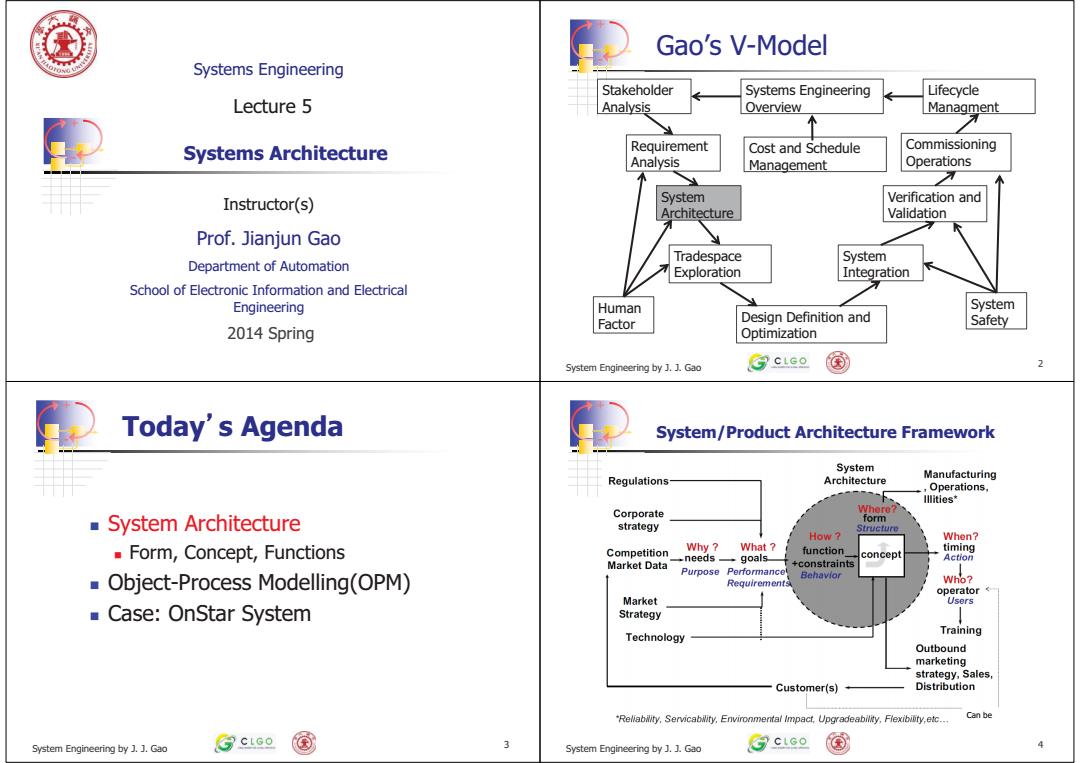
Gao's V-Model Systems Engineering Stakeholder Systems Engineering Lifecycle Lecture 5 Analysis Overview Managment Systems Architecture Requirement Cost and Schedule Commissioning Analysis Management Operations Instructor(s) System Verification and Architecture Validation Prof.Jianjun Gao Tradespace System Department of Automation Exploration Integration School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering Human System Factor Design Definition and Safety 2014 Spring Optimization System Engineering by J.J.Gao CLCO Today's Agenda System/Product Architecture Framework System Regulations Architecture Manufacturing Operations, lllities* Corporate Where? System Architecture form strategy Structure How When? Form,Concept,Functions Competition Why? What function timing →needs→goals concept Action Market Data +constraints Purpose Performance Object-Process Modelling(OPM) Behavlor Requlrement Who? operator< Market Users Case:OnStar System Strategy Technology Training Outbound marketing strategy,Sales, Customer(s) Distribution "Reliabiity,Servicablity,Environmental Impact,Upgradeability,Flexibibty,etc... Can be System Engineering by Gao ③ctGe System Engineering by .J.Gao ⑦ctGe 国
Systems Engineering Instructor(s) + - 2014 Spring Systems Architecture Prof. Jianjun Gao Department of Automation School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering Lecture 5 + - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 2 Gao’s V-Model Stakeholder Analysis Requirement Analysis System Architecture Tradespace Exploration Design Definition and Optimization System Integration Verification and Validation Commissioning Operations Lifecycle Managment Systems Engineering Overview Cost and Schedule Management Human Factor System Safety + - 3 Today䇻s Agenda System Architecture Form, Concept, Functions Object-Process Modelling(OPM) Case: OnStar System System Engineering by J. J. Gao + - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 4 System/Product Architecture Framework Can be����
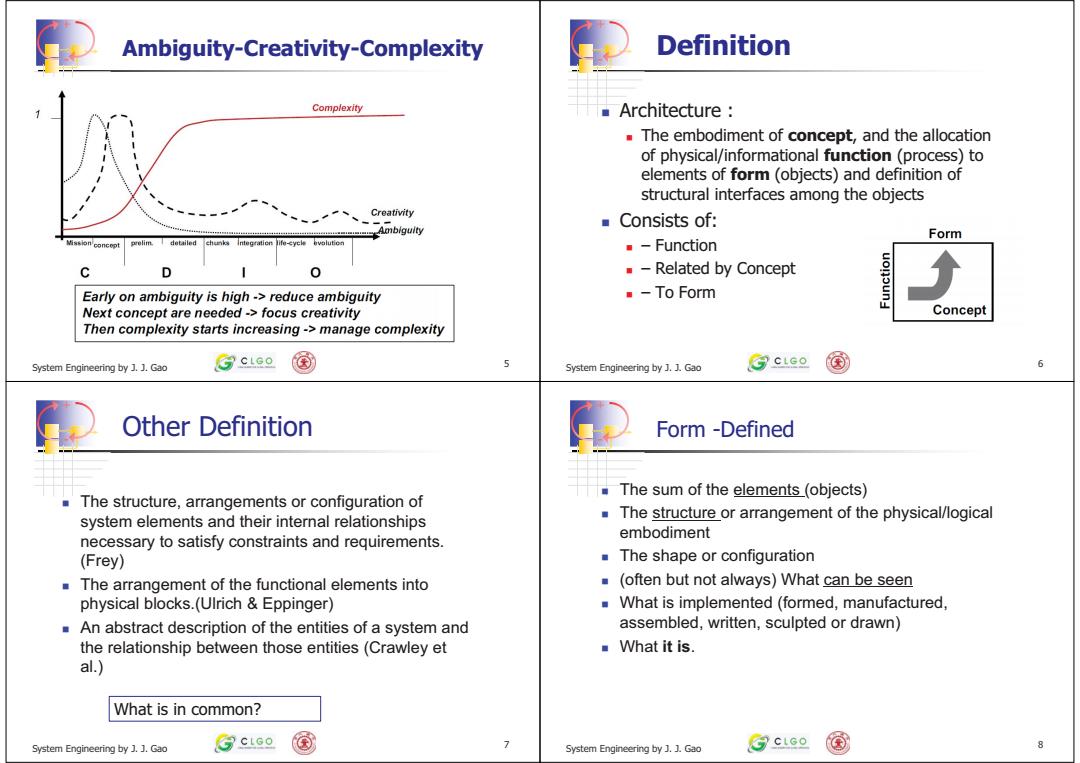
