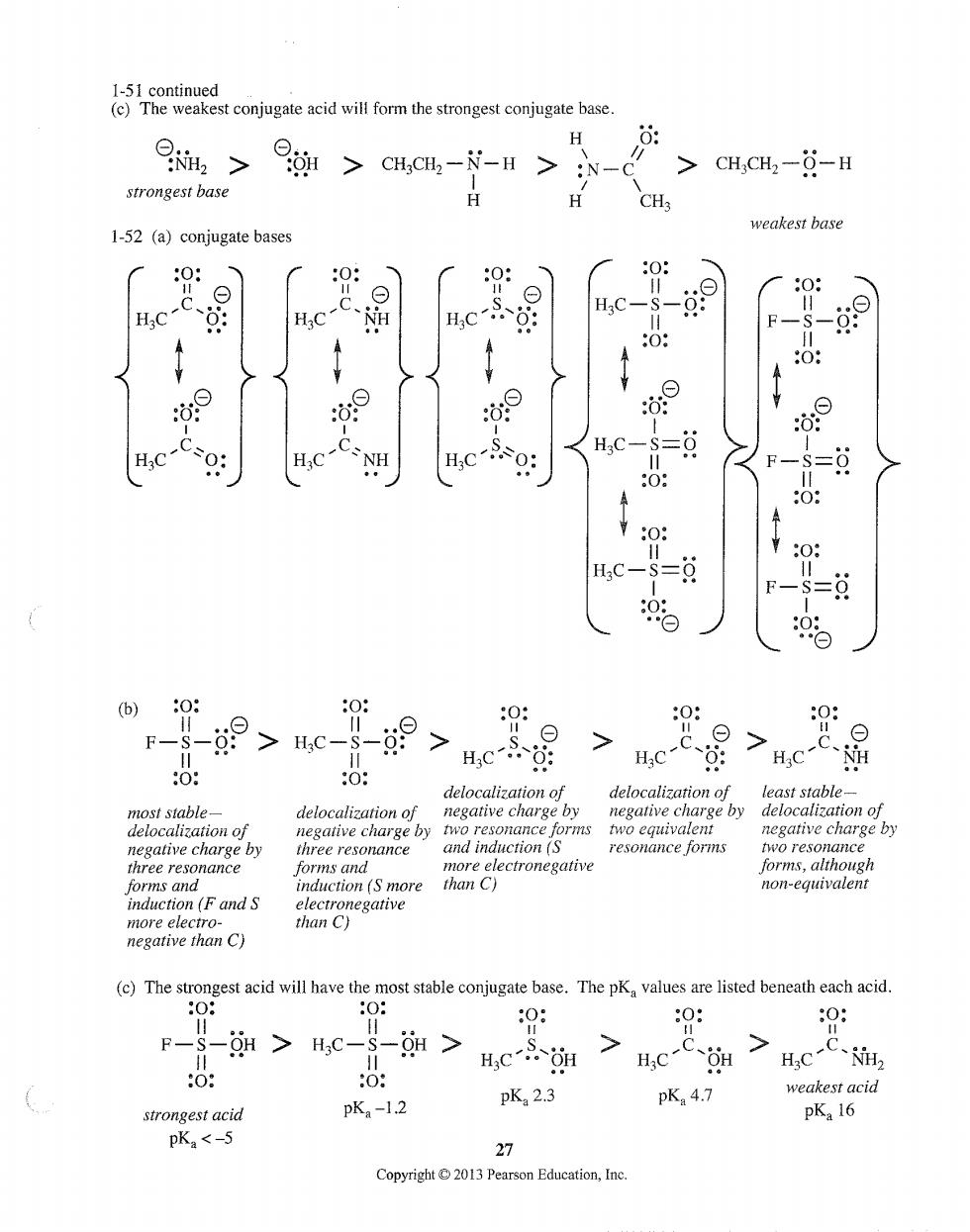
H >CH CH2- N-H CHCHa--H strongest base CH. weakest base 1-52 (a)conjugate bases : ⊙ H:C- o 0: c-C H:C t 0: Hc-Cso: HC-C NH s=9 :0: 0: H:C =9 0: F So %o -9>c- ⊙ 0: F-S > Hc > ⊙ > delocalization of least stable delocalization of by arge by harge by resonance forms two resonance three resonance forms and forms,although forms and FandS duction(S more non-equivalent uctn0 (c)The stro gest acid will have the stable con base.The p,vaue re listed beneath each acid 0: 0: F-S-H>Hc-$- > H,C 7 > HC-C、 pKa-1.2 pK2.3 pK4.7 weakest acid strongest acid pKa 16 pKa<-5 Pearson Education,Ine
