
The Matching Methodology The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: Confounding bias and sample selection bias. The covariate affects both treatment probability and potential outcome. The treatment status is not driven by the covariates:DID and IV. Control for the covariates. What if the treatment probability is same for treatment group and non-treatment group? Replication to eliminate the disturbance from confounding factors. 6
• The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: • Confounding bias and sample selection bias . • The covariate affects both treatment probability and potential outcome. • The treatment status is not driven by the covariates: DID and IV. • Control for the covariates. • What if the treatment probability is same for treatment group and non-treatment group? • Replication to eliminate the disturbance from confounding factors. 6 The Matching Methodology
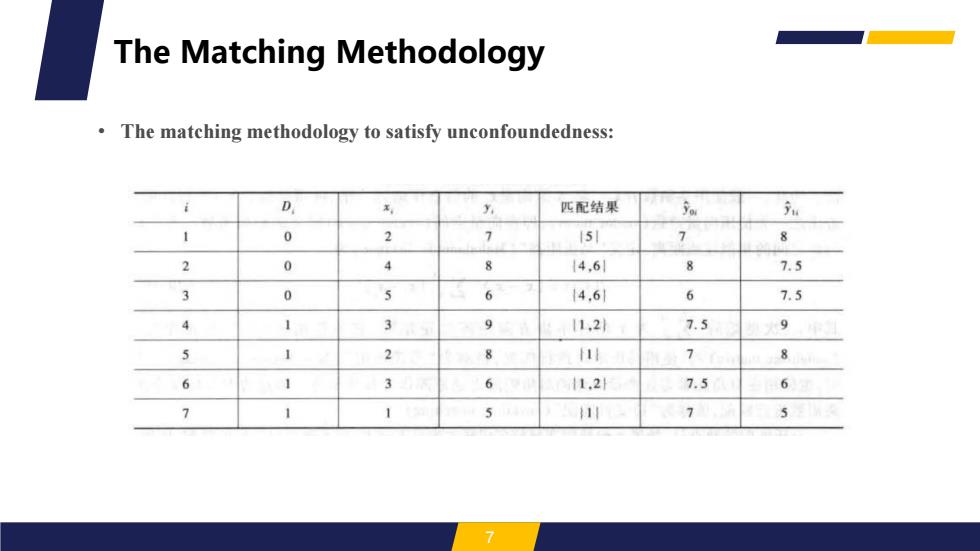
The Matching Methodology 。 The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: D 匹配结果 Yor 1 0 2 151 7 8 2 0 4 8 14,61 8 7.5 3 0 5 6 14.61 6 7.5 4 1 3 9 11,21 7.5 9 5 1 2 8 114 1 6 1 3 6 11.21 7.5 6 7 1 1 5 111 7 5 7
• The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: 7 The Matching Methodology

Outline The Matching Methodology for Causal Inference The Propensity Score Matching The Application for Propensity Score Matching 8
• The Matching Methodology for Causal Inference • The Propensity Score Matching • The Application for Propensity Score Matching 8 Outline

The Propensity Score Matching The covariate determines the treatment probability: 。A set of covariates. How to match treatment and control groups using a set of covariates? Can we ensure that all covariates are same for treatment and control groups? 9
• The covariate determines the treatment probability: • A set of covariates. • How to match treatment and control groups using a set of covariates? • Can we ensure that all covariates are same for treatment and control groups? 9 The Propensity Score Matching

The Propensity Score Matching Dimension reduction: ·A set of covariates→A function. The methodology to develop a function. The difference between treatment and control groups under a set of covariates. ·The distance function in vector space:Mahalanobis distance(马氏距离) Dy(,y)=V(-y)TE-1(-y) The limitation when using Mahalanobis distance:relative distance and absolute distance. 10
• Dimension reduction: • A set of covariates→A function. • The methodology to develop a function. • The difference between treatment and control groups under a set of covariates. • The distance function in vector space: Mahalanobis distance (马氏距离) • The limitation when using Mahalanobis distance: relative distance and absolute distance. 10 The Propensity Score Matching