Purpose of Methods The reader can judge whether the results and conclusions are valid The experiment can be repeated to evaluate whether the results are reproducible
Purpose of Methods

Methodology and method ·How did you collect or generate the data? How did you analyze the data?
Methodology and method • How did you collect or generate the data? · How did you analyze the data?

Two types of research methods Quantitative method Qualitative method If the question requires an When the question requires a experimental and scientific non-numerical explanation method
Two types of research methods Quantitative method If the question requires an experimental and scientific method Qualitative method When the question requires a non-numerical explanation

Basic procedure of a quantitative design 01 Make observations about something unknown or unexplained. 02 Investigate current theory about your problem or issue, 03 Hypothesize for observations. 04 Make a prediction of outcomes based on the hypotheses. 05 Formulate a plan to test your prediction. 06 Collect and process your data. 07 Verify and present your findings. 08 Make your final conclusions
Basic procedure of a quantitative design 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 Make observations about something unknown or unexplained. Make your final conclusions. Verify and present your findings. Investigate current theory about your problem or issue. Hypothesize for observations. Make a prediction of outcomes based on the hypotheses. Formulate a plan to test your prediction. Collect and process your data
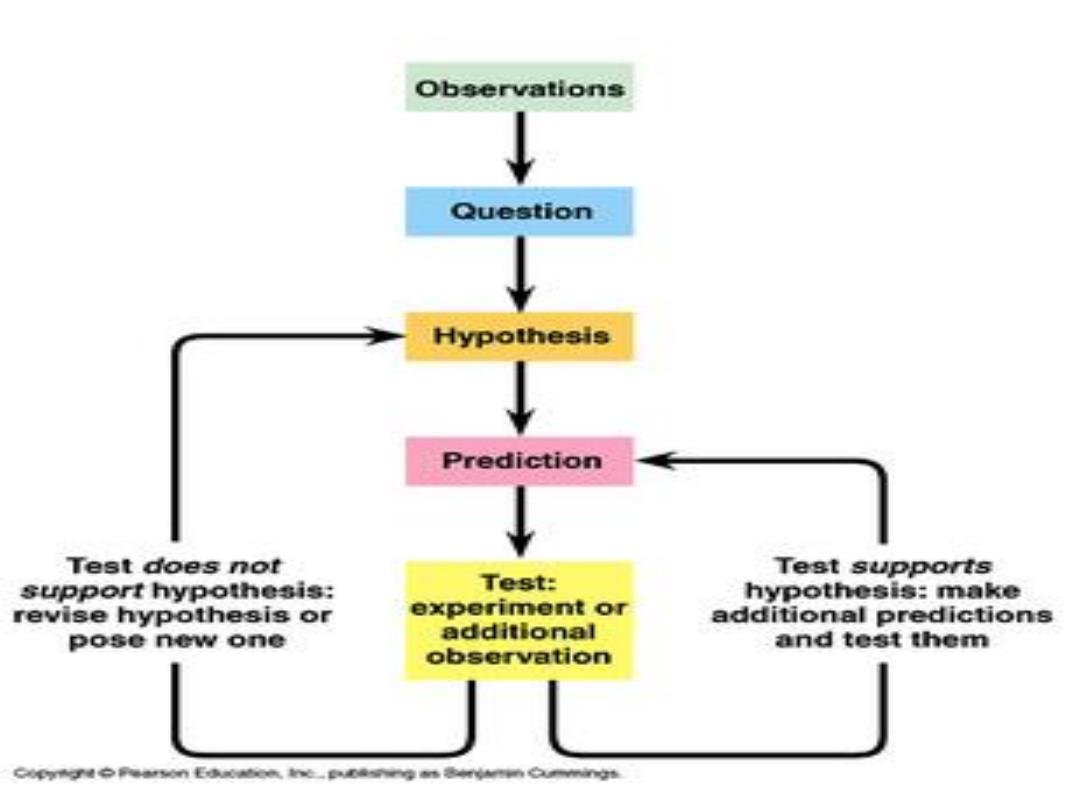
Observations ●uestion Hypothesis Prediction Test does not Test supports support hypothesis: Test: hypothesis:make revise hypothesis or experiment or additional predictions pose new one additional and test them observation