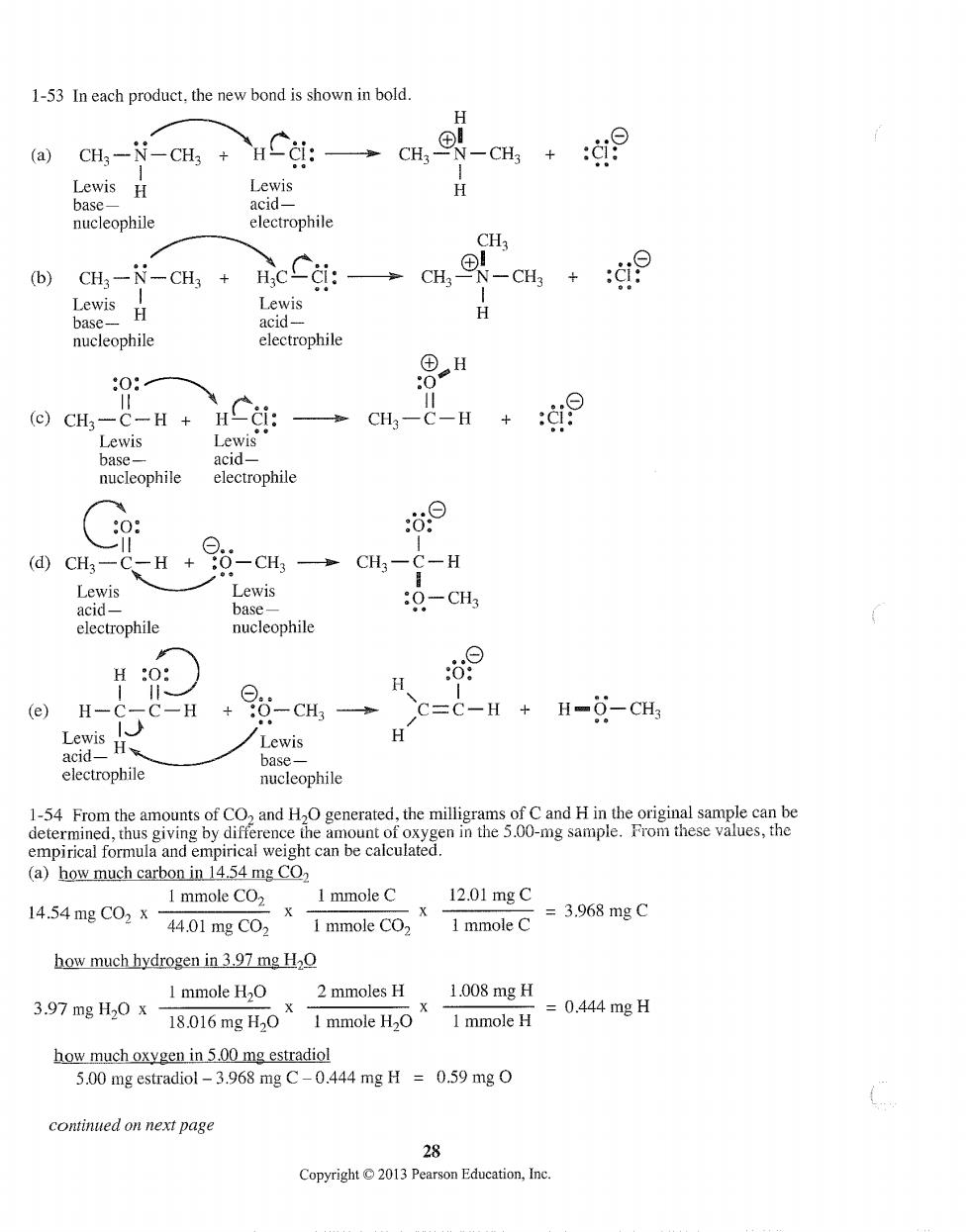
1-53 In each product,the new bond is shown in bold. H (a)CHa-N-CHg 0 Lewis H Lewis H nucleophile electrophile (b) CH3-N-CH3 →CH, -CH3 Lewis H H heieophic eectrophite ⊙cH-c-H+HCi: CH3一C-H + 汝洞 Lewis Lewis base acid- nucleophile electrophile 0: 这⊙ ⊙. (d④)CH一 -H+ 0-CH3 CH3- C-H base- :0-CH3 electrophile nucleophile HO H (e)H- 一H -CH3 C=C-H H-O-CH3 Lewis H electrophile nucleophile (a)how much carbon in 14.54 mg CO2 1 mmole CO2 I mmole C 12.01mgC 14.54mgC02x X I mmole CO2 =3.968mgC 44.01mgC02 1 mmole C how much hydrogen in397 mg HO I mmole H2O 2 mmoles H 1.008mgH 3.97mgH,0X18016mgH,0X I mmole H. =0.444mgH 