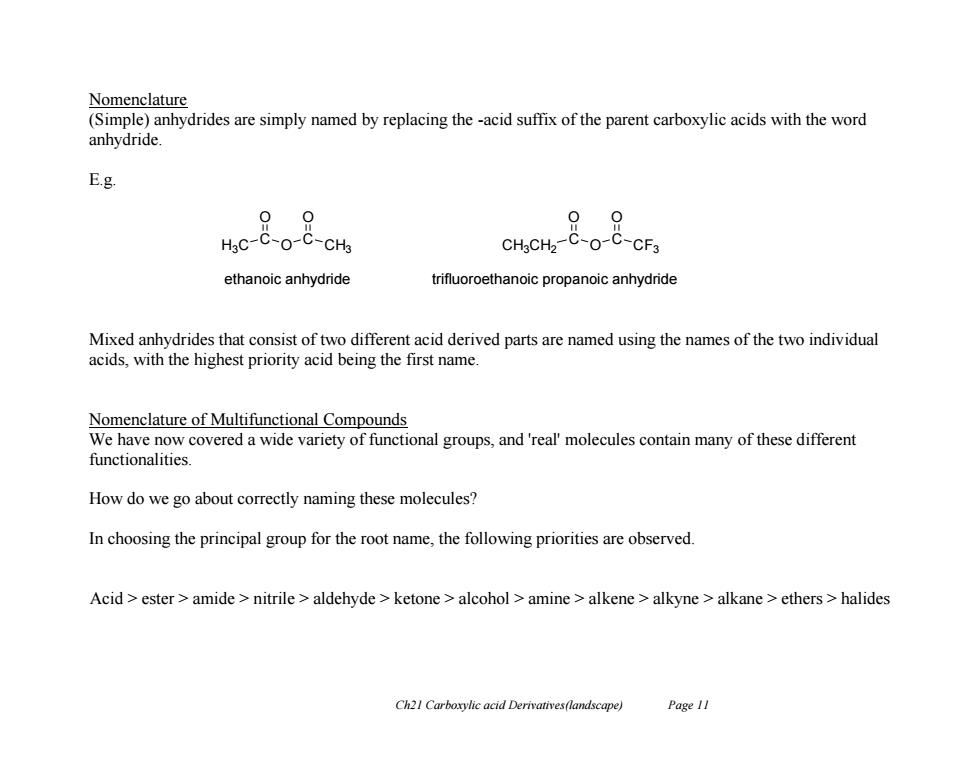
Nomenclature (Simple)anhydrides are simply named by replacing the -acid suffix of the parent carboxylic acids with the word anhydride. E.g. 09 09 HgC-C-O-C-CHs CHgCH2-C-O-C-CF3 ethanoic anhydride trifluoroethanoic propanoic anhydride Mixed anhydrides that consist of two different acid derived parts are named using the names of the two individual acids,with the highest priority acid being the first name. Nomenclature of Multifunctional Compounds We have now covered a wide variety of functional groups,and 'real'molecules contain many of these different functionalities. How do we go about correctly naming these molecules? In choosing the principal group for the root name,the following priorities are observed. Acid ester amide nitrile aldehyde ketone alcohol amine alkene alkyne alkane ethers>halides Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 11
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 11 Nomenclature (Simple) anhydrides are simply named by replacing the -acid suffix of the parent carboxylic acids with the word anhydride. E.g. Mixed anhydrides that consist of two different acid derived parts are named using the names of the two individual acids, with the highest priority acid being the first name. Nomenclature of Multifunctional Compounds We have now covered a wide variety of functional groups, and 'real' molecules contain many of these different functionalities. How do we go about correctly naming these molecules? In choosing the principal group for the root name, the following priorities are observed. Acid > ester > amide > nitrile > aldehyde > ketone > alcohol > amine > alkene > alkyne > alkane > ethers > halides H3C C O O C O CH3 ethanoic anhydride CH3CH2 C O O C O CF3 trifluoroethanoic propanoic anhydride
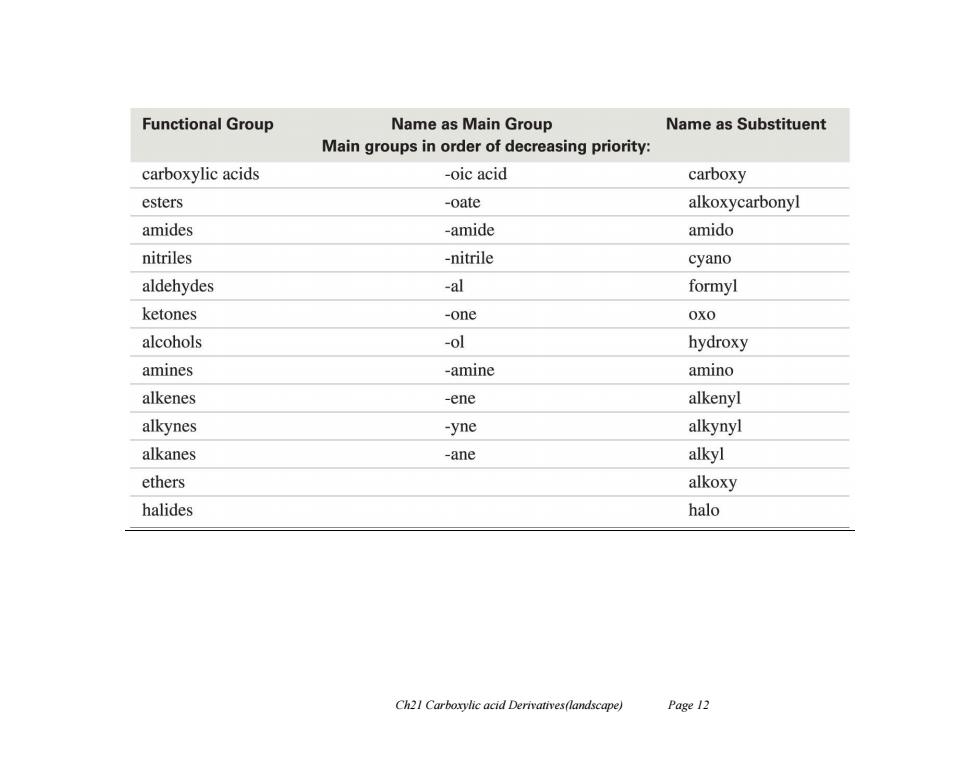
Functional Group Name as Main Group Name as Substituent Main groups in order of decreasing priority: carboxylic acids -oic acid carboxy esters -oate alkoxycarbonyl amides -amide amido nitriles -nitrile cyano aldehydes -al formyl ketones -one 0x0 alcohols -ol hydroxy amines -amine amino alkenes -ene alkenyl alkynes -yne alkynyl alkanes -ane alkyl ethers alkoxy halides halo Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 12
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 12
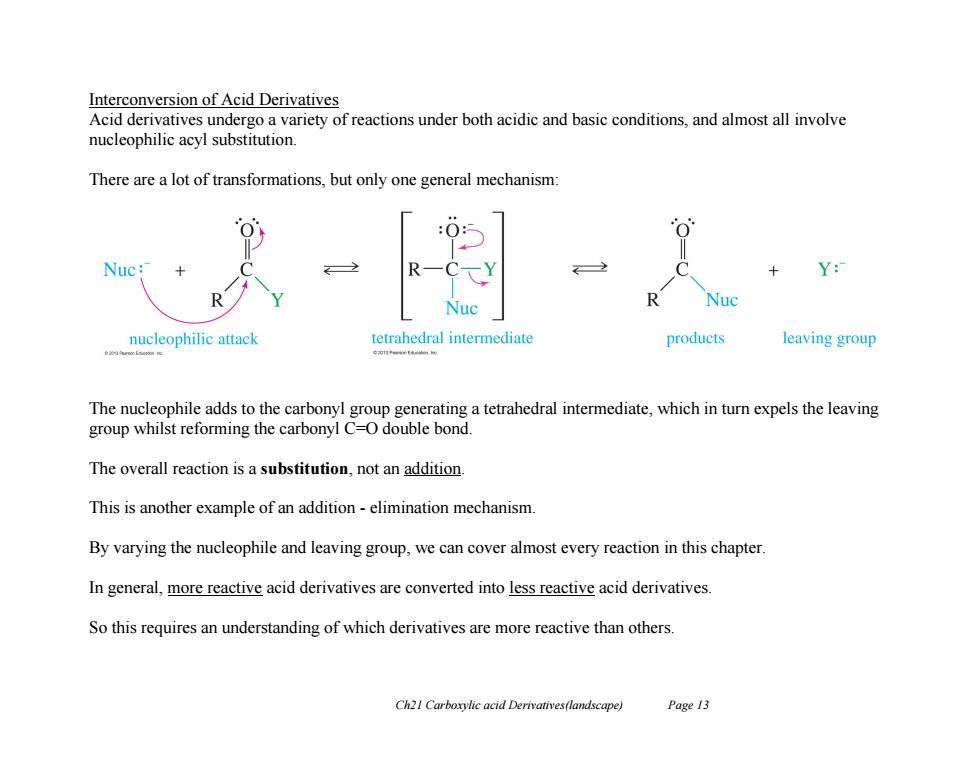
Interconversion of Acid Derivatives Acid derivatives undergo a variety of reactions under both acidic and basic conditions,and almost all involve nucleophilic acyl substitution. There are a lot of transformations,but only one general mechanism: + Y: R Nuc Nuc nucleophilic attack tetrahedral intermediate products leaving group The nucleophile adds to the carbonyl group generating a tetrahedral intermediate,which in turn expels the leaving group whilst reforming the carbonyl C=O