
Chapter 13 Nutrient Cycling and Pollution 1
1 Chapter 13 Nutrient Cycling and Pollution

What we are going to learn in this chapter? ·Material cycling·Pollution -Vater水 -Eutrophication(富营养化) -Carbon碳 -Heavy metal toxicity -Nitrogen氮 -Alkaline wastes(碱性废弃物) -Phosphorous磷 -Acid rain -Sulfur硫 -Pesticides -Potassium钾 CFCs and the ozone layer radioactivity 2
2 What we are going to learn in this chapter? • Material cycling – Water 水 – Carbon 碳 – Nitrogen 氮 – Phosphorous 磷 – Sulfur 硫 – Potassium 钾 • Pollution – Eutrophication(富营养化) – Heavy metal toxicity – Alkaline wastes(碱性废弃物) – Acid rain – Pesticides – CFCs and the ozone layer – radioactivity
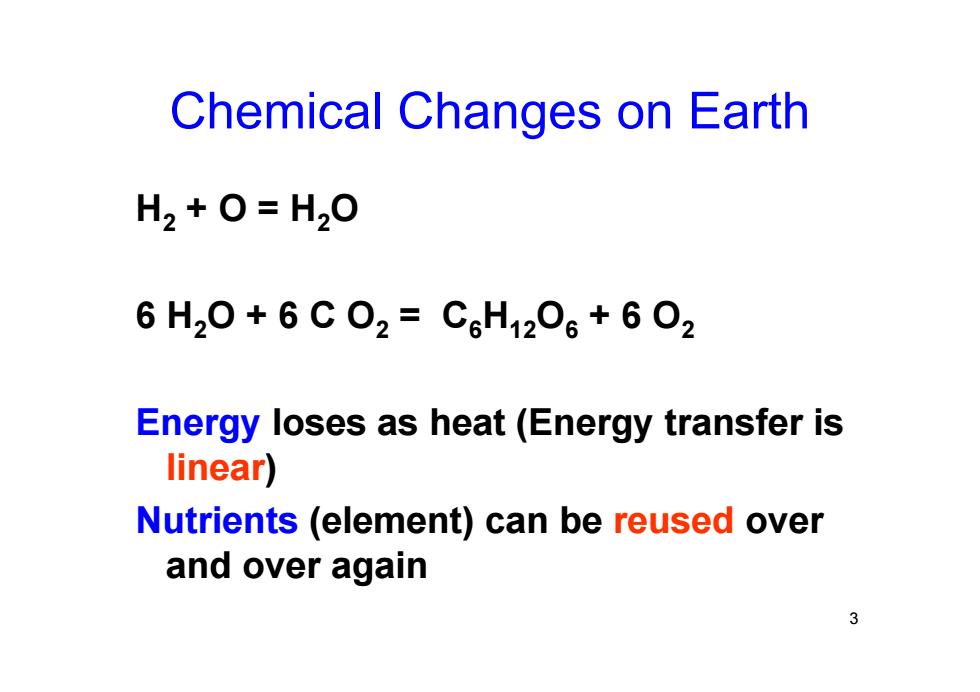
Chemical Changes on Earth H2+0=H20 6H20+6C02=C6H1206+602 Energy loses as heat(Energy transfer is linear) Nutrients (element)can be reused over and over again
3 Chemical Changes on Earth H 2 + O = H 2 O 6 H 2O + 6 C O 2 = C 6 H12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Energy loses as heat (Energy transfer is linear ) Nutrients (element) can be reused over and over again

Material Cycling and G0 0 energy transfer 。8380o Abiotic chemicals (carbon dioxide, Heat Heat Solar oxygen,nitrogen, energy minerals) Heat Decomposers Producers (bacteria,fungus) (plants) Consumers (herbivores Heat carnivores) Heat 2002 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
4 Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Abiotic chemicals (carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, minerals) Producers (plants) Decomposers (bacteria, fungus) Consumers (herbivores, carnivores) Solar energy Material Cycling and energy transfer
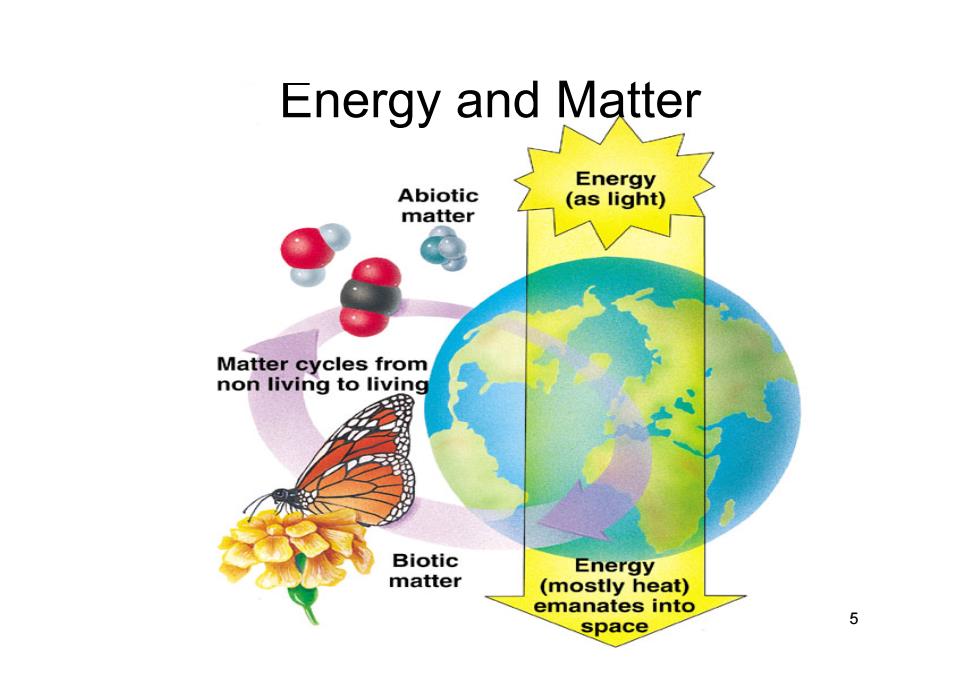
Energy and Matter Energy Abiotic (as light) matter Matter cycles from non living to living Biotic Energy matter (mostly heat) emanates into space
5 Energy and Matter