1 mmole H how much oxygen in 5.00 mg estradiol 5.00 mg estradiol-3.968 mg C-0.444 mg H 0.59 mg O continued on next pag 28 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Ine
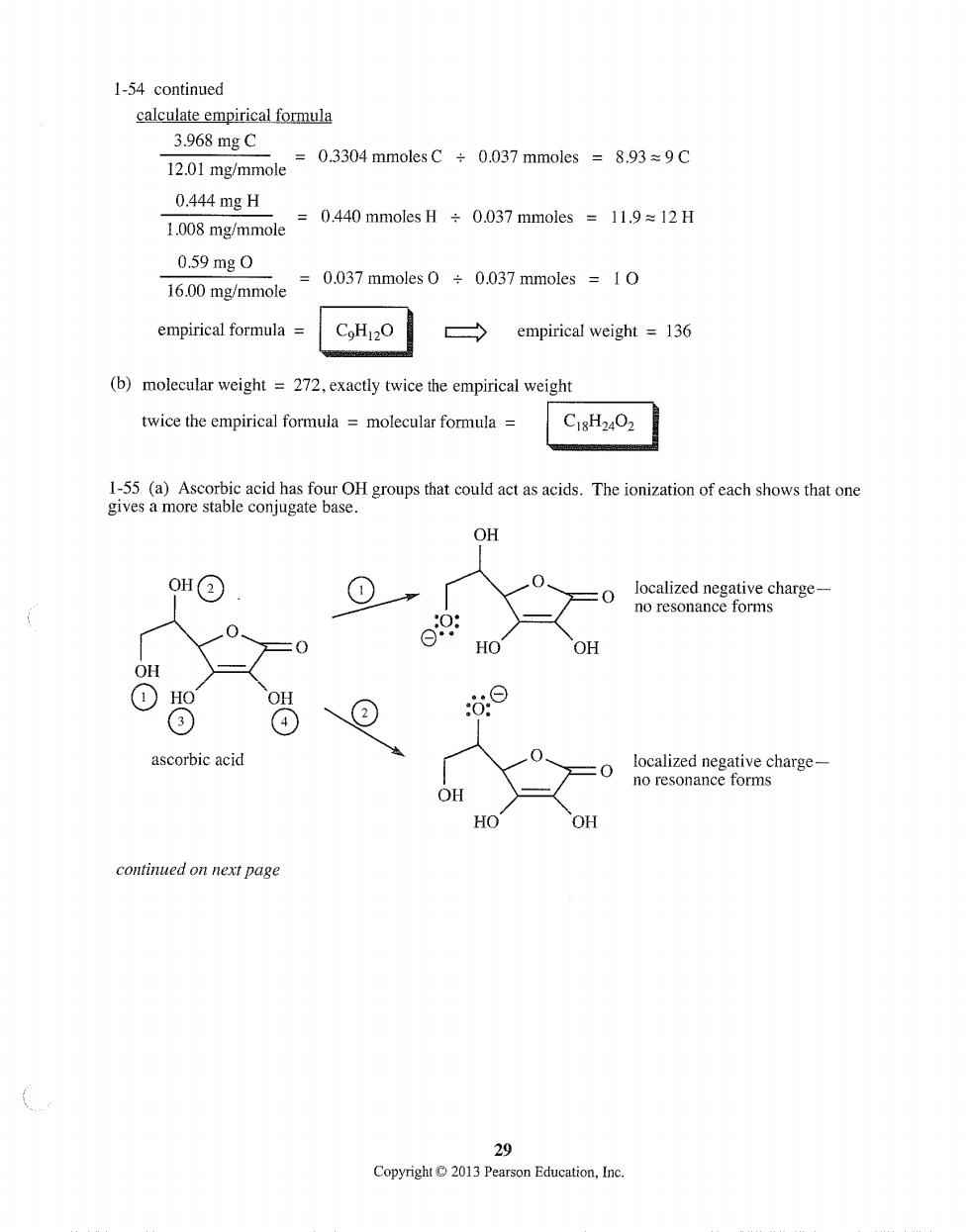
1-54 continued calculate empirical formula 3.968mgC =0.3304 mmoles C÷0.037 mmoles=8.93≈9C 12.01 mg/mmole 0.444mgH 1.008 mg/mmole =0.440 mmoles÷0.037 mmoles=11.9≈12H 0.59mg0 16.00 mg/mmole =0.037 mmoles 0 0.037 mmoles 10 empirical formula= CoH12O empirical weight =136 (b)molecular weight =272,exactly twice the empirical weight twice the empirical formula=molecular formula C18H24O2 1-55(a)Ascorbic acid has four