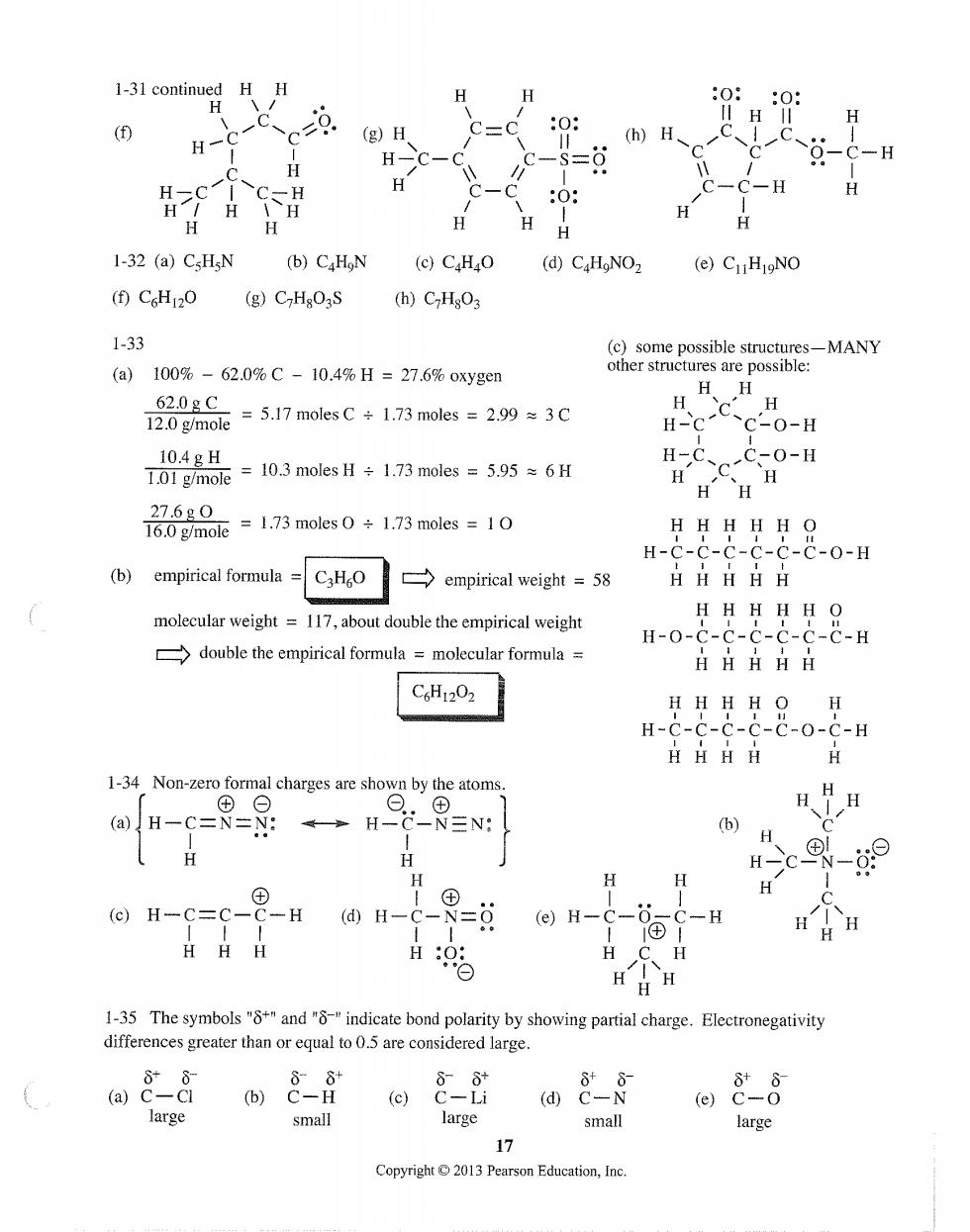
1-31 continued HH (g)H 1-32 (a)CsHN (b)CaHoN (e)C.HO (d)C.HNOz (e)CuHINO (0CH120 (g)CHgO3S (h)CzHsO3 1-33 (c)some possible structure es-MANY (a)100%-62.0%C-10.4%H=27.6%oxygen other structures are possible: 12.0mole 5.17 moles C 1.73 moles 2.99 =3C H-c-c C-0-H 10.4gH 1.01 g/mole ,=10.3 moles H÷1.73 moles=5.95≈6H 27.6g0 16.0 g/mole 1.73 moles O+1.73 moles 10 HHHHH O H-C-C-C-C-C-C-0-H (b)empirical formula=CH empirical weight=58 HHHHH molecular weight =117,about double the empirical weight HHHHH O H-0-C-C-C-C-C-C-H double the empirical formula =molecular formula HHHHH C6H1202 HHHH O H H-C-C-C-C-C-0-C-H HHHH H 1-34 Non-zero formal charges are shown by the atoms. (@)H-C=N-N: H9-9N H c9-9 H