
1-41 continued (e) CHa-N-CH3 CH3一N -CH3 CH一C-CH CH--CH CH3-C 一CH CH一 -CH3 more stable-resonance stabilized no resonance stabilization 1-42 These pK values from the text,Table 1-5 and Appendix 4,provide the answers.The lower the the stronge the aid.Water and CH are verycos least acidic most acidic NH< CHCOOH HF < H30+<H,SO4 33(or36 15.7 155 4.74 3.2 -1.7 -5 出出两 least basic most basic HSO<H2O<CH;COO<NH3 CH;O-~NaOH <NH2 from-5 from-1.7 from 4.74 from9.4 from 15.5 from 15.7 from 33(or 36) 1-44 (a) pKa =-logio Ka =-log10(5.2 x 10-5)=4.3 for phenylacetic acid for propionic acid,pKa 4.87:Ka=10-487=1.35x10-5 (b) Phenylacetic acid is39 times stronger than propionic acid. 5.2x10-5 =3.9 1.35x10-5 (c) —CH,C00+CH,CH,COOH± -CH,COOH CHCHCOO weaker acid stronger acid Equilibrium favors the weaker acid and base.In this reaction,reactants are favored. 1-45 The newly formed bond is shown in bold (a) c-g cn.Cci: →c4--c4,+9 nucleophile electrophile Lewis base Lewis acid (b) HC nucleophile Lewis base 22 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Inc