Ambiguity-Creativity-Complexity Definition Complexity Architecture The embodiment of concept,and the allocation of physical/informational function(process)to elements of form (objects)and definition of structural interfaces among the objects Creativity Ambiguity ■Consists of: Form Mission concopt prelim.detailed chunks Integration life-cycle bvolution ■-Function C D -Related by Concept Early on ambiguity is high->reduce ambiguity To Form Next concept are needed->focus creativity Concept Then complexity starts increasing->manage complexity System Engineering by J.J.Gao ③cLao 国 System Engineering by J.J.Gao ③cLco 国 6 Other Definition Form -Defined The sum of the elements_(objects) The structure,arrangements or configuration of system elements and their internal relationships The structure or arrangement of the physical/logical necessary to satisfy constraints and requirements. embodiment (Frey) The shape or configuration The arrangement of the functional elements into (often but not always)What can be seen physical blocks.(Ulrich Eppinger) What is implemented (formed,manufactured, An abstract description of the entities of a system and assembled,written,sculpted or drawn) the relationship between those entities(Crawley et What it is al.) What is in common? System Engineering by J..Gao ③ctGe System Engineering by .J.Gao ③ctse 8
+ - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 5 Ambiguity-Creativity-Complexity + - Architecture : The embodiment of concept, and the allocation of physical/informational function (process) to elements of form (objects) and definition of structural interfaces among the objects Consists of: – Function – Related by Concept – To Form System Engineering by J. J. Gao 6 Definition + - The structure, arrangements or configuration of system elements and their internal relationships necessary to satisfy constraints and requirements. (Frey) The arrangement of the functional elements into physical blocks.(Ulrich & Eppinger) An abstract description of the entities of a system and the relationship between those entities (Crawley et al.) System Engineering by J. J. Gao 7 Other Definition What is in common? + - The sum of the elements (objects) The structure or arrangement of the physical/logical embodiment The shape or configuration (often but not always) What can be seen What is implemented (formed, manufactured, assembled, written, sculpted or drawn) What it is. System Engineering by J. J. Gao 8 Form -Defined���������������
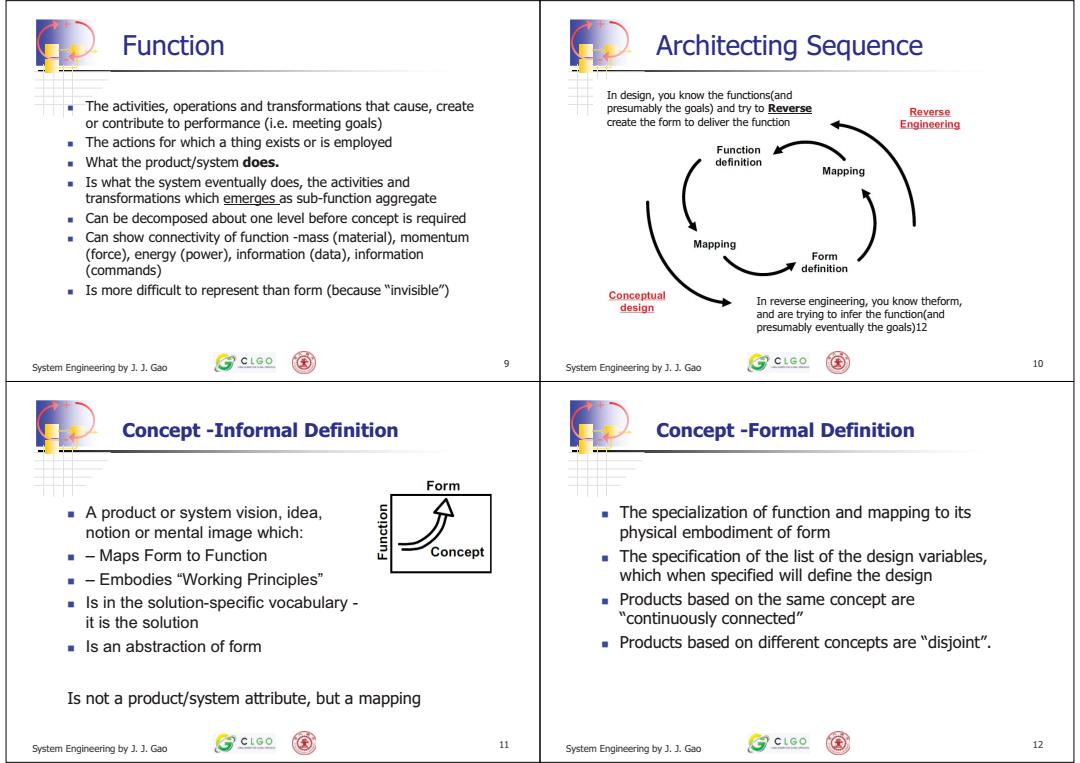