H (c)H-C=C- -H @H-C-8=过 (e)H- h9 1④ -H H H 1-35 The symbols"andindicate bond polarity by showing partial charge.Electronegativity differences greater than or equal to5 are considered large. 68 (b)C-H @88 large small large small large 17 Copyright013 Pearson Education,Inc
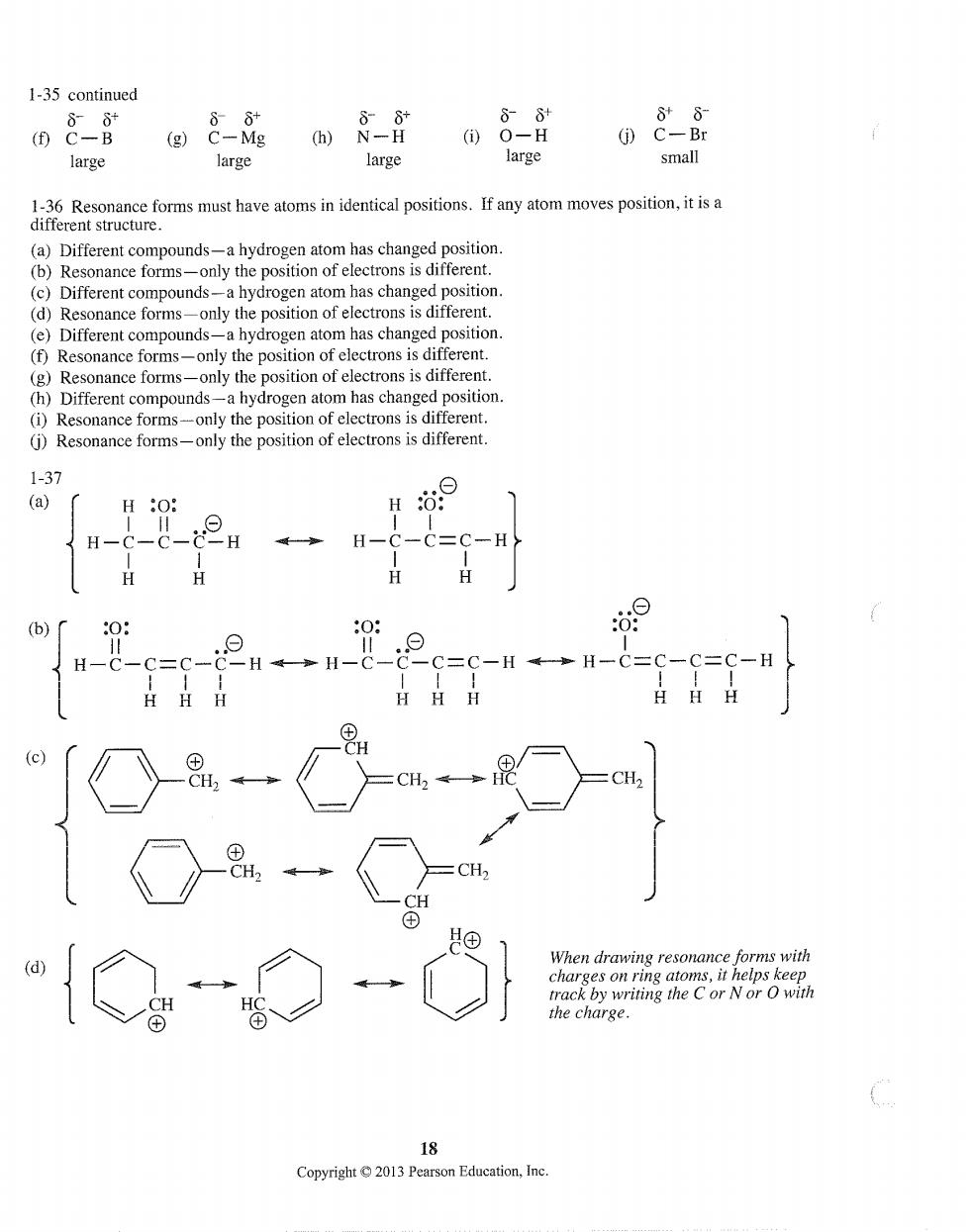
1-35 continued 88 88 88 (f)C-B (g)C-Mg (①O-H (j)C-Br large large large large small (has changed position. (b)Resonance forms-only the position of electrons is different (c)Different compounds-a hydrogen atom has changed position (d)Resonance forms-only the position of electrons is different. (e)Different compounds-a hydrogen atom has changed position. (f)Resonance forms-only the position of electrons is different. (g)Resonance