
睡眠的机制 0 控制睡眠和觉醒的最关键的神经元:脑干的NE和5-HT能弥 散性神经递质系统;部分Ach能神经元可以增加REM事 件; ·弥散性调制系统控制丘脑的节律,进而控制大脑皮层的各 种EEG节律:丘脑的慢节律可阻断感觉信息流入大脑皮 层; 睡眠时弥散性调制系统的下行投射系统抑制运动神经元的 活动。 16
16 睡眠的机制 • 控制睡眠和觉醒的最关键的神经元:脑干的NE和5‐HT能弥 散性神经递质系统;部分Ach能神经元可以增加REM事 件; • 弥散性调制系统控制丘脑的节律,进而控制大脑皮层的各 种EEG节律;丘脑的慢节律可阻断感觉信息流入大脑皮 层; • 睡眠时弥散性调制系统的下行投射系统抑制运动神经元的 活动
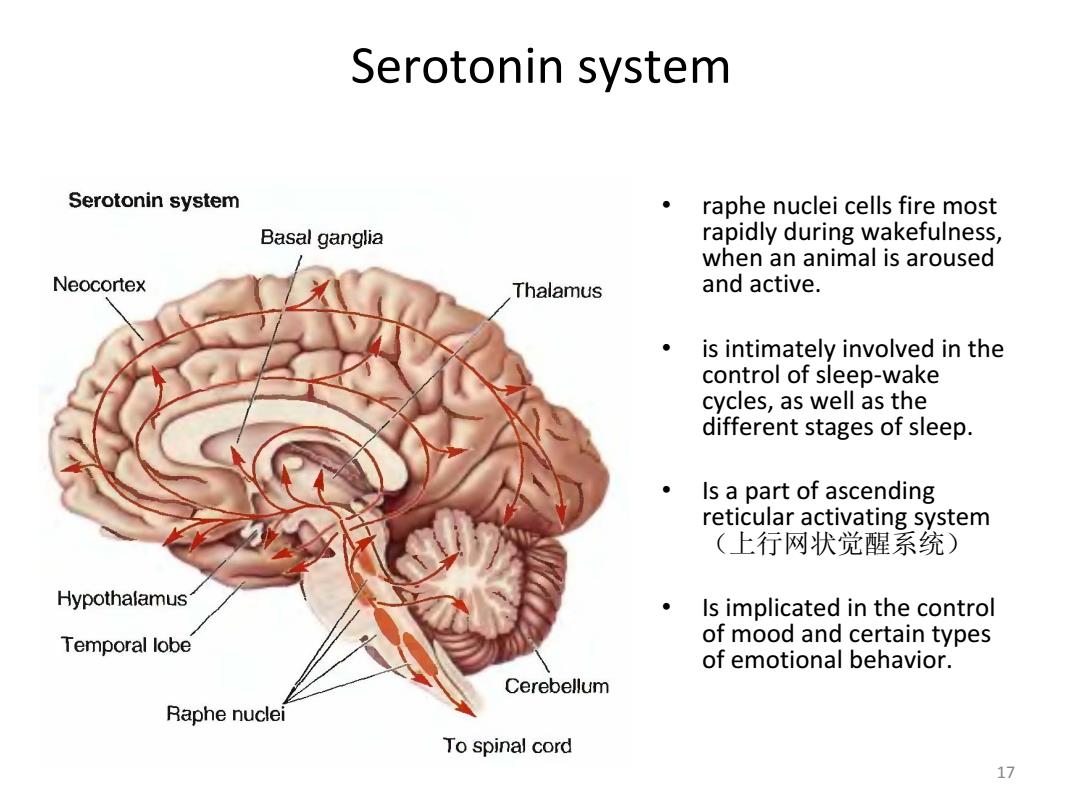
Serotonin system Serotonin system raphe nuclei cells fire most Basal ganglia rapidly during wakefulness, when an animal is aroused Neocortex Thalamus and active. is intimately involved in the control of sleep-wake cycles,as well as the different stages of sleep. Is a part of ascending reticular activating system (上行网状觉醒系统) Hypothalamus Is implicated in the control Temporal lobe of mood and certain types of emotional behavior. Cerebellum Raphe nuclei To spinal cord 17
17 Serotonin system • raphe nuclei cells fire most rapidly during wakefulness, when an animal is aroused and active. • is intimately involved in the control of sleep‐wake cycles, as well as the different stages of sleep. • Is a part of ascending reticular activating system (上行网状觉醒系统) • Is implicated in the control of mood and certain types of emotional behavior