double bond. The overall reaction is a substitution,not an addition. This is another example of an addition-elimination mechanism. By varying the nucleophile and leaving group,we can cover almost every reaction in this chapter. In general,more reactive acid derivatives are converted into less reactive acid derivatives So this requires an understanding of which derivatives are more reactive than others. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 13
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 13 Interconversion of Acid Derivatives Acid derivatives undergo a variety of reactions under both acidic and basic conditions, and almost all involve nucleophilic acyl substitution. There are a lot of transformations, but only one general mechanism: The nucleophile adds to the carbonyl group generating a tetrahedral intermediate, which in turn expels the leaving group whilst reforming the carbonyl C=O double bond. The overall reaction is a substitution, not an addition. This is another example of an addition - elimination mechanism. By varying the nucleophile and leaving group, we can cover almost every reaction in this chapter. In general, more reactive acid derivatives are converted into less reactive acid derivatives. So this requires an understanding of which derivatives are more reactive than others
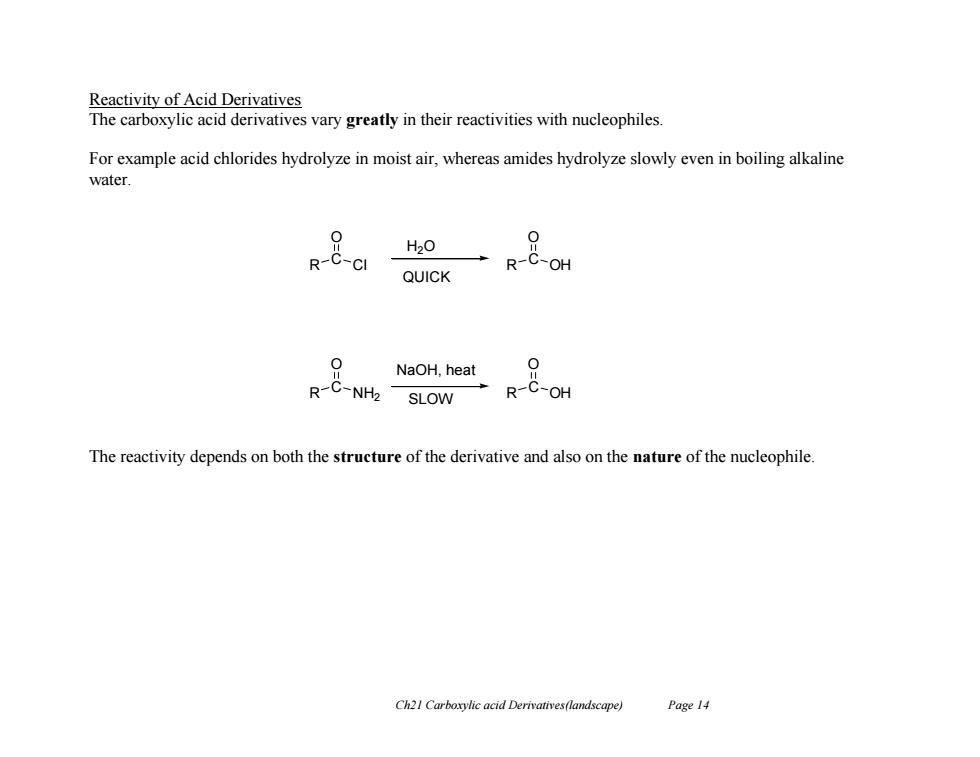