forms-only the position of electrons is different. (h)Different compounds-a hydrogen atom has changed position. (i)Resonance forms-only the position of electrons is different. (j)Resonance forms-only the position of electrons is different. -2H .0. -c “{◇ forms with rrack by writing the C or Nor O with the charge. Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Inc

1-37 continue -H+ 1 H-C=C-C- -CH→H-C=C -C=C-CH HHHHH H一9 -c-c-C-C-CH, HHHHH e charge 1-38 One of the fundamental principles of acidity is that the strength of the acid depends on the stability of the conjugate base.The two primary factors governing the strength of organic acids are resonance and Any organic structure with anHin itry strong acid because the anion has three significant eonanecoaminhtosseshegohimtanl An organic structure with a simple-OH does not have an necd.W cach roup.nule (b) (d) (a) weakest acid Clcloser to COOH strongest acid 19 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Ine
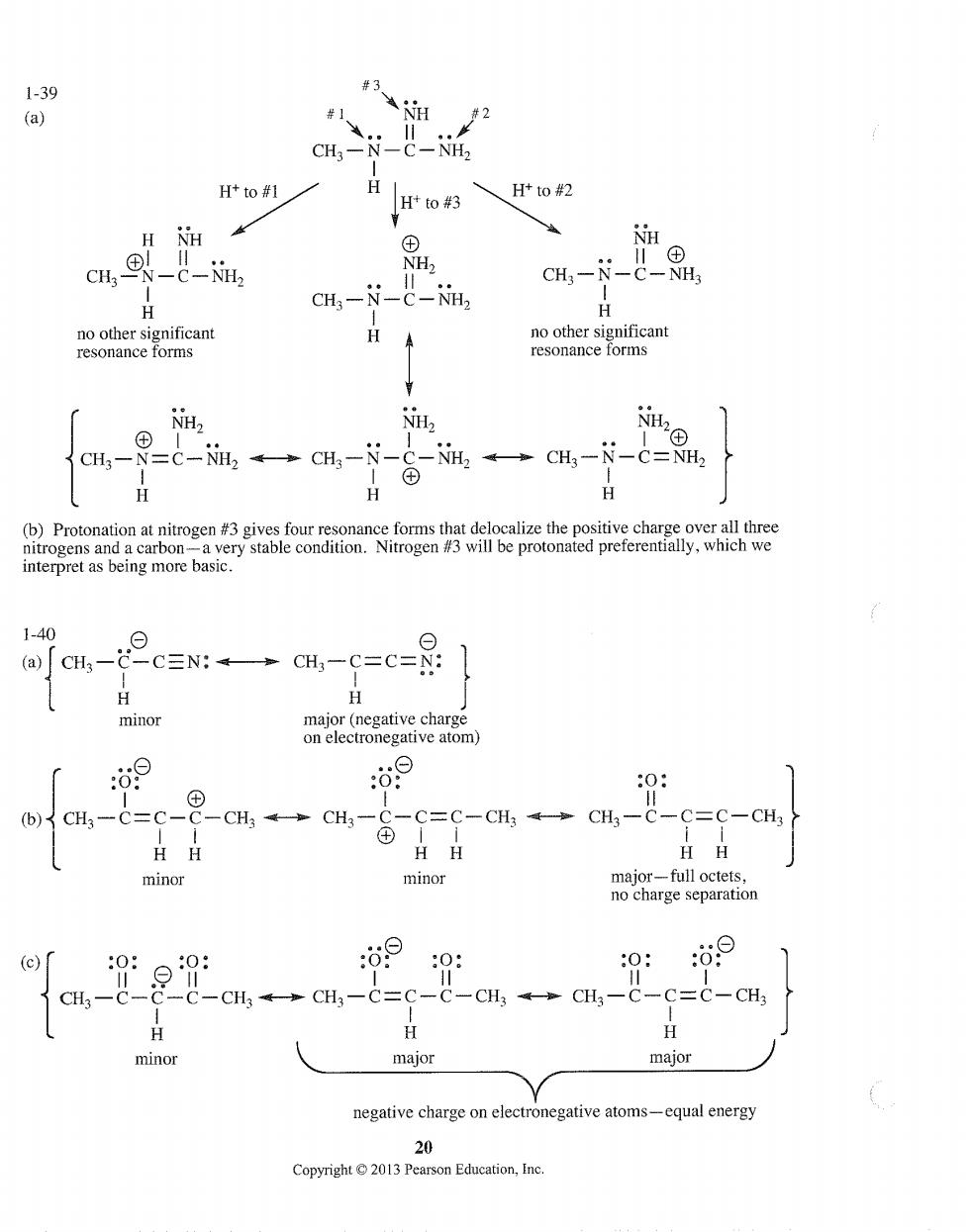
1-39 #3 (a) #1 #2 NH2 Htto#鞋 H H*to #3 、Htto#2 cH,®-&-, NH cH,-N-C-8, CH3-N-C-NH2 H本 NH. NH NH CH-N=C-2→CH,-N- G-NH→cH,-N-C=2 H interpret as being more basic. 1-40 (a)CHs-C-C=N:CH3-C=C=N: 1 minor :69 0: (b)CH3-C=C- CHqH8G=Ga4二ou-c- HH HH minor minor 699 0: C-CH3-→CH3-C=C-C-CH3。CH3-C-C=C-CH H H H minor major major negative charge on electronegative atoms-qul energy 20 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Inc