Function Architecting Sequence In design,you know the functions(and The activities,operations and transformations that cause,create presumably the goals)and try to Reverse Reverse or contribute to performance(i.e.meeting goals) create the form to deliver the function Engineering The actions for which a thing exists or is employed Function What the product/system does. definition Mapping Is what the system eventually does,the activities and transformations which emerges as sub-function aggregate Can be decomposed about one level before concept is required Can show connectivity of function-mass(material),momentum Mapping (force),energy (power),information(data),information Form (commands) definition Is more difficult to represent than form (because "invisible") Conceptual In reverse engineering,you know theform, design and are trying to infer the function(and presumably eventually the goals)12 System Engineering by J.J.Gao ③cLao 国 System Engineering by J.J.Gao ③cLco 国 10 Concept -Informal Definition Concept -Formal Definition Form A product or system vision,idea, 分 The specialization of function and mapping to its notion or mental image which: physical embodiment of form -Maps Form to Function Concept The specification of the list of the design variables, -Embodies "Working Principles" which when specified will define the design Is in the solution-specific vocabulary- Products based on the same concept are it is the solution "continuously connected" Is an abstraction of form Products based on different concepts are "disjoint". Is not a product/system attribute,but a mapping System Engineering by Gao ③ctGe 11 System Engineering by .J.Gao ③ctse 12
+ - The activities, operations and transformations that cause, create or contribute to performance (i.e. meeting goals) The actions for which a thing exists or is employed What the product/system does. Is what the system eventually does, the activities and transformations which emerges as sub-function aggregate Can be decomposed about one level before concept is required Can show connectivity of function -mass (material), momentum (force), energy (power), information (data), information (commands) Is more difficult to represent than form (because “invisible”) System Engineering by J. J. Gao 9 Function + - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 10 Architecting Sequence In reverse engineering, you know theform, and are trying to infer the function(and presumably eventually the goals)12 In design, you know the functions(and presumably the goals) and try to Reverse create the form to deliver the function + - A product or system vision, idea, notion or mental image which: – Maps Form to Function – Embodies “Working Principles” Is in the solution-specific vocabulary - it is the solution Is an abstraction of form System Engineering by J. J. Gao 11 Concept -Informal Definition Is not a product/system attribute, but a mapping + - The specialization of function and mapping to its physical embodiment of form The specification of the list of the design variables, which when specified will define the design Products based on the same concept are “continuously connected” Products based on different concepts are “disjoint”. System Engineering by J. J. Gao 12 Concept -Formal Definition����������������
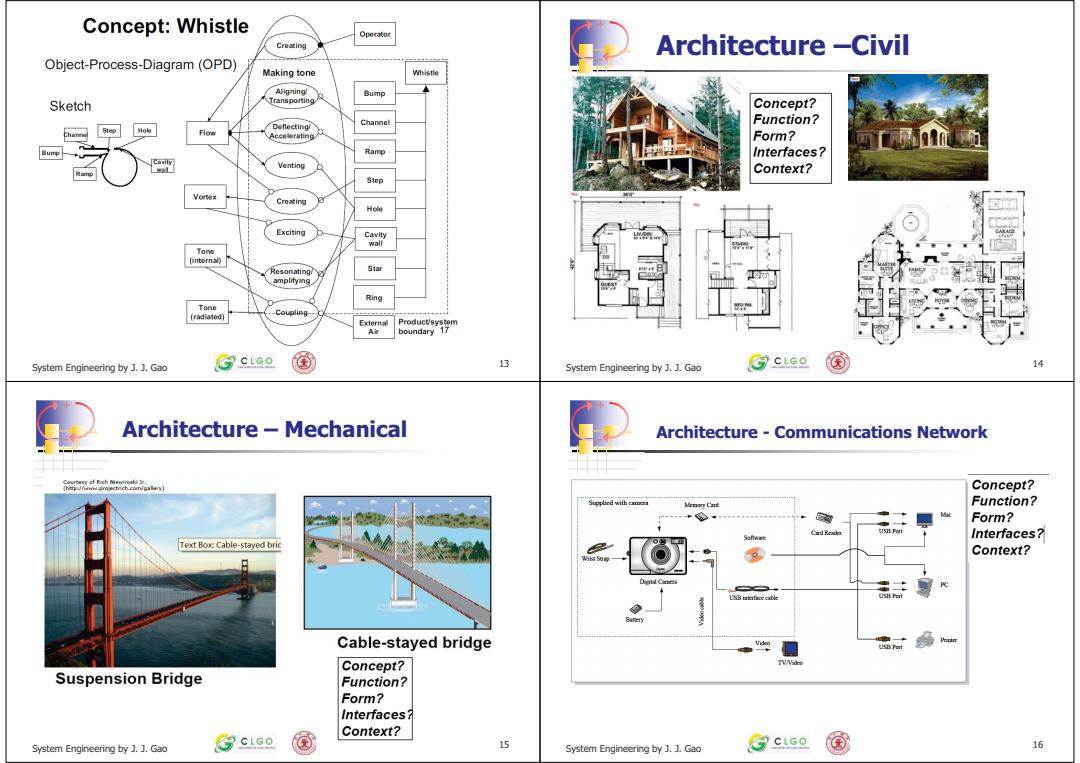
Concept:Whistle Operator Creating Architecture -Civil Object-Process-Diagram(OPD) Making tone Aligning! Bump Sketch Transporting Concept? Deflecting/ Function? Form? Ramp Interfaces? Venting Context? Step Vortex Cresirg Hole Exciting Cavity wall Tonc (internal) Resonating/ Star amplitying. Ring Tone (radiatod] Coupling- Product/system boundary 17 System Engineering by J.J.Gao ⑦c⊥ao System Engineering by J.J.Gao ⑦cLco 国 14 Architecture-Mechanical Architecture-Communications Network Concept? Supplied with cm Function? Form? Cad Read山 Interfaces? Text Box:Cable-stayed bric g Context? 品 Cable-stayed bridge Concept? Suspension Bridge Function? Form? Interfaces? Context? System Engineering by J.J.Gao ③ctGe 15 System Engineering by .]Gao ⑦ctGe 国 16
+ - Describe the concept of one of the following items: – Whistle – Automobile – Aircraft – Communications Satellite – International Space Station – Lecture System Engineering by J. J. Gao 13 Exercise + - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 14 Architecture –Civil + - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 15 Architecture – Mechanical + - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 16 Architecture - Communications Network �������
Today's Agenda Object-Process Methodology The Object-Process Methodology(OPM)is an integrated approach to the study and development of systems in ■System Architecture general. OPM unifies the system's structure and behavior .Form,Concept,Functions throughout the analysis,design and implementation of the Object-Process Modelling(OPM) system within one frame of reference using a single diagramming tool- ■Case:OnStar System the Object-Process Diagram (OPD)and a corresponding,English-like language- the Object-Process Language (OPL). System Engineering by Gao CLCO 国 17 System