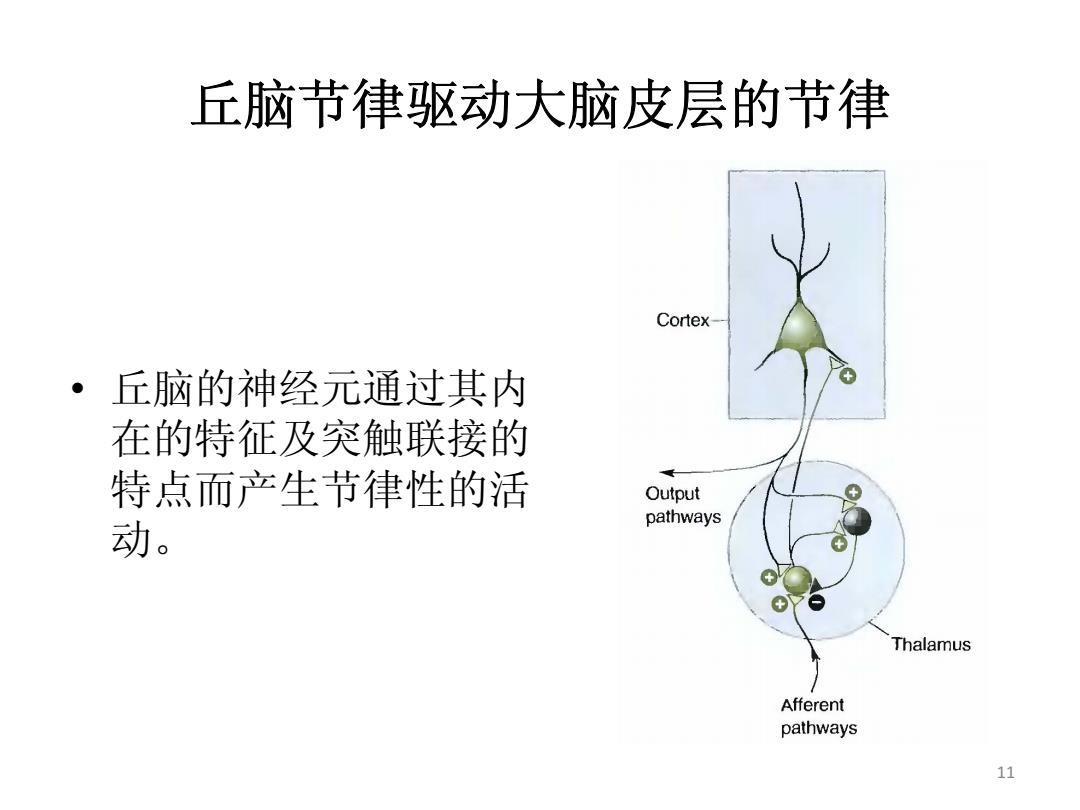
丘脑节律驱动大脑皮层的节律 Cortex 丘脑的神经元通过其内 在的特征及突触联接的 特点而产生节律性的活 Output pathways 动。 Thalamus Afferent pathways 11
11 丘脑节律驱动大脑皮层的节律 • 丘脑的神经元通过其内 在的特征及突触联接的 特点而产生节律性的活 动

脑节律的功能 ·觉醒状态下皮层的快节律: 一协同不同区域间神经元的活动: -感觉和运动皮层在觉醒状态下其EEG可在30-80Hz内振荡(有时叫 y节律); 一不同区域的这种快速振荡的同步化组合成单个的感知系统,比如 篮球。 ·大多数无直接的意义? 病理状态:癫痫(epilepsy) 泛化发作(generalized seizure) 部分发作(partial seizure) 12
12 脑节律的功能 • 觉醒状态下皮层的快节律: – 协同不同区域间神经元的活动; – 感觉和运动皮层在觉醒状态下其EEG可在30‐80 Hz内振荡(有时叫 γ节律); – 不同区域的这种快速振荡的同步化组合成单个的感知系统,比如 篮球。 • 大多数无直接的意义? 病理状态:癫痫(epilepsy) 泛化发作(generalized seizure) 部分发作(partial seizure)
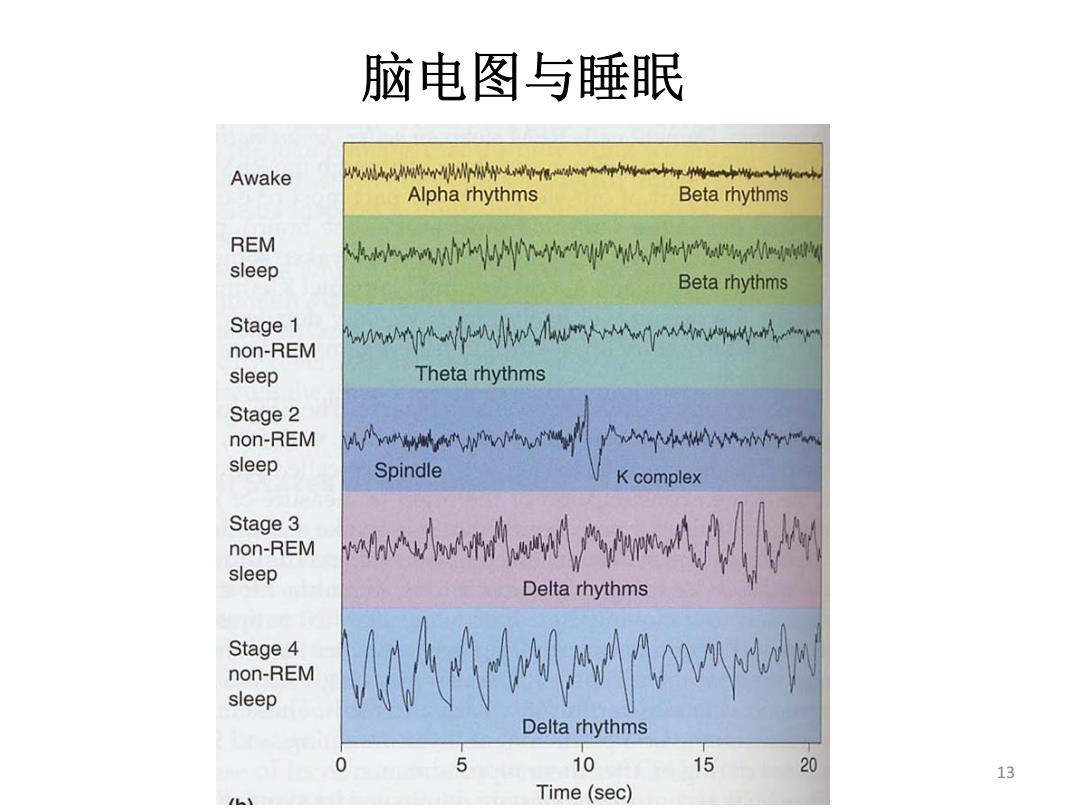
