
During part of the water cycle,the sun heats up liquid water and changes it to a gas by the process of evaporation.Water that evaporates from Earth's oceans,lakes,rivers,and moist soil rises up into the atmosphere.蒸发 The process of evaporation from plants is called transpiration. (In other words,it's like plants sweating.) As water(in the form of gas)rises higher in the atmosphere,it starts to cool and become a liquid again.This process is called condensation.When a large amount of water vapor condenses,it results in the formation of clouds. When the water in the clouds gets too heavy,the water falls back to the earth.This is called precipitation. When rain falls on the land,some of the water is absorbed into the ground forming pockets of water called groundwater.Most groundwater eventually returns to the ocean.Other precipitation runs directly into streams or rivers.Water thata1 collects in rivers,streams,and oceans is called runoff
21 • During part of the water cycle, the sun heats up liquid water and changes it to a gas by the process of evaporation. Water that evaporates from Earth’s oceans, lakes, rivers, and moist soil rises up into the atmosphere.蒸发 • The process of evaporation from plants is called transpiration. (In other words, it’s like plants sweating.) 蒸腾 • As water (in the form of gas) rises higher in the atmosphere, it starts to cool and become a liquid again. This process is called condensation. When a large amount of water vapor condenses, it results in the formation of clouds. 凝结 • When the water in the clouds gets too heavy, the water falls back to the earth. This is called precipitation. 降雨 • When rain falls on the land, some of the water is absorbed into the ground forming pockets of water called groundwater. Most groundwater eventually returns to the ocean. Other precipitation runs directly into streams or rivers. Water that collects in rivers, streams, and oceans is called runoff. 径流