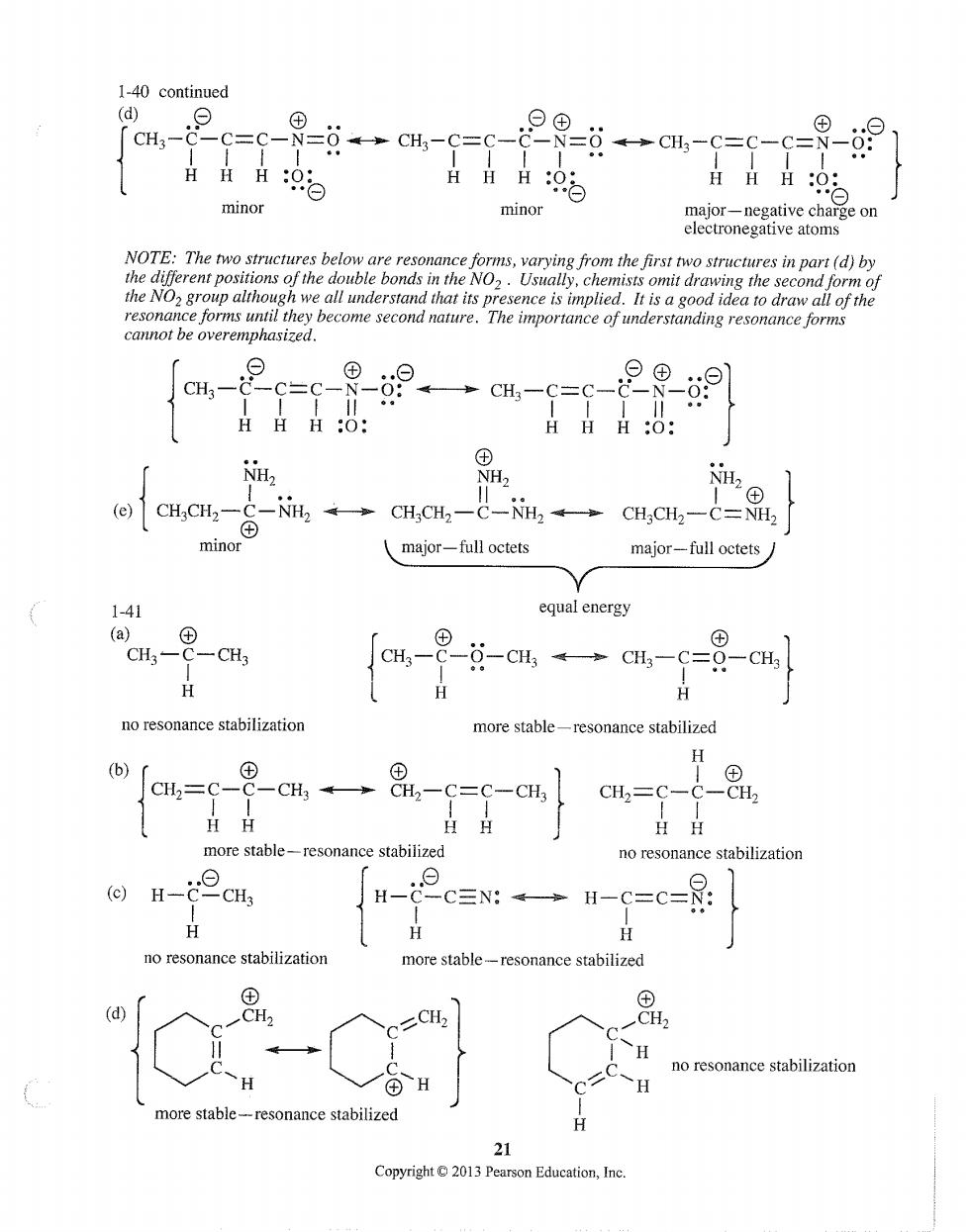
1-40 continued (d) CH3-C- C=C- C= 日HH9 minor minor major-negative chae on electronegative atoms NOTE:The two structures below are resonance forms,varying from the first two structures in part (d)by cannot be overemphasized. ®-9 HHH:O: HHH:: NH @)CH,CH,-C-2。→CH,CH2-C-NH2→CH,CH,-C=, minor major-full octets major-full octets 1-41 equal energy [aH-9-日-a4一a4-G=8-c H no resonance stabilizatior more stable-resonance stabilized H (b) cn- -cH→8,-c=c-cH】 9 2=C- C-CH R H more stable -resonance stabilized no resonance stabilization H-cHs H- c三N:→H-c=C= no resonance stabilizatio more stable-resonance stabilized a-o no resonance stabilization esonance stabilized 21 Copyright2013 Pearson Education,Ine