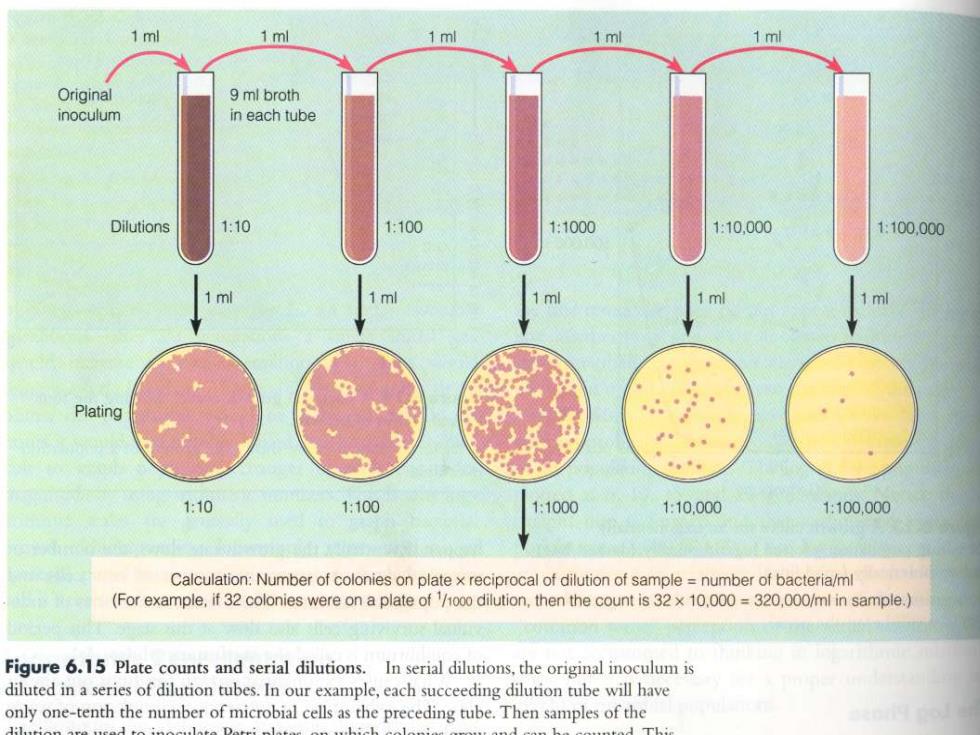
1 ml 1 ml 1 ml Original 9 ml broth inoculum in each tube Dilutions 1:10 1:100 1:1000 1:10.000 1:100.000 m Plating 1:10 1100 1:1000 1:10.000 1100,000 Calculation:Number of colonies on plate x reciprocal of dilution of sample number of bacteria/ml (For example,if 32 colonies were on a plate of 1/1000 dilution,then the count is 32x 10.000=320,000/ml in sample.) Figure 6.15 Plate counts and serial dilutions.In serial dilutions,the original inoculum is diluted in a series of dilution tubes.In our example,each succeeding dilution tube will have only one-tenth the number of microbial cells as the preceding tube.Then samples of the
第一节 微生物生长的测定 (一)以数量变化对微生物生长情况进行测定 通常用来测定细菌、酵母菌等单细胞微 生物的生长情况或样品中所含微生物个体 的数量(细菌、孢子、酵母菌) 1、培养平板计数法 (参见P152)

ARTEK COUNTER 20 anter illuminates the petri plate unifor an electric probe is touched to each col s of the desired size range in any part 以在科研中一 般菌洛形成平co1 ony forming units,.CFU)来表 示,而不是直接表示为细胞数