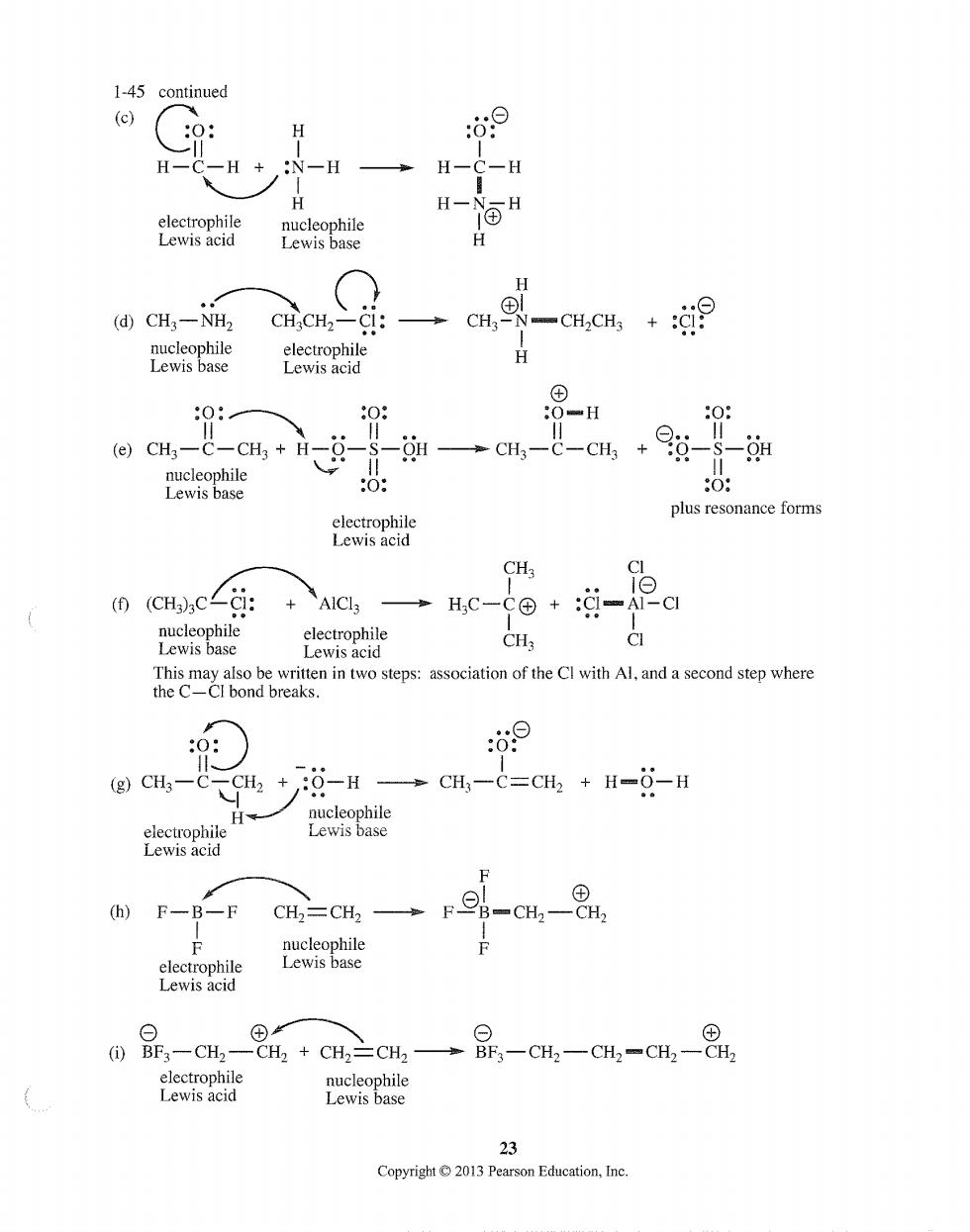
1-45 continued (c) 0: H o9 H-C-H +:N-H-H-C-H H H (d)CH3-NH2 CHCH2-CI: c9-0H,0+9 H -H (e)CH3一C-CH3+H ++海 electrophile plus resonance forms Lewis acid (CH)cci: H,C-C+:i-A2C lecophie e2gomanintwosepssociionofteCwih.andaeoadsepwhae ò9 (g)Cils-CCHa+:-CH-C=CH2+H-6-H c (h)F-B-F ucepa ⊙ 08,-H,_e+CH三=c→品-H-H-H,-8 electrophile Lewis acid 23 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Inc
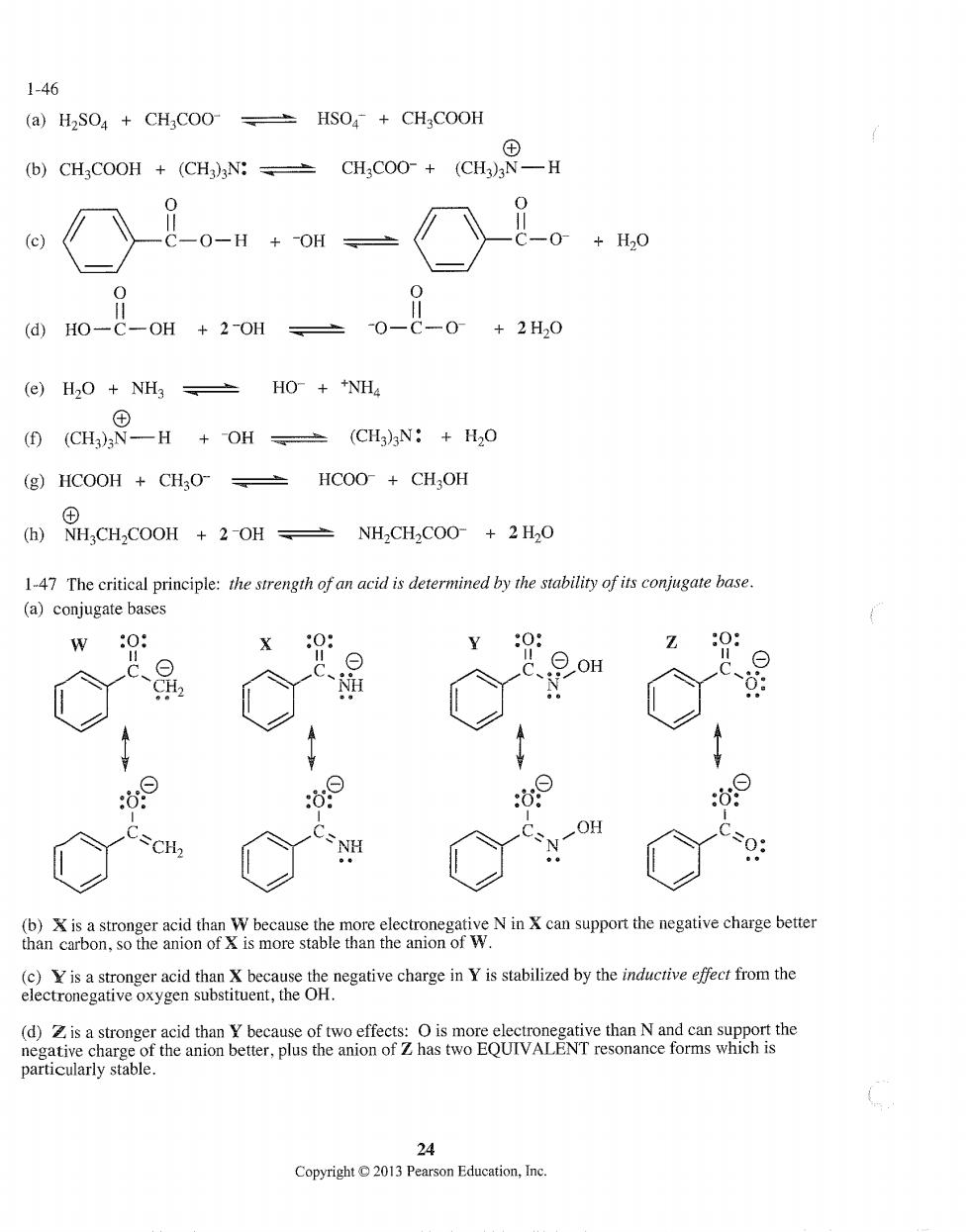
1-46 (a)H2SO4+CH COO HSO+CHCOOH (CHCOOH+CHCH.COO+(C -0-H+0 +H,0 0 @H0-C-0H+2-0H=0-C-0+2H,0 (e)H,0+NH3±H0+NH4 C9-H+OH、CHN:+0 (g)HCOOH CHO-HCOO CH,OH (h)NHCH2COOH +2-OH NH2CH2COO-2H2O 1-47 The critical principle:the strength of an acid is determined by the stability of its conjugate base (a)conjugate bases w0: 0: Y0: Z0: oH :⊙ 次⊙ OH CH (b)Xis astronger acid than W because the more electronegative Nin can suppor the negative charge better than carbon,so the anion of is more stable than the anion of W. (c)Yis a stronger acid than X because the negative charge in Y is stabilized by the inducrive effect from the electronegative oxygen substituent,the OH. (d)is a stron anion b particularly stable. 