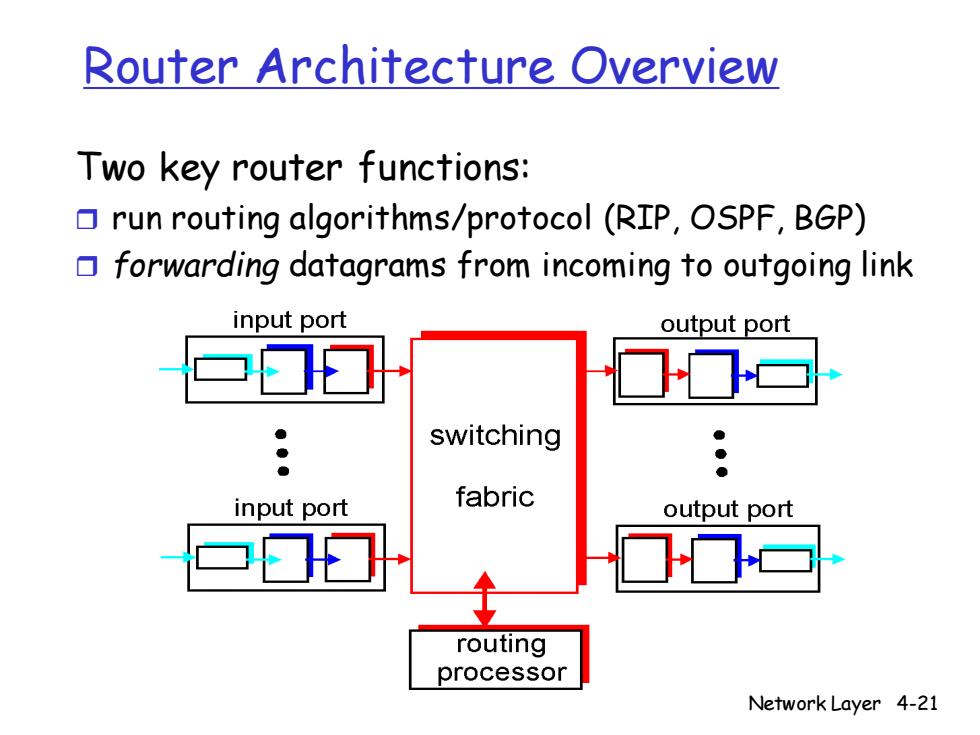
Router Architecture Overview Two key router functions: run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP,OSPF,BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link input port output port switching input port fabric output port routing processor Network Layer 4-21
Network Layer 4-21 Router Architecture Overview Two key router functions: run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link
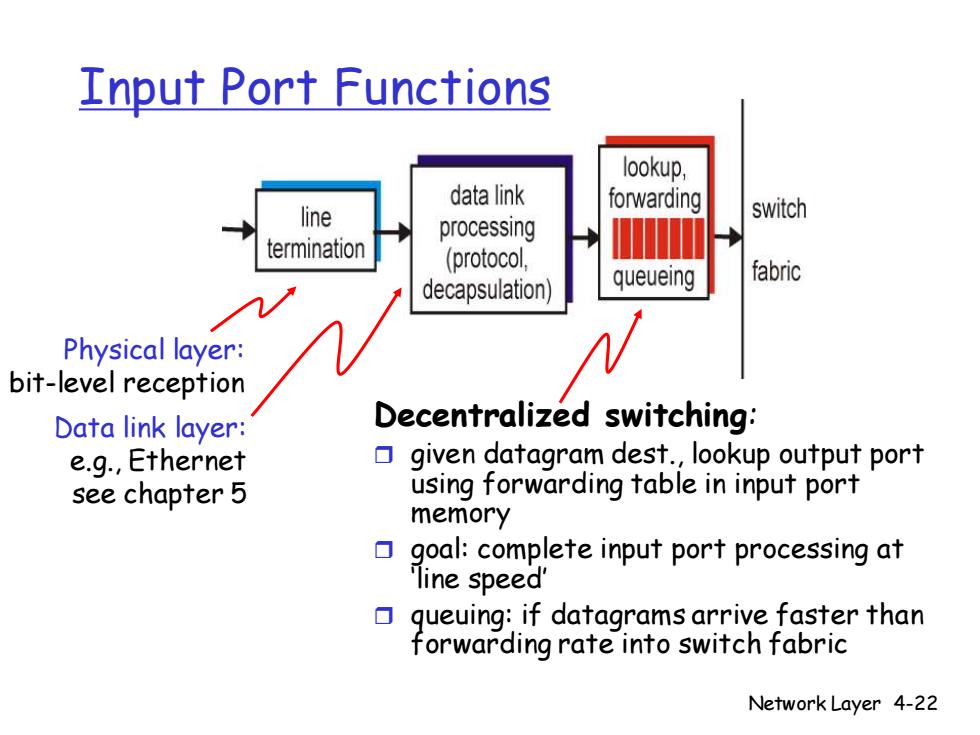
Input Port Functions lookup, data link forwarding line switch processing termination (protocol, fabric decapsulation) queueing Physical layer: bit-level reception Data link layer: Decentralized switching: e.g.,Ethernet given datagram dest.,lookup output port see chapter 5 using forwarding table in input port memory goal:complete input port processing at line speed' queuing:if datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric Network Layer 4-22