采用培养平板计数法要求操作熟 练,准确,否则难以得到正确的结果: 样品充分混匀; 每支移液管及涂布棒只能 接触一个稀释度的菌液; 同一稀释度三个以上重 复,取平均值; 每个平板上的菌落数目合 适,便于准确计数; 一个菌落可能是多个细胞一起形成,所以在科研中一 般用菌落形成单位(colony forming units, CFU)来表 示,而不是直接表示为细胞数

(一)以数量变化对微生物生长情况进行测定 2、膜过滤培养法 当样品中菌数很低时,可以将一定体积的湖水 海水或饮用水等样品通过膜过滤器,然后将将 膜转到相应的培养基上进行培养,对形成的菌 落进行统计。 Figure 6.17 Counting bacteria by filtration.(a)The bacteria in 100 ml of water were sieved out onto the surface of a membrane filter.(b)Such a filter,with the bacteria much more widely spaced, was placed on a pad saturated with liquid nutrient medium,and the individual bacteria grew into visible colonies.One hundred twenty four colonies are visible,so we would record 124 bacteria per 100 ml of water sample. Bacteria can be counted by filtra- tion when their quantity is very small
(一)以数量变化对微生物生长情况进行测定 2、膜过滤培养法 当样品中菌数很低时,可以将一定体积的湖水、 海水或饮用水等样品通过膜过滤器,然后将将 膜转到相应的培养基上进行培养,对形成的菌 落进行统计
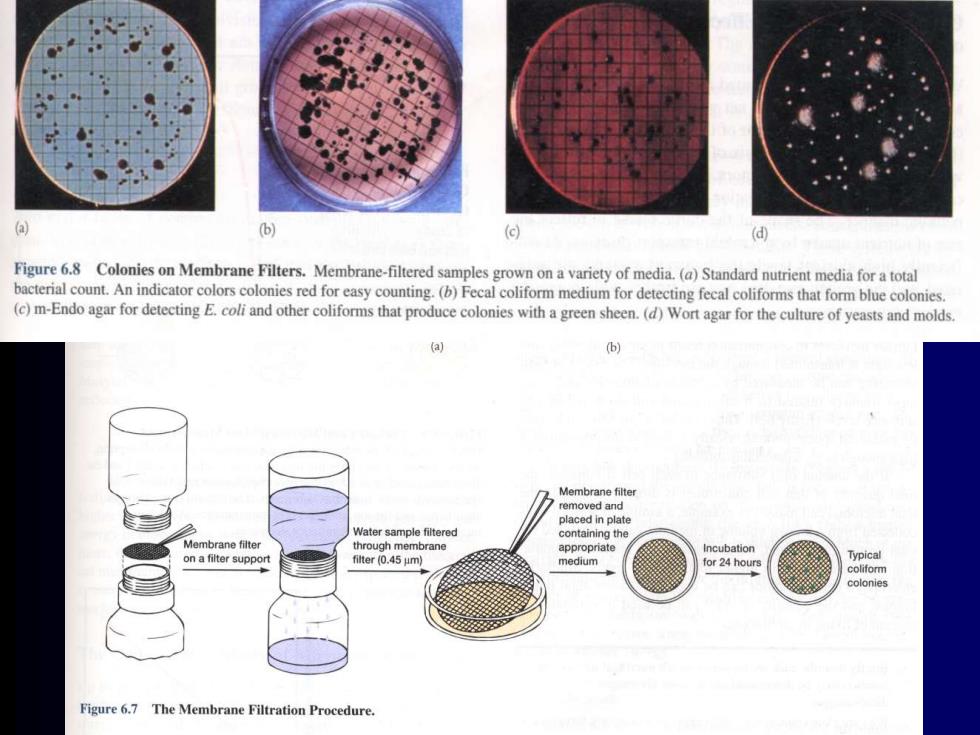
(b) (© Figure 6.8 Colonies on Membrane Filters.Membrane-filtered samples grown on a variety of media.(a)Standard nutrient media for a total bacterial count.An indicator colors colonies red for easy counting.