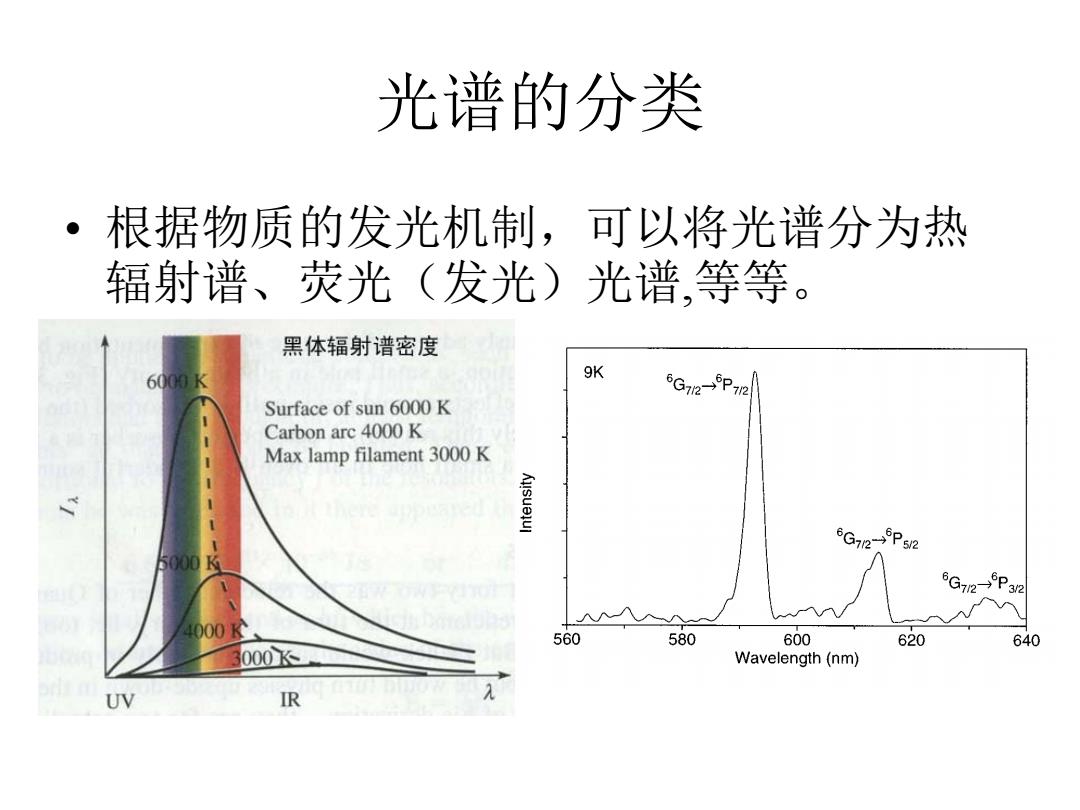
光谱的分类 ·根据物质的发光机制,可以将光谱分为热 辐射谱、荧光(发光)光谱,等等。 黑体辐射谱密度 6000K 9K 6G72-P72 Surface of sun 6000 K Carbon arc 4000 K Max lamp filament 3000 K G72-P52 5000 6G72-P32 4000K 560 580 600 620 640 000K图 Wavelength(nm) UV R
光谱的分类 • 根据物质的发光机制,可以将光谱分为热 辐射谱、荧光(发光)光谱,等等

H Na Ne Hg H2 太阳光谱
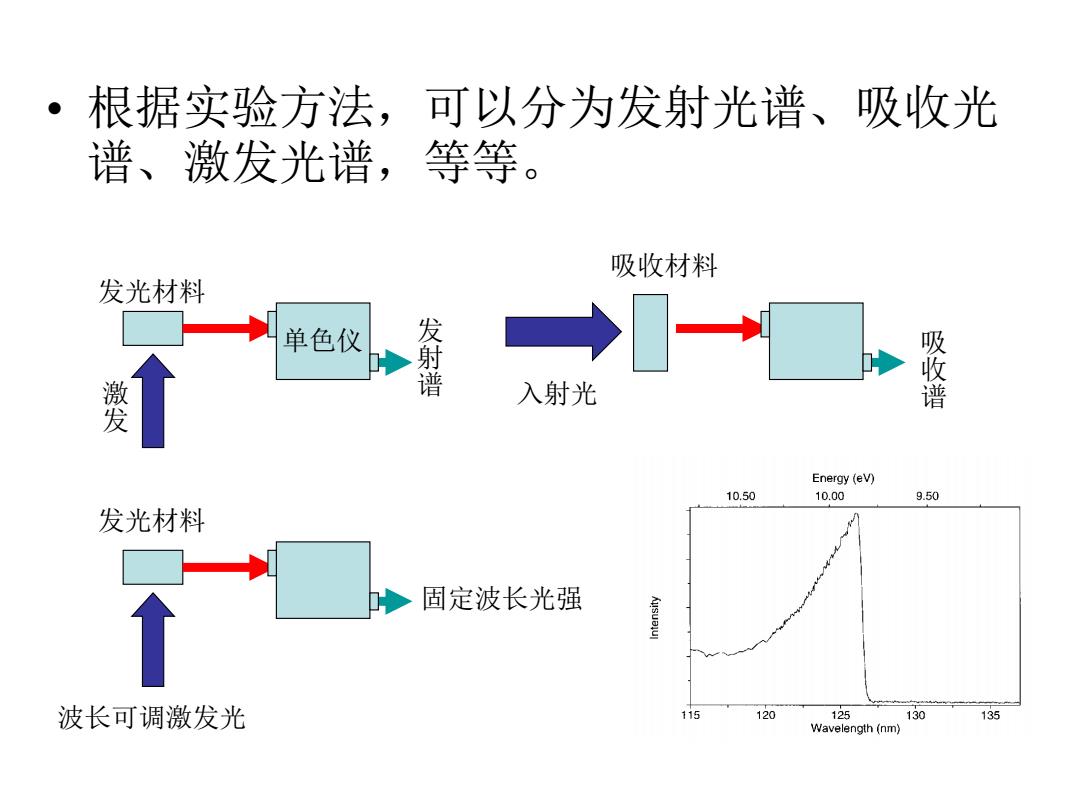
·根据实验方法, 可以分为发射光谱、吸收光 谱、激发光谱,等等。 吸收材料 发光材料 单色仪 发射谱 →- 變 入射光 吸收谱 Energy (eV) 10.50 10.00 9.50 发光材料 ◆固定波长光强 波长可调激发光 115 120 125 130 135 Wavelength(nm)
