
Physical examination.Patients with pericarditis may have an irregular or rapid pulse secondary to atrial arrhythmias or tamponade.A pericardial friction rub is the hallmark of the disease.This superficial scraping, scratchy,or grating sound is frequently evanescent or intermittent.Persistent rubs are most often heard with Pericarditis secondary to neoplasm,uremia,viral infection,and tuberculosis.Evanescent rubs are common in pericarditis associated with Ml.Rubs may have one,two,or three components occurring with the following stages of cardiac cycle:(1)rapid filling in early diastole,(2)atrial contraction in late diastole,and (3) systole.On occasion,one-or two-component rubs are confused with systolic or to-and-fro murmurs.Sometimes a patient with pericarditis has an early diastolic sound or pericardial knock,which can be confused with a third heart sound (S3).Other systemic findings in patients with pericarditis depend on the underlying condition
• Physical examination. Patients with pericarditis may have an irregular or rapid pulse secondary to atrial arrhythmias or tamponade. A pericardial friction rub is the hallmark of the disease. This superficial scraping, scratchy, or grating sound is frequently evanescent or intermittent. Persistent rubs are most often heard with Pericarditis secondary to neoplasm, uremia, viral infection, and tuberculosis. Evanescent rubs are common in pericarditis associated with MI. Rubs may have one, two, or three components occurring with the following stages of cardiac cycle: (1) rapid filling in early diastole, (2) atrial contraction in late diastole, and (3) systole. On occasion, one- or two-component rubs are confused with systolic or to-and-fro murmurs. Sometimes a patient with pericarditis has an early diastolic sound or pericardial knock, which can be confused with a third heart sound (S3). Other systemic findings in patients with pericarditis depend on the underlying condition

ECG.The ECG is often abnormal in patients with pericarditis.ECG findings include diffusely elevated S-T segments,widespread T wave changes, and P-R segment depression.Elevated S-T segments can mimic the ECG findings of acute Ml.ECG findings in pericarditis are as follows: Elevation of S-T segment Flattening and inversion of T waves Depression of P-R segment
• ECG. The ECG is often abnormal in patients with pericarditis. ECG findings include diffusely elevated S-T segments, widespread T wave changes, and P-R segment depression. Elevated S-T segments can mimic the ECG findings of acute MI. ECG findings in pericarditis are as follows: Elevation of S-T segment Flattening and inversion of T waves Depression of P-R segment

Their differentiation from ECG changes of acute MI are listed in Table 2.The S-T segment elevations of early repolarization occasionally may be confused with those of pericarditis; however,S-T segment elevation of early repolarization usually is limited to the precordial leads,while that of pericarditis occurs throughout limb and precordial leads.Supraventricular arrhythmias are frequently noted in patients with pericarditis
• Their differentiation from ECG changes of acute MI are listed in Table 2. The S-T segment elevations of early repolarization occasionally may be confused with those of pericarditis; however, S-T segment elevation of early repolarization usually is limited to the precordial leads, while that of pericarditis occurs throughout limb and precordial leads. Supraventricular arrhythmias are frequently noted in patients with pericarditis
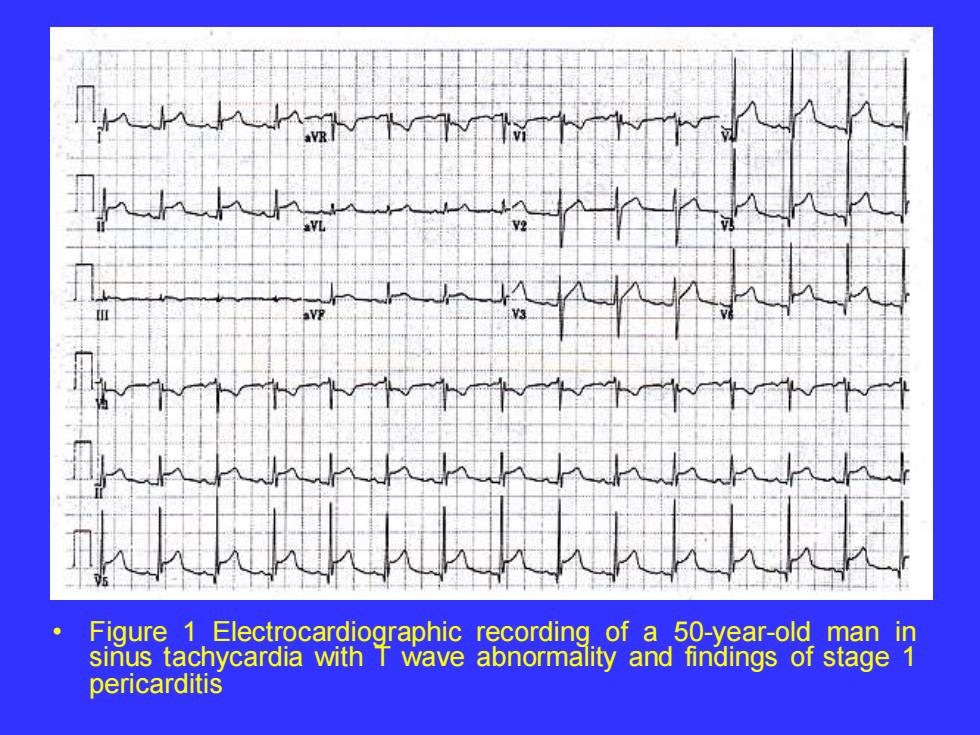
Figure 1 Electrocardiographic recording of a 50-year-old man in sinus tachycardia with T wave abnormality and findings of stage 1 pericarditis
• Figure 1 Electrocardiographic recording of a 50-year-old man in sinus tachycardia with T wave abnormality and findings of stage 1 pericarditis

Table 2 Differentiation of ECG finding in pericarditis from ECG changes in acute MI Pericarditis MI S-T segment elevations S-T segment elevations localized Widespread;no S-T segment to certain leads with reciprocal Depressions present S-T segment depressions in other leads S-T segment elevation with S-T segment elevation with Upward concavity or straight upward convexity Morphology Simultaneous T wave inversion T waves not simultaneously In lead I,Il,and Ill inverted in leads 1,Il,and Ill Significant Q waves not seen significant Q waves frequently With pericarditis seen with MI QRS often normal QRS often abnormal
• Table 2 Differentiation of ECG finding in pericarditis from ECG changes in acute MI Pericarditis MI S-T segment elevations S-T segment elevations localized Widespread; no S-T segment to certain leads with reciprocal Depressions present S-T segment depressions in other leads S-T segment elevation with S-T segment elevation with Upward concavity or straight upward convexity Morphology Simultaneous T wave inversion T waves not simultaneously In lead I, II, and III inverted in leads I, II, and III Significant Q waves not seen significant Q waves frequently With pericarditis seen with MI QRS often normal QRS often abnormal