24 Copyright 2013 Pearson Education,Inc
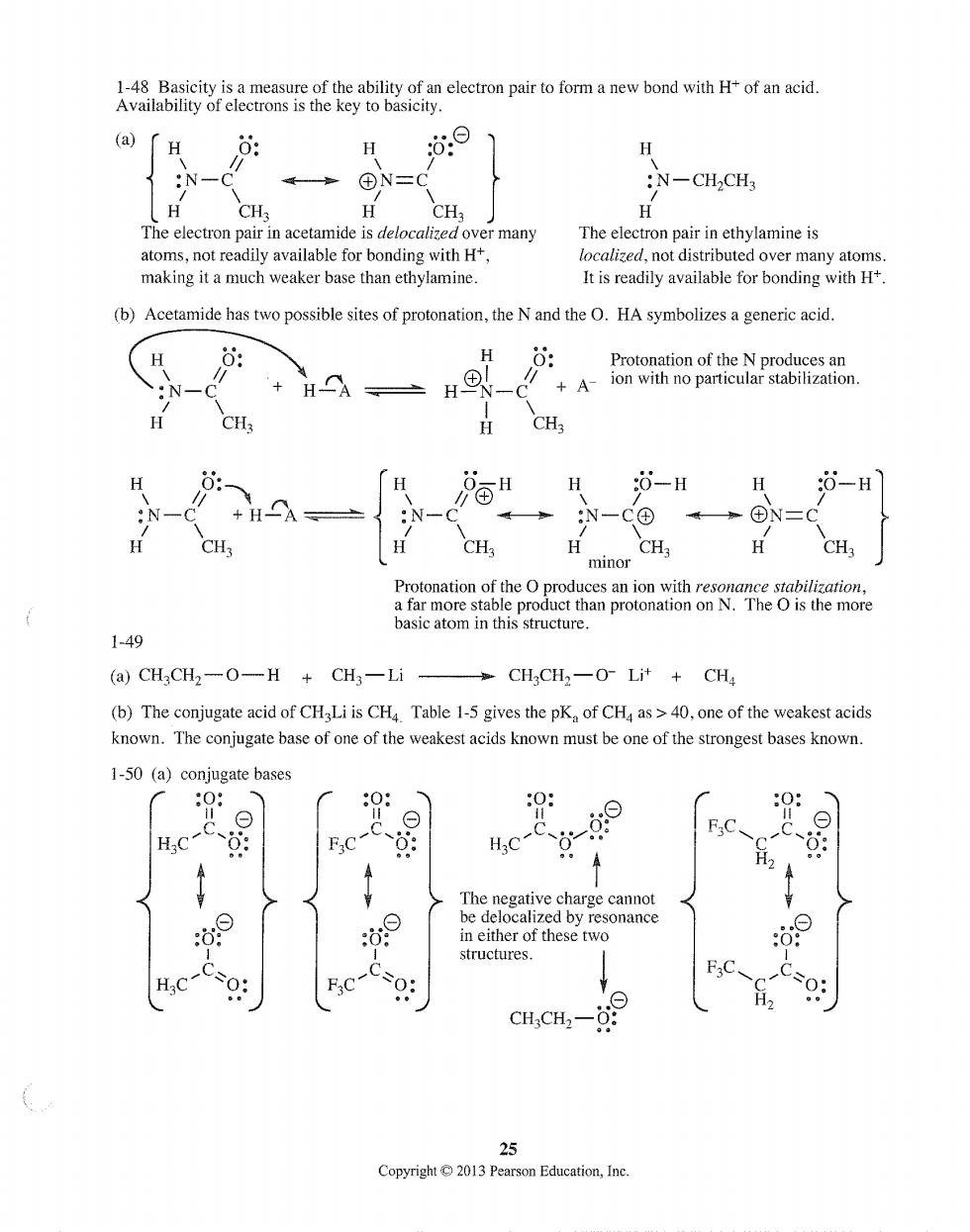
(a) H 0: H :N-CH2CH CH. CH The electron pair in acetamide is delocalize many The elec on pair inethylamine is ot readily available for bonding with H localized,not dist d over many atoms making it a much weaker base than ethylamine. It is readily available for bonding with H (b)Acetamide has two possible sites of protonation,the N and the O.HA symbolizes a generic acid. HO: +HA、H +A 6 酒H :0-H δ-H CO CH. CH H CH3 minor Protonation of the O produces an ion with resonance stabilization a far more stable product than protonation on N.The O is the more basic atom in this structure. 1-49 (a)CHCH2一OH+CH3一Li CHCH2一OLit+CH (b)The conjugate acid of CHaLi is CH Table 1-5 gives the pK of CHa as>40,one of the weakest acids known.The conjugate base of one of the weakest acids known must be one of the strongest bases known. 1-50 (a)conjugate bases 0 0: 0: 0: H.C-C F.C-C FC、 A 4 The negative charge cannot c,4-的9 25 Copyright013 Pearson Education,Inc

1-50 continued (b) 0 7 0: 0: >F;C. co: H.C delocalizat veak least stable-no delocalization of negative charge by negative charge by delocalization of delocalizationo resonance only negative charge resonance and a egative f) are farther away (c)The strongest acid will have the most stable conjugate base.The actual pK values(some from text Appendix 4)are listed beneath each acid. 0 E.C-COH OH CH:CH OH OH 01 weakest acid strongest acid pKa 15.9 DK30.2 pK.3.07 pK4.7 pK,8.2 1-51 (a)conjugate acids H than the nit H )on the previous page. H H CH:CH2- :0-H H-0c,-2HH-N H δ-H N=C CH (b)order of decreasing stability (pK values from Appendix 4 in the text) H H-NH2 H-OH CH.CH- -H >CH;CH2-O-H most stable lecule H H least stable NH bonds.lower pKa 15.7 positive charge on less h e on more electronegative atom electronegativity pK210.7 but resonance. abilized pK-2.4 pK0. 26 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Inc