• 根据实验方法,可以分为发射光谱、吸收光 谱、激发光谱,等等。 单色仪 激发 发光材料 发射谱 入射光 吸收谱 吸收材料 波长可调激发光 固定波长光强 发光材料
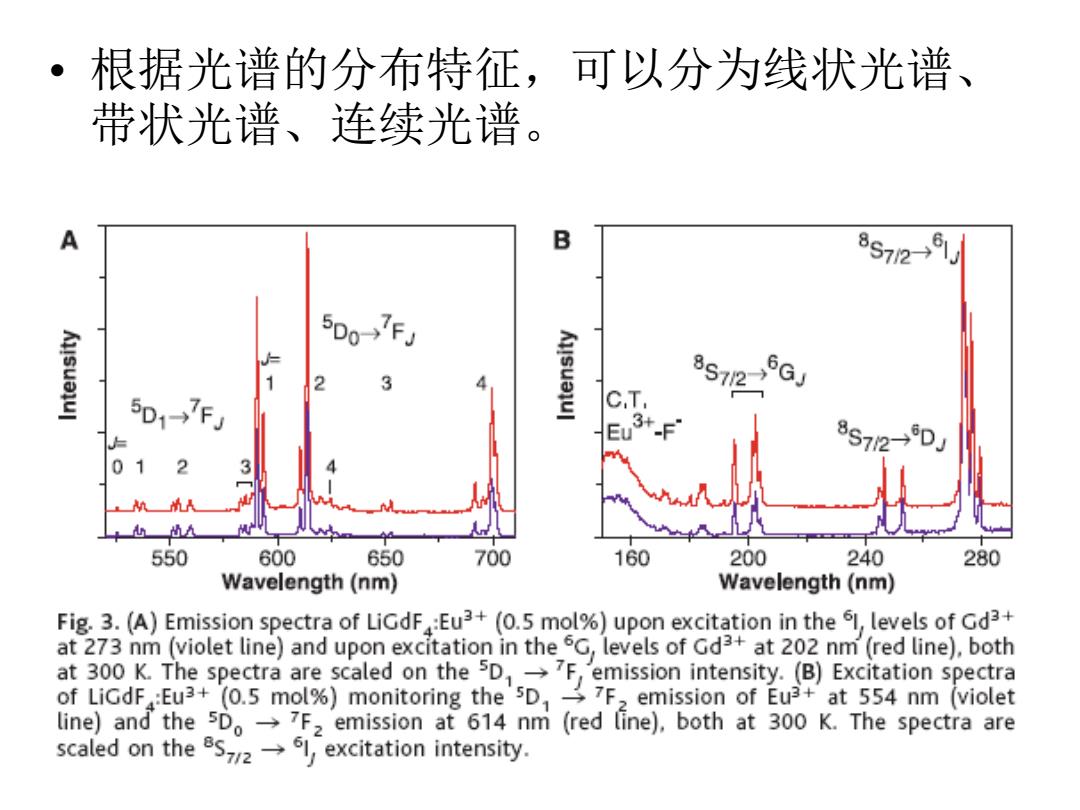
根据光谱的分布特征,可以分为线状光谱、 带状光谱、连续光谱。 B 8s712-9 5D0-FJ 2 3 8S12 6GJ 5D1→7F C.T, Eu3+-F 8S72→DJ 01 3 出的 550 600 650 700 160 200 240 280 Wavelength(nm) Wavelength(nm) Fig.3.(A)Emission spectra of LiGdF:Eu3+(0.5 mol%)upon excitation in the 61,levels of Gd3+ at 273 nm (violet line)and upon excitation in the 5G,levels of Gd3+at 202 