Network Layer 4-22 Input Port Functions Decentralized switching: given datagram dest., lookup output port using forwarding table in input port memory goal: complete input port processing at ‘line speed’ queuing: if datagrams arrive faster than forwarding rate into switch fabric Physical layer: bit-level reception Data link layer: e.g., Ethernet see chapter 5
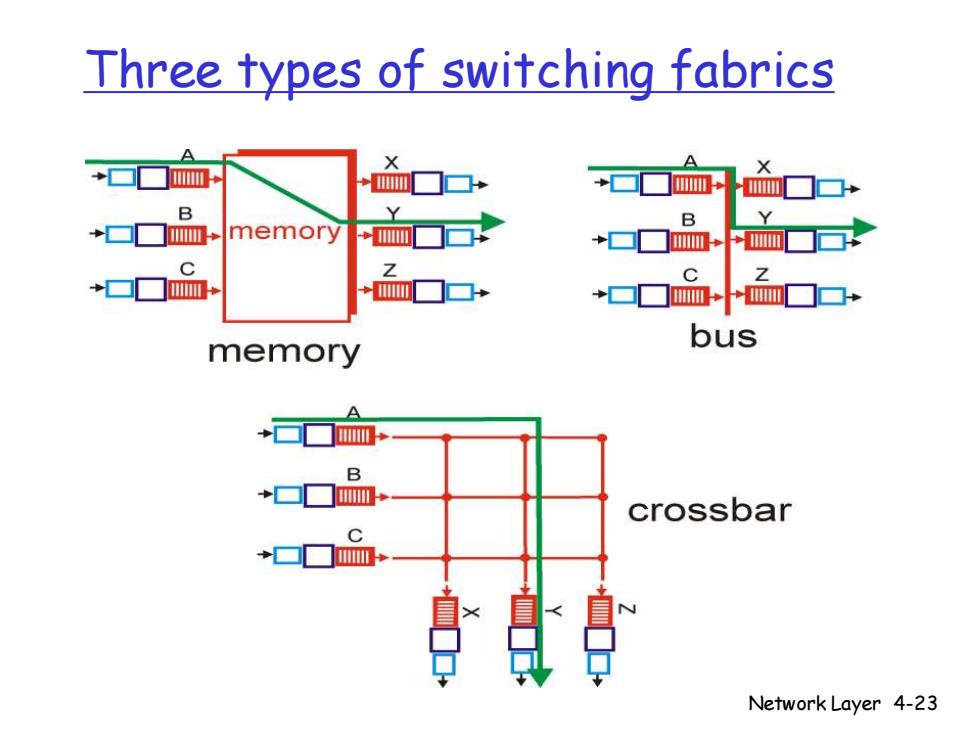
Three types of switching fabrics A ☑ B +▣☐mm,memory ◆m口 C C Z bus memory →▣ B +口口m crossbar → Network Layer 4-23
Network Layer 4-23 Three types of switching fabrics
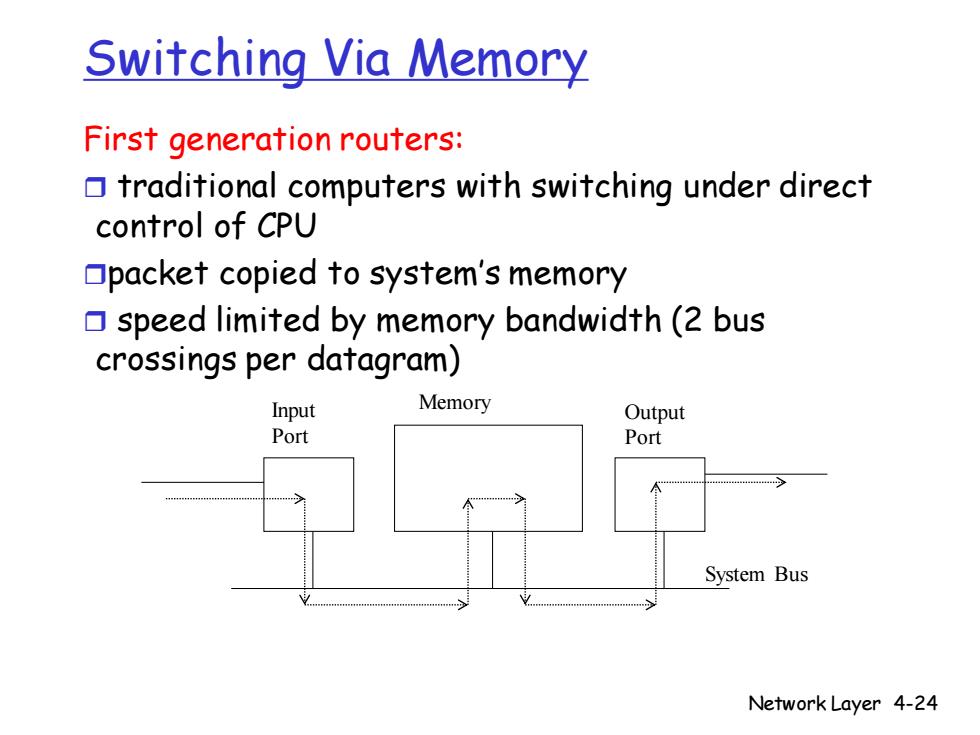
Switching Via Memory First generation routers: traditional computers with switching under direct control of CPU Opacket copied to system's memory speed limited by memory bandwidth(2 bus crossings per datagram) Input Memory Output Port Port System Bus Network Layer 4-24
