
190> 4.3 Compressive test A compression test is conducted in a manner similar to the tensile test, except that the force is compressive and the specimen contracts along the direction of the stress. By convention,a compressive force is taken to be negative,which yields a negative stress. Furthermore,since lo is greater than li compressive strains are necessarily also negative. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS 4.3 Compressive test A compression test is conducted in a manner similar to the tensile test, except that the force is compressive and the specimen contracts along the direction of the stress. By convention, a compressive force is taken to be negative, which yields a negative stress. Furthermore, since l0 is greater than li compressive strains are necessarily also negative

190> 4.4 Shear and torsional tests Shear stress F T三 Ao Shear strain y 4-tang h Application of a shear stress y(y=tane)or torsional stress angle o created by a applied torque. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS 4.4 Shear and torsional tests Shear stress Shear strain 𝜏 = 𝐹 𝐴0 𝛾 = 𝑎 ℎ =tan𝜃 Application of a shear stress γ(γ=tanθ) or torsional stress angle φ created by a applied torque
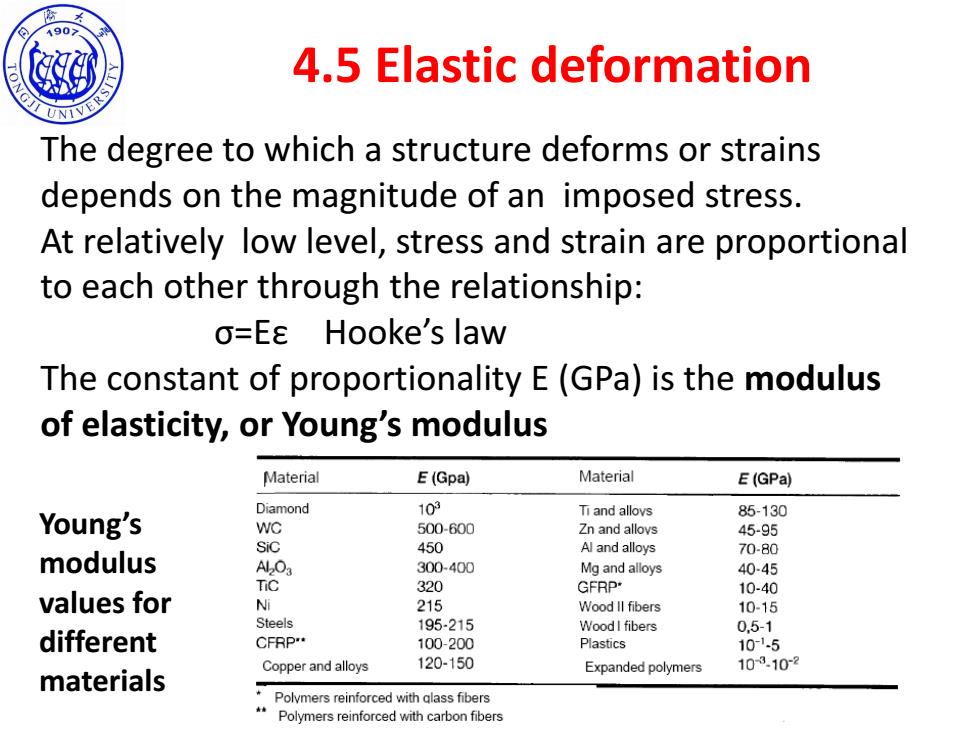
190 4.5 Elastic deformation The degree to which a structure deforms or strains depends on the magnitude of an imposed stress. At relatively low level,stress and strain are proportional to each other through the relationship: o=Ea Hooke's law The constant of proportionality E(GPa)is the modulus of elasticity,or Young's modulus Material E(Gpa) Material E(GPa) Diamond 103 Ti and allovs 85-130 Young's WC 500-600 Zn and alloys 45-95 Sic 450 Al and alloys 70-80 modulus Al2O3 300-400 Mg and alloys 40-45 TiC 320 GFRP 10-40 values for Ni 215 Wood ll fibers 10-15 Steels 195-215 Wood I fibers 0.5-1 different CFRP** 100-200 Plastics 10-1.5 Copper and alloys 120-150 Expanded polymers 103.102 materials Polymers reinforced with glass fibers Polymers reinforced with carbon fibers
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS 4.5 Elastic deformation The degree to which a structure deforms or strains depends on the magnitude of an imposed stress. At relatively low level, stress and strain are proportional to each other through the relationship: σ=Eε Hooke’s law The constant of proportionality E (GPa) is the modulus of elasticity, or Young’s modulus Young’s modulus values for different materials

190> Deformation in which stress and strain are G proportional is called elastic deformation The slope of this linear segment corresponds to the modulus of elasticity E. This modulus may be thought of as stiffness,or a material's resistance to elastic deformation. The greater the modulus,the stiffer the material,or the smaller the Unload elastic strain that results from the Slope=modulus application of a given stress. of elasticity Elastic deformation is nonpermanent, Load which means that when the applied load is released,the piece returns to Strain its original shape. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Deformation in which stress and strain are proportional is called elastic deformation The slope of this linear segment corresponds to the modulus of elasticity E. This modulus may be thought of as stiffness, or a material’s resistance to elastic deformation. The greater the modulus, the stiffer the material, or the smaller the elastic strain that results from the application of a given stress. Elastic deformation is nonpermanent, which means that when the applied load is released, the piece returns to its original shape

190> There are some materials(e.g.gray cast iron, concrete,and many polymers)for which this elastic portion of the stress-strain curve is not linear hence, it is not possible to determine a modulus of elasticity as previous described. For this nonlinear behavior, either tangent or secant modulus is normally used. g-Tangont modulus (at z】 Tangent modulus is taken as the slope of the stress-strain curve at some specified level of stress. Secant modulus Secant modulus represents the (between crigin and) slope of a secant drawn from the origin to some given point Strain of the curve. SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS There are some materials (e.g. gray cast iron, concrete, and many polymers) for which this elastic portion of the stress-strain curve is not linear hence, it is not possible to determine a modulus of elasticity as previous described. For this nonlinear behavior, either tangent or secant modulus is normally used. Tangent modulus is taken as the slope of the stress-strain curve at some specified level of stress. Secant modulus represents the slope of a secant drawn from the origin to some given point of the curve