
Financial Econometrics Chapter 4.Causal Inference framework 2 Channel and Mechanism identification Jin Ling School of Finance,Zhongnan University of Economics and Law
Financial Econometrics Chapter 4. Causal Inference framework 2 Channel and Mechanism identification Jin Ling School of Finance, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law 1

Outline The Definition of Channel and Mechanism Causal Directed Acyclic Graph The Methodology for Channel and Mechanism Identification 2
• The Definition of Channel and Mechanism • Causal Directed Acyclic Graph • The Methodology for Channel and Mechanism Identification 2 Outline

The Definition of Channel and Mechanism ·The definition: Channel and mechanism depict how treatment leads to changes of outcome variables. ·作用渠道或作用机制刻画因果效应何以存在、如何存在。 Managers'education and corporate operation;Bank competition and financial constraints;Retail investors trading and market stability. Why the identification of channel or mechanism is important? Convince us that the Causal effect does not originate from coincidence. To verify the financial theories. Further applications. 3
• The definition: • Channel and mechanism depict how treatment leads to changes of outcome variables. • 作用渠道或作用机制刻画因果效应何以存在、如何存在。 • Managers' education and corporate operation; Bank competition and financial constraints; Retail investors trading and market stability. • Why the identification of channel or mechanism is important? • Convince us that the Causal effect does not originate from coincidence. • To verify the financial theories. • Further applications. 3 The Definition of Channel and Mechanism
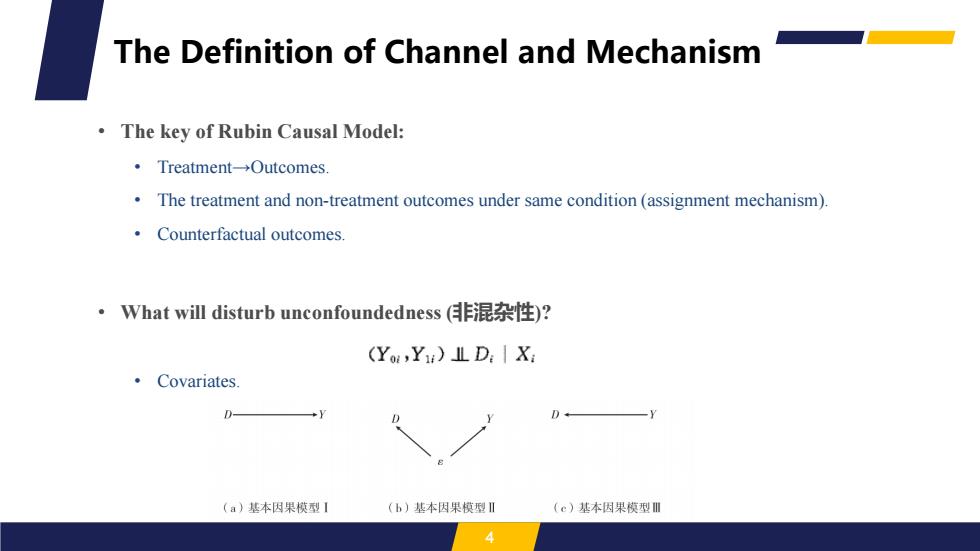
The Definition of Channel and Mechanism The key of Rubin Causal Model: ·Treatment-→Dutcomes. The treatment and non-treatment outcomes under same condition(assignment mechanism). Counterfactual outcomes. ·What will disturb unconfoundedness(非混杂性)? (Yo,Yu)IL D:Xi Covariates. D (a)基本因果模型I (b)基本因果模型Ⅱ (e)基本因果模型Ⅲ
• The key of Rubin Causal Model: • Treatment→Outcomes. • The treatment and non-treatment outcomes under same condition (assignment mechanism). • Counterfactual outcomes. • What will disturb unconfoundedness (非混杂性)? • Covariates. 4 The Definition of Channel and Mechanism
The Definition of Channel and Mechanism The correlation and causal effect: Causal inference:Causal identification and statistical inference. Causal identification:if A is not correlated with B,there is no causal effect between A and B.If A is corelated with B and there is only a causal model to identify the correlation,A leads to B or B leads to A. Statistical inference:Significant or insignificant correlation. If the coefficient for variable A in a regression on B is insignificant,can we conclude A has no causal effect on B? If the coefficient for variable A in a regression on B is significant,can we conclude A has a causal effect on B?
• The correlation and causal effect: • Causal inference: Causal identification and statistical inference. • Causal identification: if A is not correlated with B, there is no causal effect between A and B. If A is corelated with B and there is only a causal model to identify the correlation, A leads to B or B leads to A. • Statistical inference: Significant or insignificant correlation. • If the coefficient for variable A in a regression on B is insignificant, can we conclude A has no causal effect on B? • If the coefficient for variable A in a regression on B is significant, can we conclude A has a causal effect on B? 5 The Definition of Channel and Mechanism