400 R 300 200 150 Profit 100 50 5 10 15 20 Example of Profit Maximization 8 40 MC 30 AC 20 AR 15 MR 10 15 20
Example of Profit Maximization

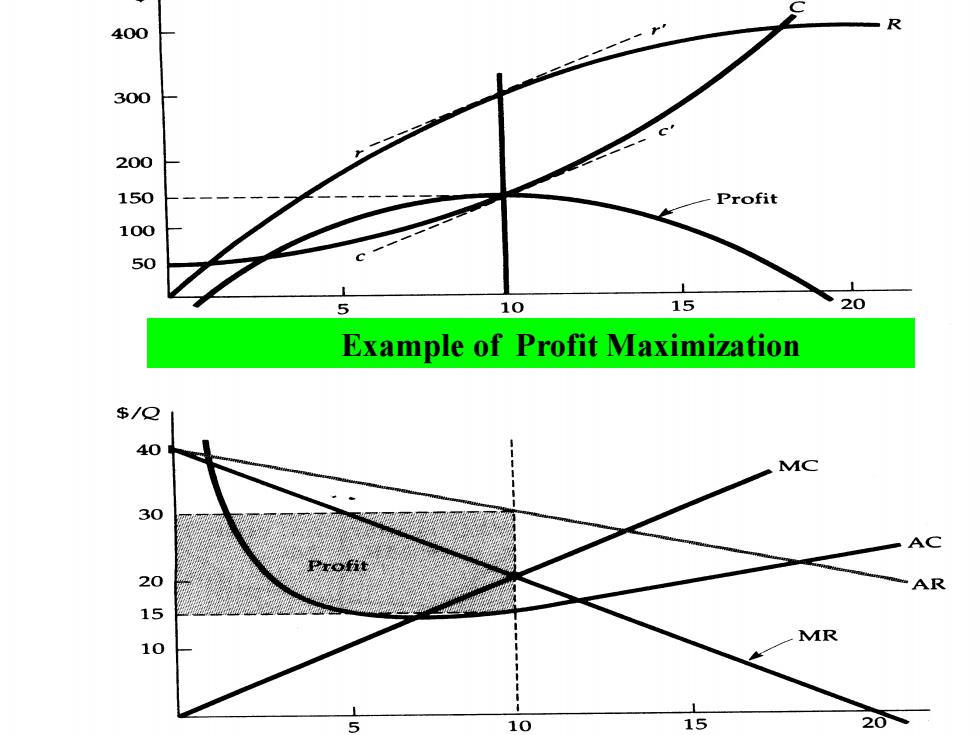
Part (a)shows total revenue R,total cost C,and profit,the difference between the two.Part(b)shows average and marginal revenue and average and marginal cost. Marginal revenue is the slope of the total revenue curve,and marginal cost is the slope of the total cost curve. Suppose:C(Q)=50+Q2(MC=△C/△Q=2Q) P(Q)=40-Q R=P(Q)Q=(40-Q)Q MR=40-2Q MC=MR 40-2Q=20 Q=10
Part (a) shows total revenue R, total cost C, and profit, the difference between the two. Part (b) shows average and marginal revenue and average and marginal cost. Marginal revenue is the slope of the total revenue curve, and marginal cost is the slope of the total cost curve. Suppose: C(Q) = 50 + Q2 (MC = △C/△Q = 2Q) P(Q) = 40 – Q R = P(Q)Q =( 40 – Q)Q MR = 40 – 2Q MC =MR 40 – 2Q = 2Q Q = 10

The profit-maximizing output is Q*=10,the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.At this output level, the slope of the profit curve is zero,and the slopes of the total revenue and total cost curves are equal. The profit per unit is $15,the difference between average revenue and average cost.Because 10 units are produced, total profit is $150
The profit-maximizing output is Q* = l0, the point where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. At this output level, the slope of the profit curve is zero, and the slopes of the total revenue and total cost curves are equal. The profit per unit is $15, the difference between average revenue and average cost. Because 10 units are produced, total profit is $150

A Rule of Thumb for Pricing(定价的简单(经验)法则) MR=△R/△Q=△(PQ)/△Q=P+Q(△P/△Q) =P+P(QP)(△P/△Q)=P+P(△P/P)/△Q/Q) =P+P(1/E) Because the firm's objective is to maximize profit,we can set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost: MR=P+P(1/E)=MC Which can be rearranged to give us P-MC)/P=-(1/Ea)
MR = △R/△Q = △(PQ)/△Q = P + Q (△P/△Q ) = P + P(Q/P) (△P/△Q ) = P + P (△P/P)/(△Q/Q ) = P + P (1/Ed ) Because the firm’s objective is to maximize profit, we can set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost: MR = P + P (1/Ed ) = MC Which can be rearranged to give us (P – MC)/P = - (1/Ed ) A Rule of Thumb for Pricing (定价的简单(经验)法则)

Equivalently,we can rearrange this equation to express price directly as a markup(标高的价格)over marginal cost: P=MC/1+(1/E)
Equivalently, we can rearrange this equation to express price directly as a markup (标高的价格) over marginal cost: P = MC/(1+(1/Ed ))