Engineering by J.J.Gao ③ctco 18 Object-Process Methodology Object-Process Methodology(OPM)Principles The basic premise of OPM is that objects and Objects and processes are the two types of processes are two types of equally important equally important things(entities)required to classes of things,that together faithfully describe describe a system in a single,unifying model. both the structure and the behavior of systems in a single model in virtually any domain. Processes transform objects by changing their At any point in time,each object is at some state, state.Transformation includes creation and and object states are transformed through the elimination. occurrence of a process. Complexity is controlled through recursive and Scaling can be applied recursively and selectively selective scaling (zooming)of objects and/or to both objects and processes. processes to any desired level of detail. ③ctGe ③ctGe 国
+ - 17 Today䇻s Agenda System Architecture Form, Concept, Functions Object-Process Modelling(OPM) Case: OnStar System System Engineering by J. J. Gao + - System Engineering by J. J. Gao 18 Object-Process Methodology The Object-Process Methodology (OPM) is an integrated approach to the study and development of systems in general. OPM unifies the system’s structure and behavior throughout the analysis, design and implementation of the system within one frame of reference using a single diagramming tool – the Object-Process Diagram (OPD) and a corresponding, English-like language – the Object-Process Language (OPL). + - The basic premise of OPM is that objects and processes are two types of equally important classes of things, that together faithfully describe both the structure and the behavior of systems in a single model in virtually any domain. At any point in time, each object is at some state, and object states are transformed through the occurrence of a process. Complexity is controlled through recursive and selective scaling (zooming) of objects and/or processes to any desired level of detail. Object-Process Methodology + - Object-Process Methodology (OPM) Principles Objects and processes are the two types of equally important things (entities) required to describe a system in a single, unifying model. Processes transform objects by changing their state. Transformation includes creation and elimination. Scaling can be applied recursively and selectively to both objects and processes. ������������