OH groups that could act as acids.The ionization of each shows that one gives a more stable conjugate base. OH 0H@ =0 =0 HO OH OH ⊙ ② ⊙ ascorbic acid 0 localized negative charge- no resonance forms OH HO OH continued on next page 29 Copyright013Pearson Education,Inc
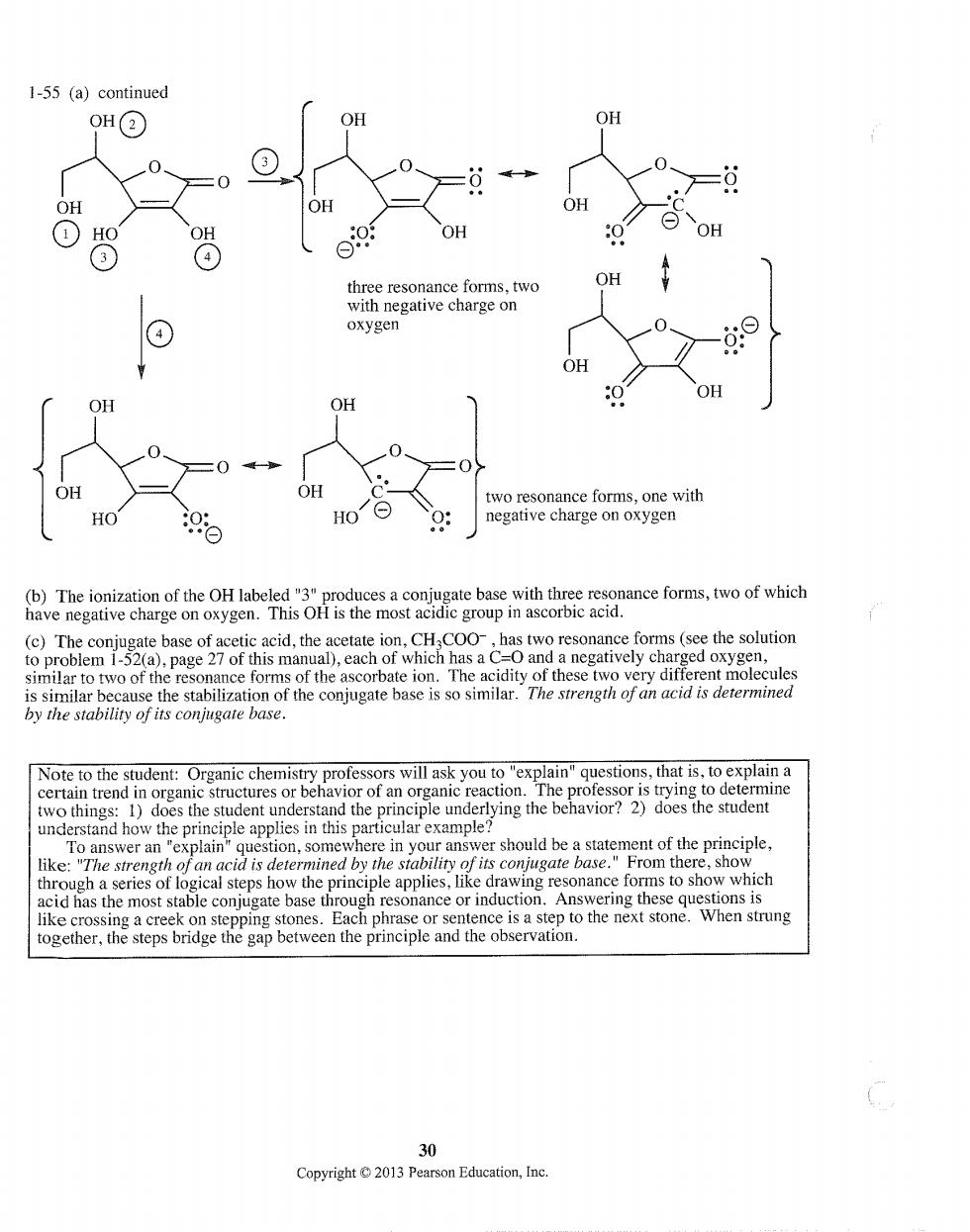
1-55 (a)continued OH② ③ OH OH ①H ⊙0 esonance forms,two OH with negative charge on oxygen OH OH o resonance forms.one with HO negative charge on oxygen c group in asc adthe cetale ion 2( )page 27 of this manu ormer the f th omolecules onjug ngth of an acid is determined by the stability of its conjugate base. that is.t d