脑电图与睡眠 Awake 州j-o中pwe+aar+ Alpha rhythms Beta rhythms REM sleep kvnhrwWW%are Beta rhythms Stage 1 non-REM wnwmwrpw sleep Theta rhythms Stage 2 non-REM w-wwwwnm-w sleep Spindle K complex Stage 3 non-REM sleep naewm Delta rhythms Stage 4 non-REM sleep Aro Delta rhythms 0 5 10 15 20 13 Time(sec)
13 脑电图与睡眠

睡眠的机制 0 控制睡眠和觉醒的最关键的神经元:脑干的NE和5-HT能弥 散性神经递质系统;部分Ach能神经元可以增加REM事 件; ·弥散性调制系统控制丘脑的节律,进而控制大脑皮层的各 种EEG节律:丘脑的慢节律可阻断感觉信息流入大脑皮 层; 睡眠时弥散性调制系统的下行投射系统抑制运动神经元的 活动。 14
14 睡眠的机制 • 控制睡眠和觉醒的最关键的神经元:脑干的NE和5‐HT能弥 散性神经递质系统;部分Ach能神经元可以增加REM事 件; • 弥散性调制系统控制丘脑的节律,进而控制大脑皮层的各 种EEG节律;丘脑的慢节律可阻断感觉信息流入大脑皮 层; • 睡眠时弥散性调制系统的下行投射系统抑制运动神经元的 活动
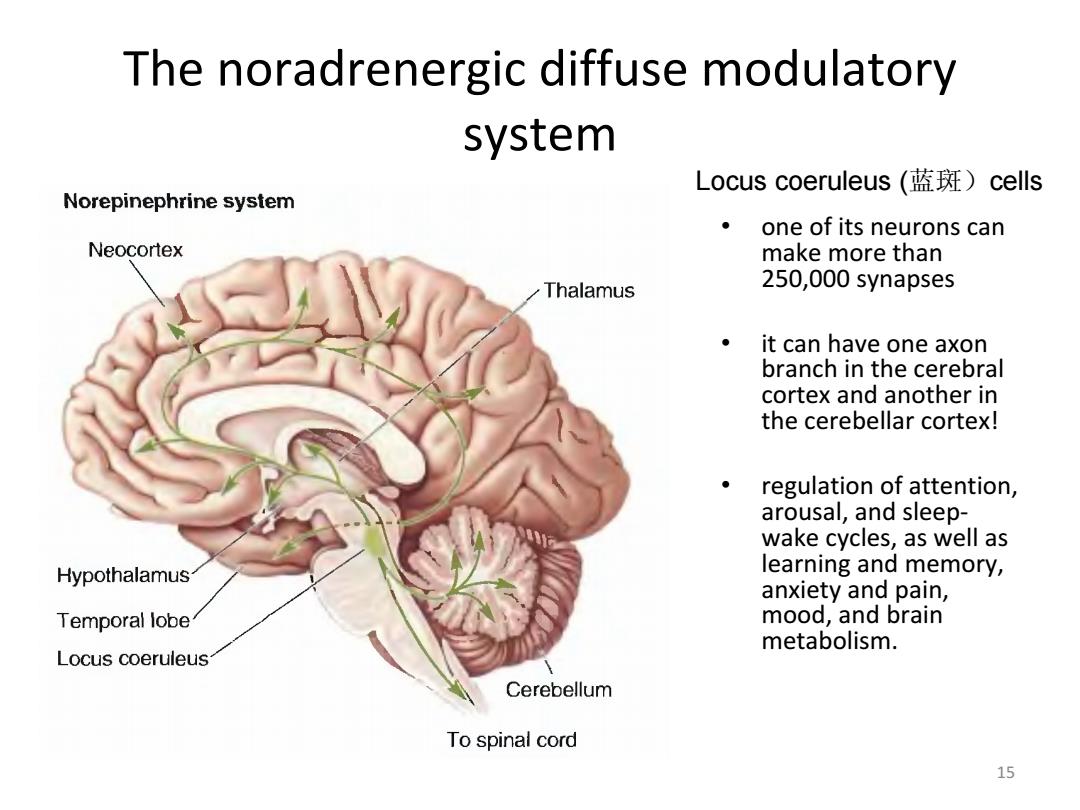
The noradrenergic diffuse modulatory system Locus coeruleus(蓝斑)cells Norepinephrine system one of its neurons can Neocortex make more than Thalamus 250,000 synapses it can have one axon branch in the cerebral cortex and another in the cerebellar cortex! regulation of attention, arousal,and sleep- wake cycles,as well as Hypothalamus learning and memory, anxiety and pain, Temporal lobe mood,and brain metabolism. Locus coeruleus Cerebellum To spinal cord 15
15 The noradrenergic diffuse modulatory system • one of its neurons can make more than 250,000 synapses • it can have one axon branch in the cerebral cortex and another in the cerebellar cortex! • regulation of attention, arousal, and sleep‐ wake cycles, as well as learning and memory, anxiety and pain, mood, and brain metabolism. Locus coeruleus (蓝斑)cells