
1907 Solid solutions UNIVE A solid solution is a solid made up of two or more elements,dispersed in a mono-phase structure. A solid solution is defined when,adding atoms of the solute in the host material,the crystal structure is maintained and no new structure is formed. Two types of solid solution: -substitutional -interstitial
Solid solutions A solid solution is a solid made up of two or more elements, dispersed in a mono-phase structure. A solid solution is defined when, adding atoms of the solute in the host material, the crystal structure is maintained and no new structure is formed. Two types of solid solution: -substitutional -interstitial
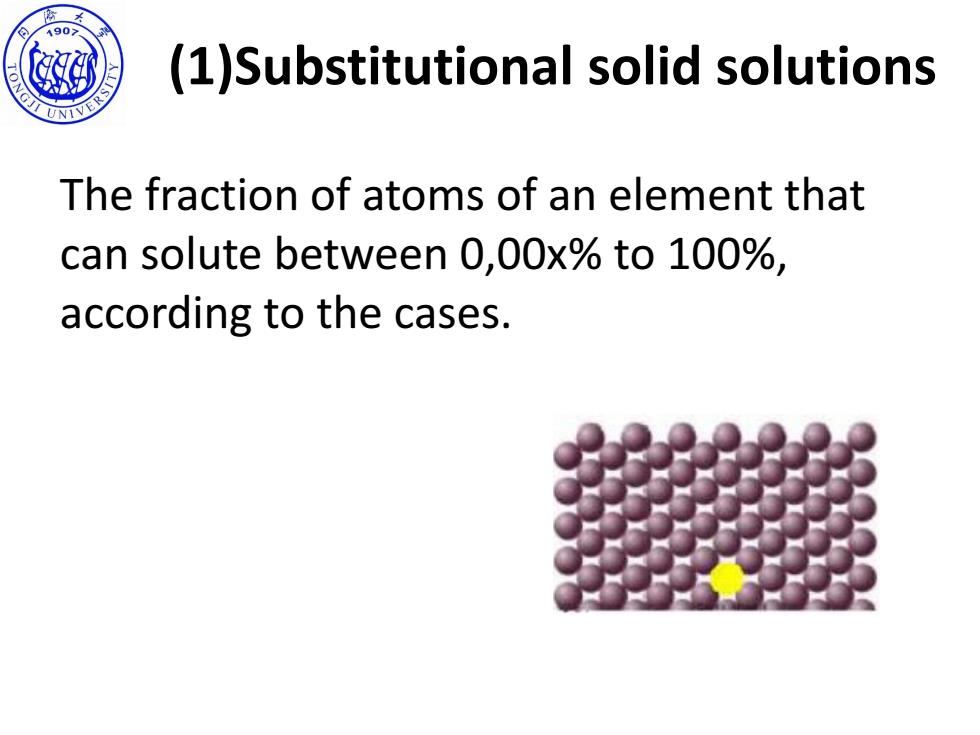
190 (1)Substitutional solid solutions The fraction of atoms of an element that can solute between 0,00x%to 100%, according to the cases
(1)Substitutional solid solutions The fraction of atoms of an element that can solute between 0,00x% to 100%, according to the cases

190> Conditions to improve solubility: 1.Atomic size factor Appreciable quantities of a solute may be accommodated in this type of solid solution only when the difference in atomic radii between the two atom types is less than about 15% 2.Crystal structure For appreciable solid solubility the crystal structures for metals of both atom types must be the same
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS Conditions to improve solubility: 1. Atomic size factor Appreciable quantities of a solute may be accommodated in this type of solid solution only when the difference in atomic radii between the two atom types is less than about 15% 2. Crystal structure For appreciable solid solubility the crystal structures for metals of both atom types must be the same

190> 3.Electronegativity The more electropositive one element and the more electronegative the other,the greater is the likehood that they will form an intermetallic compound instead of a substitutional solid solution. 4.Valences Other factors being equal,a metal will have more of a tendency to dissolve another metal of higher valency than one of a lower valency
SINO-ITALIAN CAMPUS 3. Electronegativity The more electropositive one element and the more electronegative the other, the greater is the likehood that they will form an intermetallic compound instead of a substitutional solid solution. 4. Valences Other factors being equal, a metal will have more of a tendency to dissolve another metal of higher valency than one of a lower valency

490>2 TONGJI UNIVERSY Substitutional solid solutions
Substitutional solid solutions