the rinciple underlying the behavior?2)does the student inciple applies in this particular example like: To answer an "explain the hrase or. 30 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Inc
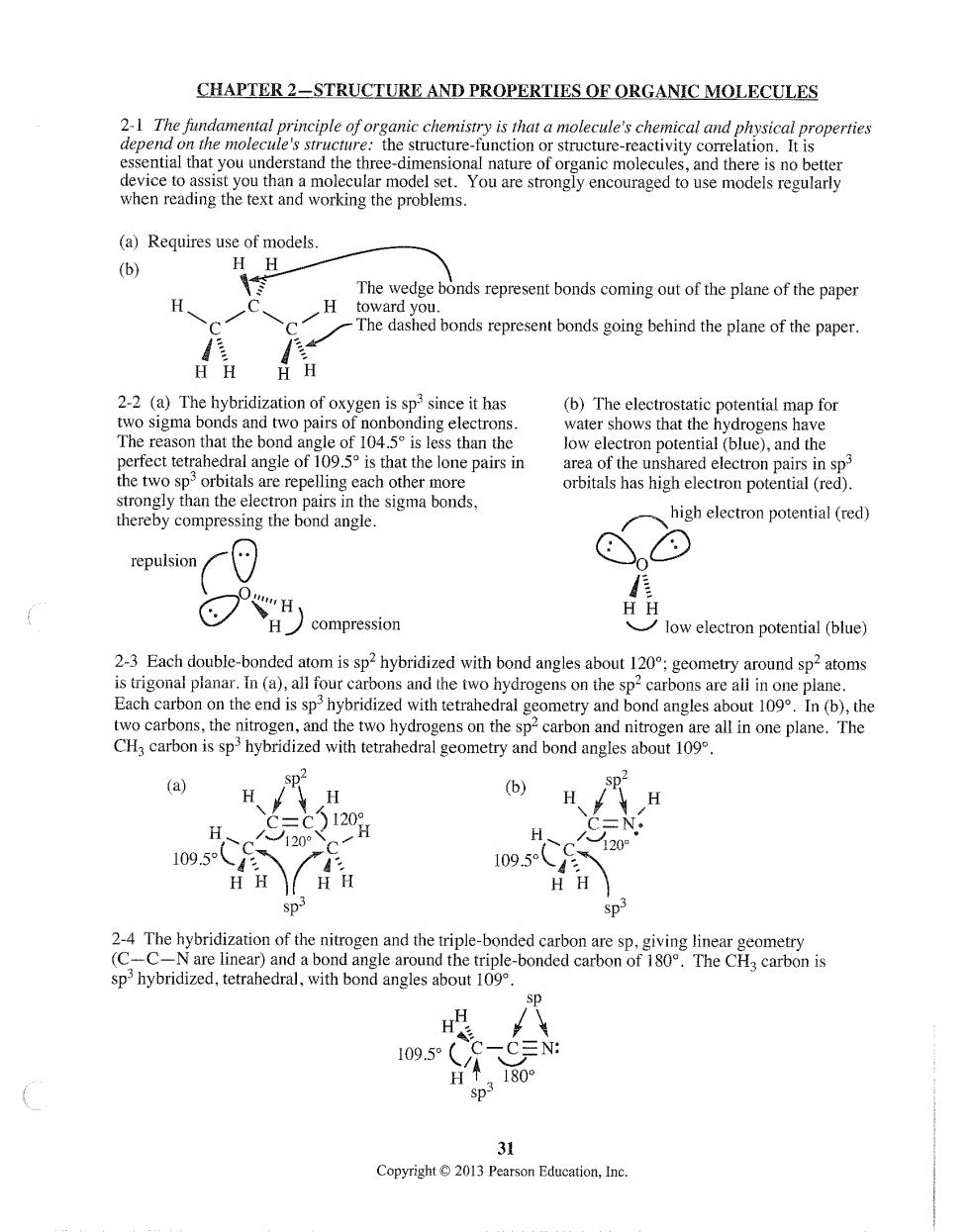
CHAPTER 2-STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 2-1 The fundamental principle of organic chemistry is that a molecule's chemical and p (a)Requires use of models. (b) The wedge bonds represent bonds coming out of the plane of the paper going behind the pae of thepaper. 品 oxygen is sp since it has (b)The electrostatic potential map for two pair perfect tetrahedral e),and th h. the two sporbitals are repelling each other more strongly than the electron pairs in the sigma bonds, thereby compressing the bond angle. high electron potential (red) repulsion H H compression low electron potential (blue) 11 e two hydrogens on the on the h tetra sp-ca two hydrogens on the sp an nitrogen (a) sp2 H (b) 1209 109.5 2-4 The hybridization of the nitrogen and the triple-bonded carbon are sp,giving linear geometry -C-N are linear)and a bond angle around the triple-bonded carbon of 180.The CH carbon is sp hybridized,tetrahedral,with bond angles about 109 31 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Ine