nm(red line),both at 300 K.The spectra are scaled on the 5DFemission intensity.(B)Excitation spectra of LiGdF:Eu3+(0.5 mol%)monitoring the'5D,7F>emission of Eu3+at 554 nm (violet line)and the 5Do-7F2 emission at 614 nm (red [ine),both at 300 K.The spectra are scaled on theexcitation intensity
• 根据光谱的分布特征,可以分为线状光谱、 带状光谱、连续光谱
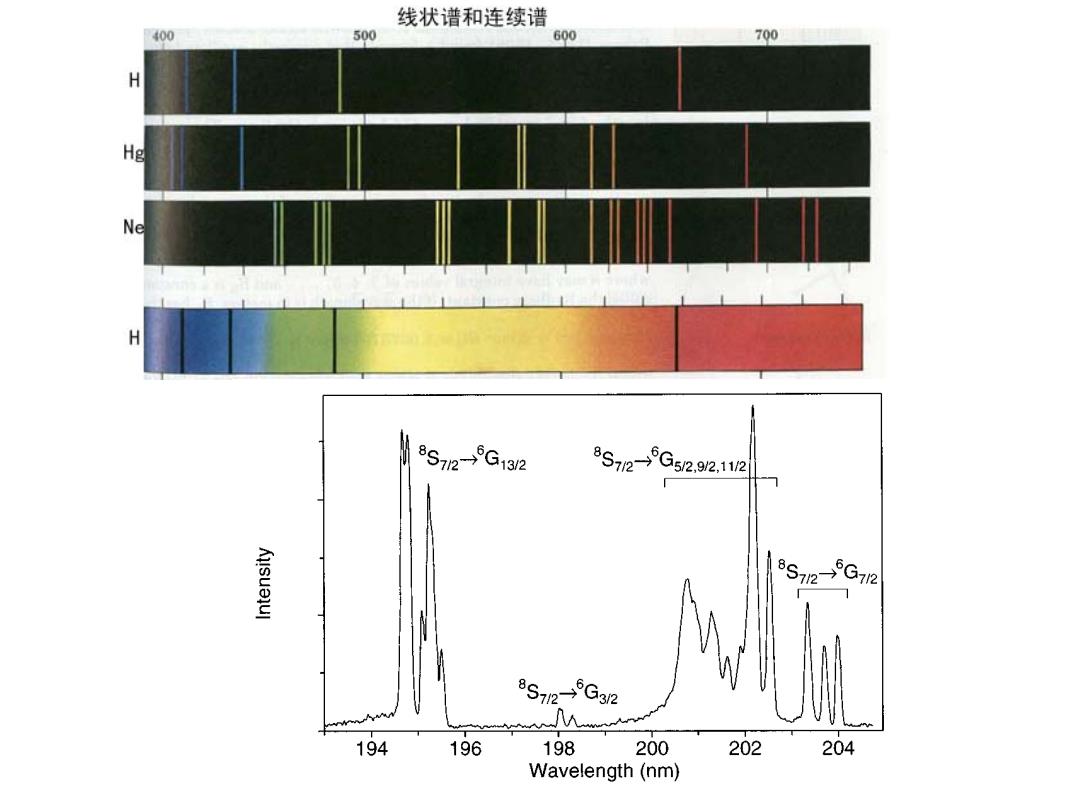
线状谱和连续谱 400 500 600 700 H He Ne H 8s72-G1328s72-5C2212 5G72 8S72-G32 194 196 198 200 202 204 Wavelength(nm)