Reactivity of Acid Derivatives The carboxylic acid derivatives vary greatly in their reactivities with nucleophiles For example acid chlorides hydrolyze in moist air,whereas amides hydrolyze slowly even in boiling alkaline water. H20 0 R-C-CI R-C-OH QUICK R&oea NaOH,heat 0 R-C-OH The reactivity depends on both the structure of the derivative and also on the nature of the nucleophile. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 14
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 14 Reactivity of Acid Derivatives The carboxylic acid derivatives vary greatly in their reactivities with nucleophiles. For example acid chlorides hydrolyze in moist air, whereas amides hydrolyze slowly even in boiling alkaline water. The reactivity depends on both the structure of the derivative and also on the nature of the nucleophile. R C Cl O R C OH O R C NH2 O R C OH O H2O NaOH, heat SLOW QUICK
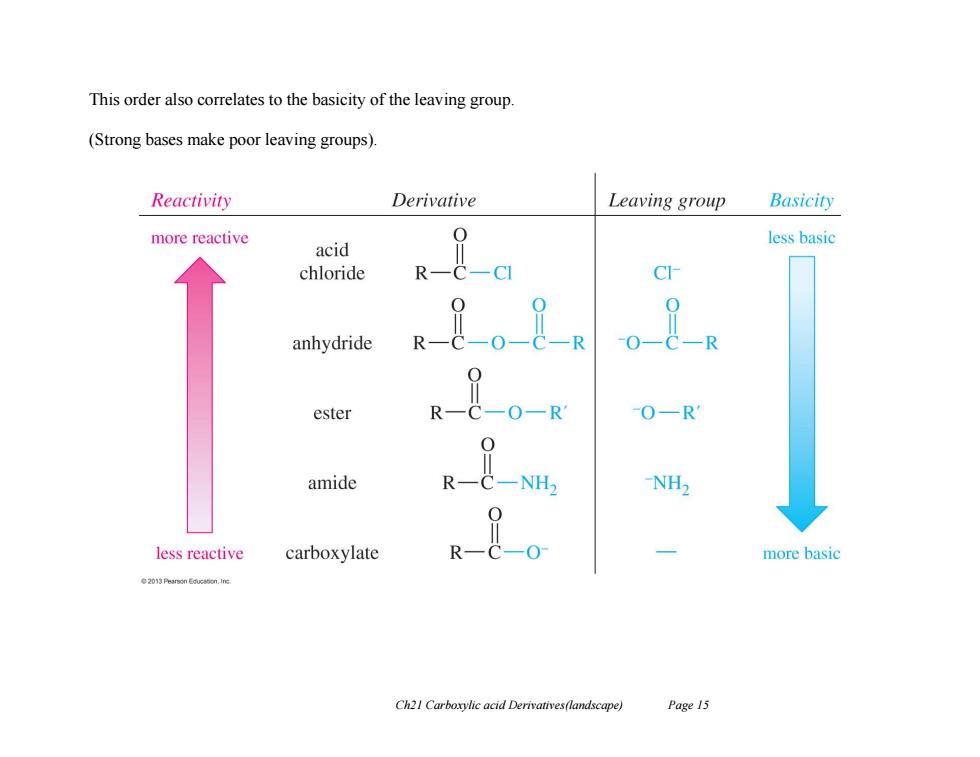
This order also correlates to the basicity of the leaving group. (Strong bases make poor leaving groups). Reactivity Derivative Leaving group Basicity more reactive less basic acid chloride R-C-CI C anhydride O-C-R ester R-C-O-R 0-R amide -NH2 less reactive carboxylate R-c-o more basic 201 Pearson Educaon.ine Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 15
Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape) Page 15 This order also correlates to the basicity of the leaving group. (Strong bases make poor leaving groups)