Network Layer 4-24 Switching Via Memory First generation routers: traditional computers with switching under direct control of CPU packet copied to system’s memory speed limited by memory bandwidth (2 bus crossings per datagram) Input Port Output Port Memory System Bus
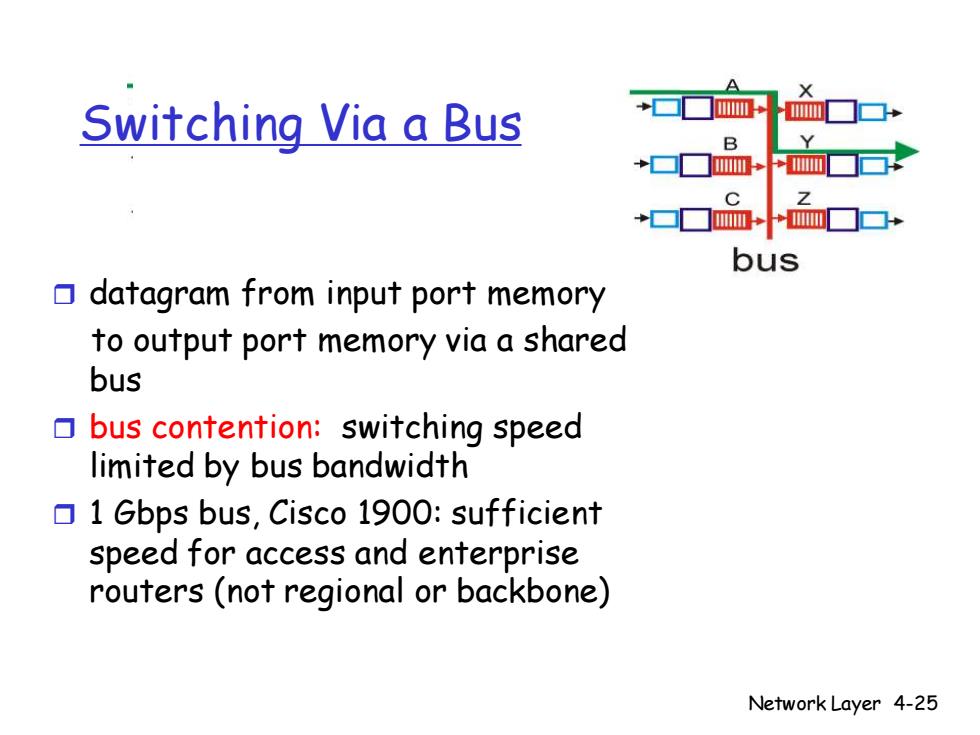
Switching Via a Bus B bus datagram from input port memory to output port memory via a shared bus bus contention:switching speed limited by bus bandwidth 1 Gbps bus,Cisco 1900:sufficient speed for access and enterprise routers (not regional or backbone) Network Layer 4-25
Network Layer 4-25 Switching Via a Bus datagram from input port memory to output port memory via a shared bus bus contention: switching speed limited by bus bandwidth 1 Gbps bus, Cisco 1900: sufficient speed for access and enterprise routers (not regional or backbone)