(b)Fecal coliform medium for detecting fecal coliforms that form blue colonies. (c)m-Endo agar for detecting E.coli and other coliforms that produce colonies with a green sheen.(d)Wort agar for the culture of yeasts and molds. (a) Membrane filter removed and placed in plate Water sample filtered containing the Membrane filter through membrane app rop on a filter support filter(0.45μml medium or 24 hours Typical coliform colonies Figure 6.7 The Membrane Filtration Procedure
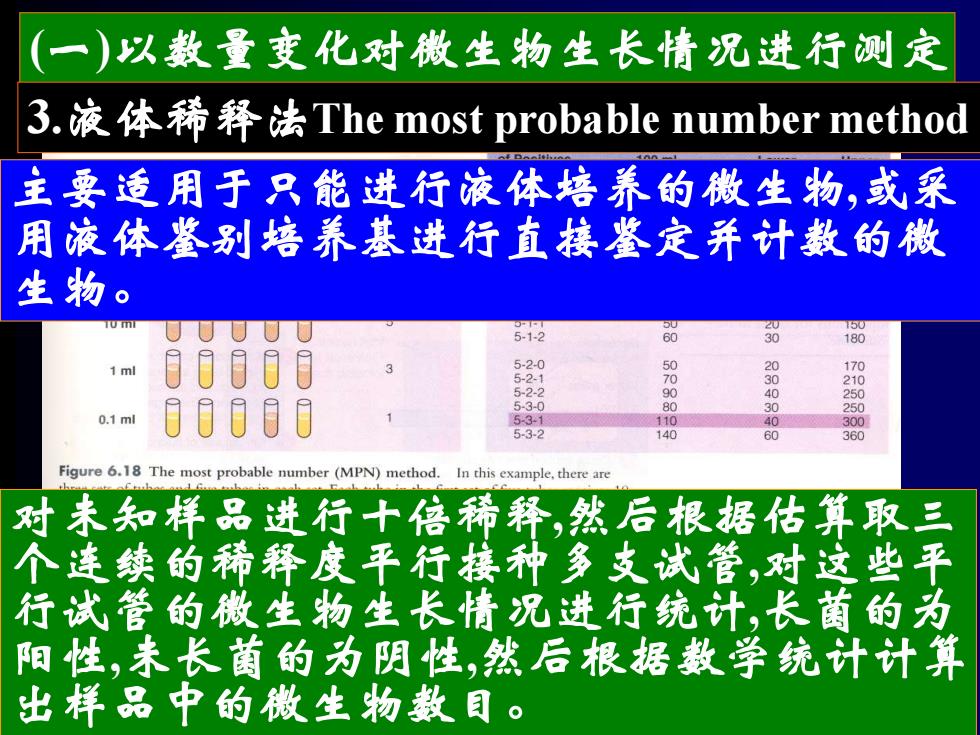
(一)以数量变化对微生物生长情况进行测定 3.液体稀释法The most probable number method 主要适用于只能进行液体培养的微生物,或采 用液体鉴别培养基进行直接鉴定并计数的微 生物。 5 60 四 180 1ml 00000 5-20 5-2.1 5-2.2 900 5-3-0 0 0306000 0.1ml 00000 5-3-1 110 53-2 10 0 360 Figure 6.18 The most probable number(MPN)method. In this example,there are 对未知样品进行十倍稀释,然后根据估算取三 个连续的稀释度平行接种多支试管,对这些平 行试管的微生物生长情况进行统计,长菌的为 阳性,未长菌的为阴性,然后根据数学统计计算 出样品中的微生物数目
(一)以数量变化对微生物生长情况进行测定 主要适用于只能进行液体培养的微生物,或采 用液体鉴别培养基进行直接鉴定并计数的微 生物。 对未知样品进行十倍稀释,然后根据估算取三 个连续的稀释度平行接种多支试管,对这些平 行试管的微生物生长情况进行统计,长菌的为 阳性,未长菌的为阴性,然后根据数学统计计算 出样品中的微生物数目。 3.液体稀释法The most probable number method