR Ratings 81~100 61~80 41~60 21~40 <20 Rock mass class A B c D E fair rock Description very good good rock poor rock very poor rock mass mass mass mass rock mass Average stand-up 10 year for 6 months for 1 week for 10 hours for 30 minutes for time 15 m span 8m span 5m span 2.5 m span 0.5 m span 9微s62kPa) >400 300~400 200~300 100~200 <100 mass friction >45° 35°~45° 25°~35 15°~259 <15° 百年同濟21 TONGII UNIVERSITY
21 RMR Ratings 81 ~100 61 ~80 41 ~60 21 ~40 < 20 Rock mass class A B C D E Description very good rock mass good rock mass fair rock mass poor rock mass very poor rock mass Average stand-up time 10 year for 15 m span 6 months for 8 m span 1 week for 5 m span 10 hours for 2.5 m span 30 minutes for 0.5 m span Rock mass cohesion (KPa) > 400 300 ~400 200 ~ 300 100 ~200 < 100 Rock mass friction angle > 45° 35° ~45° 25° ~ 35° 15° ~ 25° < 15° RMR Rating and Rock Mass Quality 2.2 Empirical model 2. Design Models for Underground Structures