
Electrochemistry PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,cn
Electrochemistry PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn
Introduction Chemical Energy Electrical Energy Chemical reactions caused by passage of electric current(reverse of voltaic process- electric current produced by chemical reactions) This chapter will discuss the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. Including three parts: .Electrolyte Solution .Electrochemical Cell .Electrolytic Cell and Polarization PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建wnm,fineprint.com,cn
Introduction Chemical Energy Electrical Energy Chemical reactions caused by passage of electric current (reverse of voltaic process - electric current produced by chemical reactions) This chapter will discuss the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. Including three parts: •Electrolyte Solution •Electrochemical Cell •Electrolytic Cell and Polarization PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 !www.fineprint.com.cn
Electrolyte Solution What is the conductor?The matter can flow current is called a conductor. There are two kinds of conductors. .Electronic conductor ·lonic conductor metallic conductors electrolyte electron ion Tincreasing,electric Tincreasing,electric ability decreasing ability increasing no chemical reaction existence of chemical reactions PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建m,fineprint.com,cn
Electrolyte Solution What is the conductor? The matter can flow current is called a conductor. There are two kinds of conductors. •Electronic conductor metallic conductors electron T increasing, electric ability decreasing no chemical reaction •Ionic conductor electrolyte ion T increasing, electric ability increasing existence of chemical reactions PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn
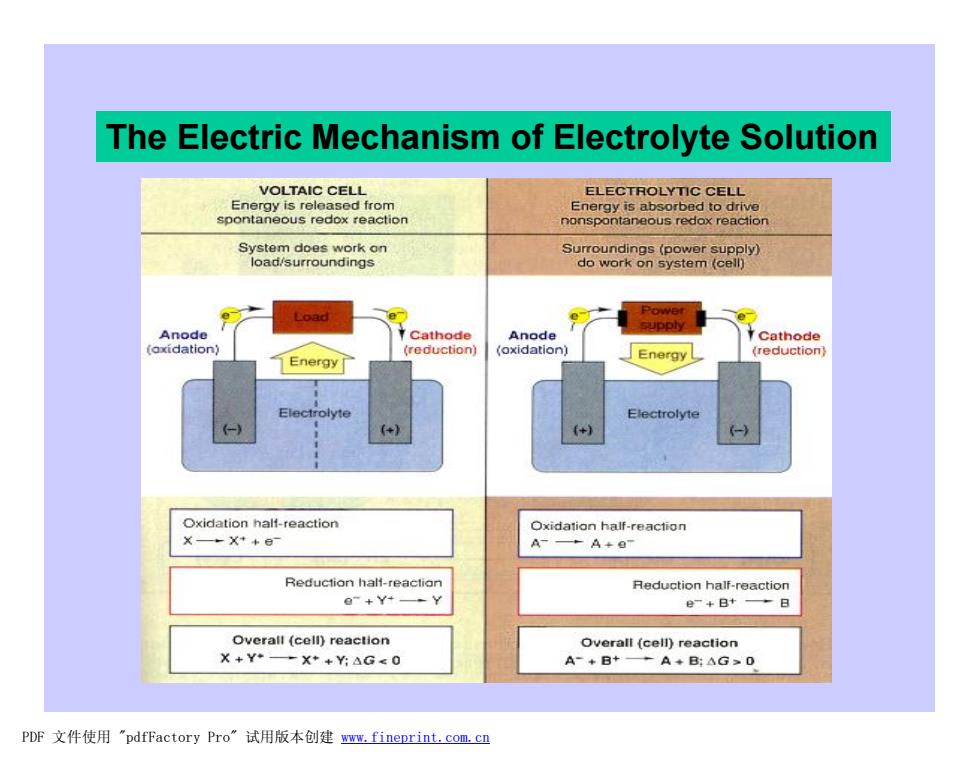
The Electric Mechanism of Electrolyte Solution VOLTAIC CELL ELECTROLYTIC CELL Energy is released from Energy is absorbed to drive spontaneous redox reaction nonspontaneous redox reaction System does work on Surroundings(power supply) load/surroundings do work on system (cell) Load e Anode t Cathode Anode supply Cathode (reduction) (oxidation) Energy (reduction Energy rolyte Electrolyte +) (+) Oxidation half-reaction Oxidation half-reaction X—+X++日 A---A+o Reduction halt-reactian Reduction half-reaction e-+Y+-Y e-+B+→日 Overall (cell)reaction Overall (cell)reaction X+Y◆-X*+Y:△G≤0 A-+B+→A+B:△G≥0 PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建www.fineprint.com.cn
The Electric Mechanism of Electrolyte Solution PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn
.Electrolytic Cell: Electrical Energy Chemical Energy A non-spontaneous reaction is driven by an external source of current. .Electrochemical Cell: Chemical Energy Electrical Energy It produces electricity as a result of the spontaneous reaction occurring inside it. In the electrochemical cell,chemical energy is being turned into electrical energy,while in the electrolytic cell,electrical energy is being turned into chemical energy. PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建ww.fineprint.com,cn
•Electrolytic Cell: Electrical Energy Chemical Energy A non-spontaneous reaction is driven by an external source of current. •Electrochemical Cell: Chemical Energy Electrical Energy It produces electricity as a result of the spontaneous reaction occurring inside it. In the electrochemical cell, chemical energy is being turned into electrical energy, while in the electrolytic cell, electrical energy is being turned into chemical energy. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn