
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 16 1). The thermodynamic definition of entropy a). Heat stimulates disorderly motion in the surroundings; work stimulates uniform motion of atoms in the surroundings, does not change the degree of disorder, and so does not change the entropy. b). A change in the extent to which energy is dispersed in a disorderly manner depends on the quantity of energy transferred as heat. 4.2 Entropy
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 16 1). The thermodynamic definition of entropy a). Heat stimulates disorderly motion in the surroundings; work stimulates uniform motion of atoms in the surroundings, does not change the degree of disorder, and so does not change the entropy. b). A change in the extent to which energy is dispersed in a disorderly manner depends on the quantity of energy transferred as heat. 4.2 Entropy

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 17 1). The thermodynamic definition of entropy T q S d rev d = The thermodynamic definition of entropy is based on The units of entropy: J K -1. The units of Molar entropy: J K -1 mol –1 (the same as that of R) 4.2 Entropy
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 17 1). The thermodynamic definition of entropy T q S d rev d = The thermodynamic definition of entropy is based on The units of entropy: J K -1. The units of Molar entropy: J K -1 mol –1 (the same as that of R) 4.2 Entropy

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 18 1). The thermodynamic definition of entropy For a measurable change between two states i and f this expression integrates to: ∫ = fi rev dTq ΔS To calculate the difference in entropy between any two states of a system, integrate the heat supplied at each stage of the path divided by the temperature at which the heat is supplied. 4.2 Entropy
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 18 1). The thermodynamic definition of entropy For a measurable change between two states i and f this expression integrates to: ∫ = fi rev dTq ΔS To calculate the difference in entropy between any two states of a system, integrate the heat supplied at each stage of the path divided by the temperature at which the heat is supplied. 4.2 Entropy

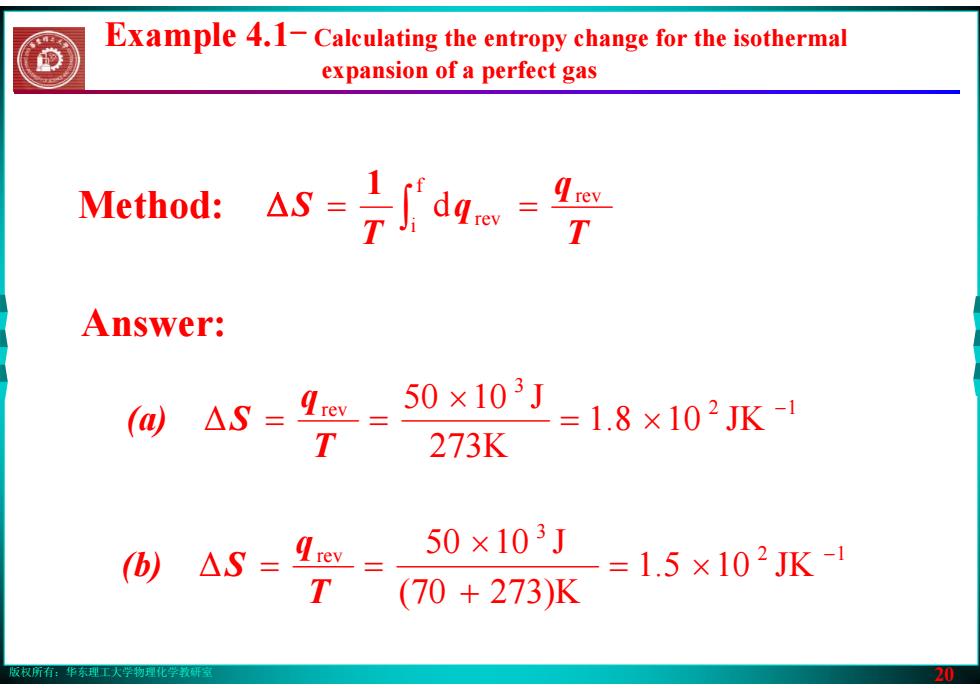
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 19 Example Calculate the change in entropy when 50kJ of energy is transferred reversibly and isothermally as heat to a large block of copper at (0) ℃, and (b) 70 ℃
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 19 Example Calculate the change in entropy when 50kJ of energy is transferred reversibly and isothermally as heat to a large block of copper at (0) ℃, and (b) 70 ℃
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 20 Example 4.1- Calculating the entropy change for the isothermal expansion of a perfect gas Answer: ∫ = = fi rev d rev Tq q T S 1 Method: Δ 2 1 3 rev 1.8 10 JK 273K 50 10 J Δ − = × × = = T q (a) S 2 1 3 rev 1.5 10 JK (70 273)K 50 10 J Δ − = × + × = = T q (b) S
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 20 Example 4.1- Calculating the entropy change for the isothermal expansion of a perfect gas Answer: ∫ = = fi rev d rev Tq q T S 1 Method: Δ 2 1 3 rev 1.8 10 JK 273K 50 10 J Δ − = × × = = T q (a) S 2 1 3 rev 1.5 10 JK (70 273)K 50 10 J Δ − = × + × = = T q (b) S