全球的水循环 水循环的三个基本环节:降水(P)、蒸发(E)、 径流(R),这三个基本环节相连构成了水循环。水 在生物圈的循环可以看作是从水域开始,再回到水 域而终止。 1)水域中的水受太阳辐射而蒸发(E)进入大气 •2)大气中的水汽随气压变化而流动,并聚集为云 3)云以雨、雪、雾等形式降落到地球表面 4)到达地表面的水,一部分直接形成地表径流进入 江河,汇入海洋。一部分渗入土壤内部:大部分通 过地下径流而进入海洋,接近土壤部分为植物吸收 22
22 全球的水循环 水循环的三个基本环节:降水(P)、蒸发(E)、 径流(R),这三个基本环节相连构成了水循环。水 在生物圈的循环可以看作是从水域开始,再回到水 域而终止。 •1)水域中的水受太阳辐射而蒸发(E)进入大气 •2)大气中的水汽随气压变化而流动,并聚集为云 •3)云以雨、雪、雾等形式降落到地球表面 •4)到达地表面的水,一部分直接形成地表径流进入 江河,汇入海洋。一部分渗入土壤内部:大部分通 过地下径流而进入海洋,接近土壤部分为植物吸收
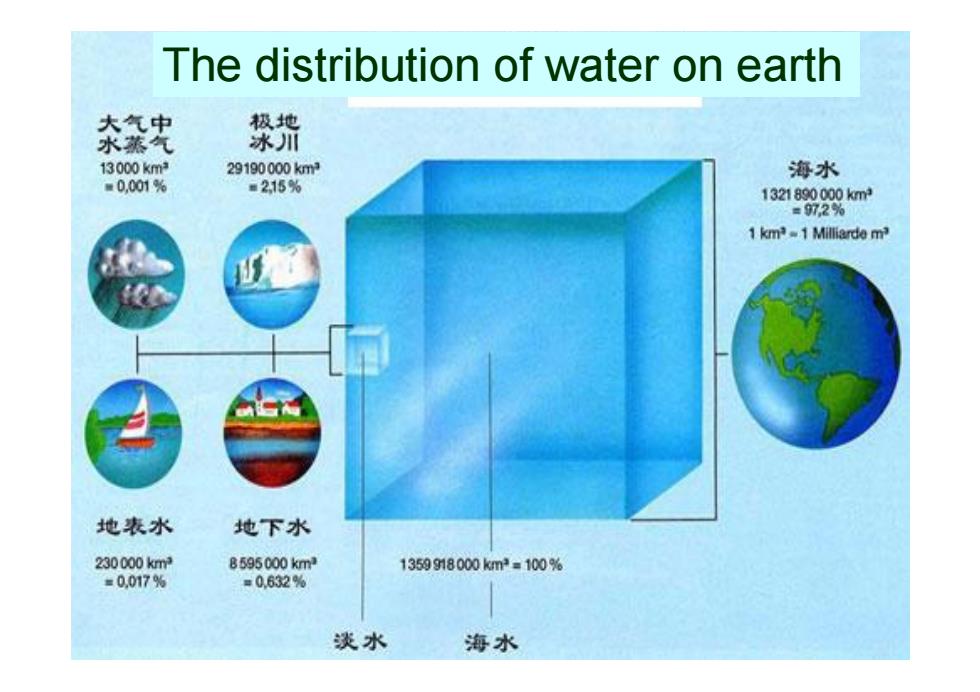
The distribution of water on earth 大气中 极地 水蒸气 冰川 13000km2 29190000km 海水 ■0,001% =215% 1321890000km =972%的 1 km-1 Milliarde m 地表水 地下水 230000kmd 8595000kmd 1359918000km2=100% =0.017% =0.632% 淡水 海水
23 The distribution of water on earth
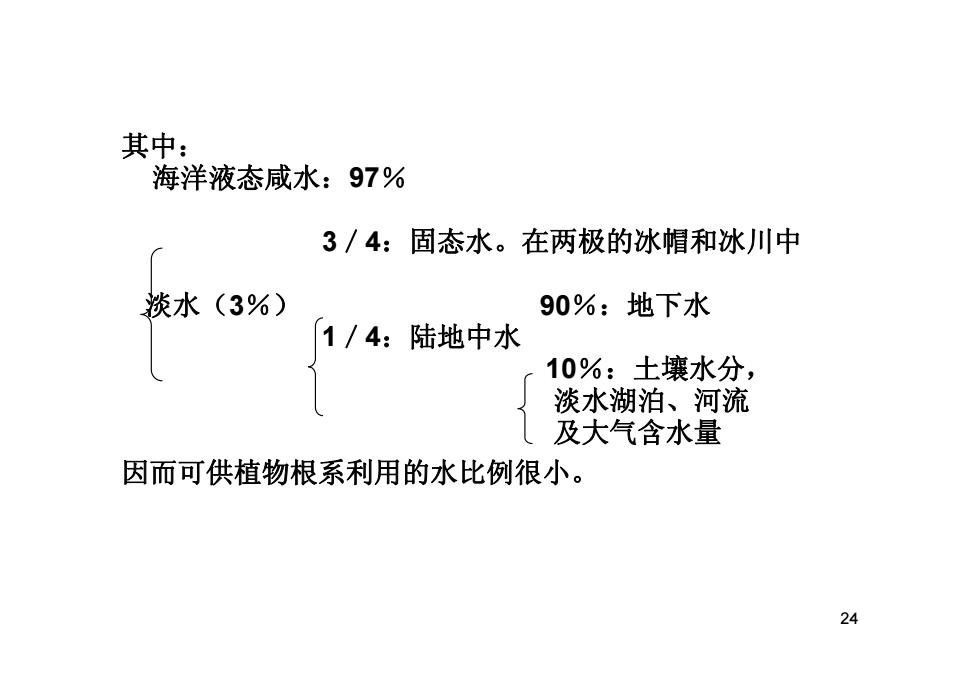
其中: 海洋液态咸水:97% 3/4:固态水。在两极的冰帽和冰川中 淡水(3%) 90%:地下水 1/4:陆地中水 10%:土壤水分, 淡水湖泊、河流 及大气含水量 因而可供植物根系利用的水比例很小。 24
24 其中: 海洋液态咸水:97% 3/4:固态水。在两极的冰帽和冰川中 淡水(3%) 90%:地下水 1/4:陆地中水 10%:土壤水分, 淡水湖泊、河流 及大气含水量 因而可供植物根系利用的水比例很小
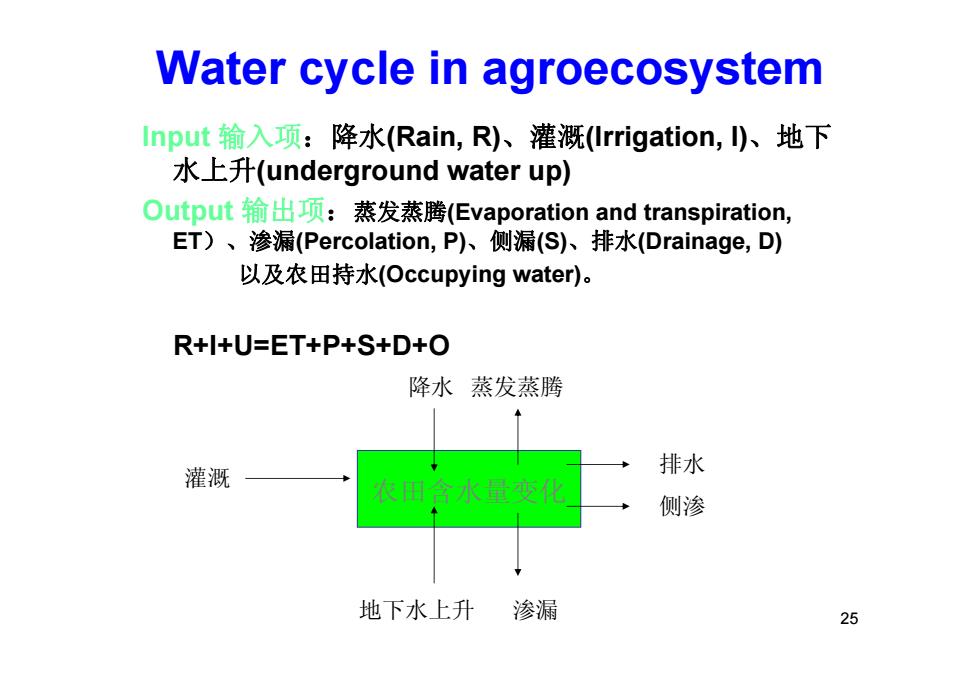
Water cycle in agroecosystem Input输入项:降水(Rain,R)、灌溉(Irrigation,)、地下 水上升(underground water up) Output输出项:蒸发蒸腾(Evaporation and transpiration, ET)、渗漏(Percolation,P)、侧漏(S)、排水(Drainage,D) 以及农田持水(Occupying water)。 R+l+U=ET+P+S+D+O 降水蒸发蒸腾 灌溉 排水 农田含水量变化 侧渗 地下水上升 渗漏 25
25 Water cycle in agroecosystem Input 输入项:降水(Rain, R)、灌溉(Irrigation, I)、地下 水上升(underground water up) Output 输出项:蒸发蒸腾(Evaporation and transpiration, ET)、渗漏(Percolation, P)、侧漏(S)、排水(Drainage, D) 以及农田持水(Occupying water) 。 R+I+U=ET+P+S+D+O 农田含水量变化 灌溉 排水侧渗 地下水上升 渗漏 降水 蒸发蒸腾