Network layer connection and connection-less service Odatagram network provides network-layer connectionless service VC network provides network-layer connection service analogous to the transport-layer services, but: o service:host-to-host o no choice:network provides one or the other o implementation:in network core Network Layer 4-11
Network Layer 4-11 Network layer connection and connection-less service datagram network provides network-layer connectionless service VC network provides network-layer connection service analogous to the transport-layer services, but: service: host-to-host no choice: network provides one or the other implementation: in network core
Virtual circuits source-to-dest path behaves much like telephone circuit" o performance-wise o network actions along source-to-dest path call setup,teardown for each call before data can flow each packet carries VC identifier(not destination host address) every router on source-dest path maintains "state"for each passing connection link,router resources(bandwidth,buffers)may be allocated to VC(dedicated resources=predictable service) Network Layer 4-12
Network Layer 4-12 Virtual circuits call setup, teardown for each call before data can flow each packet carries VC identifier (not destination host address) every router on source-dest path maintains “state” for each passing connection link, router resources (bandwidth, buffers) may be allocated to VC (dedicated resources = predictable service) “source-to-dest path behaves much like telephone circuit” performance-wise network actions along source-to-dest path
VC implementation a VC consists of: 1.path from source to destination 2. VC numbers,one number for each link along path 3.entries in forwarding tables in routers along path ▣ packet belonging to VC carries VC number (rather than dest address) VC number can be changed on each link. o New VC number comes from forwarding table Network Layer 4-13
Network Layer 4-13 VC implementation a VC consists of: 1. path from source to destination 2. VC numbers, one number for each link along path 3. entries in forwarding tables in routers along path packet belonging to VC carries VC number (rather than dest address) VC number can be changed on each link. New VC number comes from forwarding table
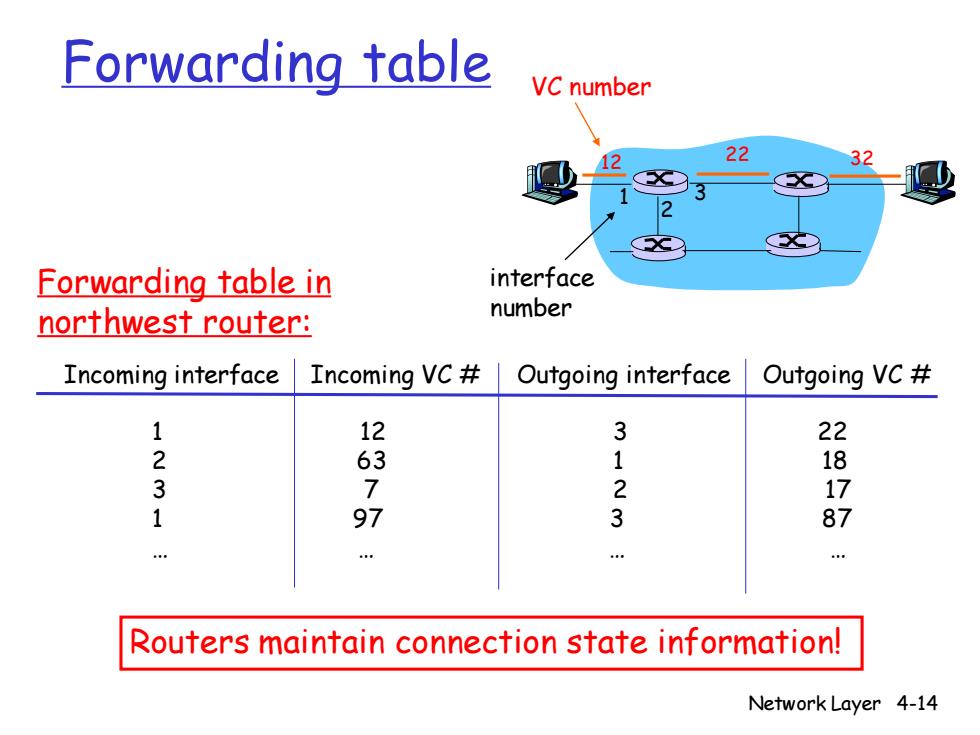
Forwarding table VC number 22 32 Forwarding table in interface northwest router: number Incoming interface Incoming VC# Outgoing interface Outgoing VC# 1 12 3 2 63 1 18 3 2 17 1 97 3 87 Routers maintain connection state information! Network Layer 4-14
Network Layer 4-14 Forwarding table 12 22 32 1 2 3 VC number interface number Incoming interface Incoming VC # Outgoing interface Outgoing VC # 1 12 3 22 2 63 1 18 3 7 2 17 1 97 3 87 . . . . Forwarding table in northwest router: Routers maintain connection state information!
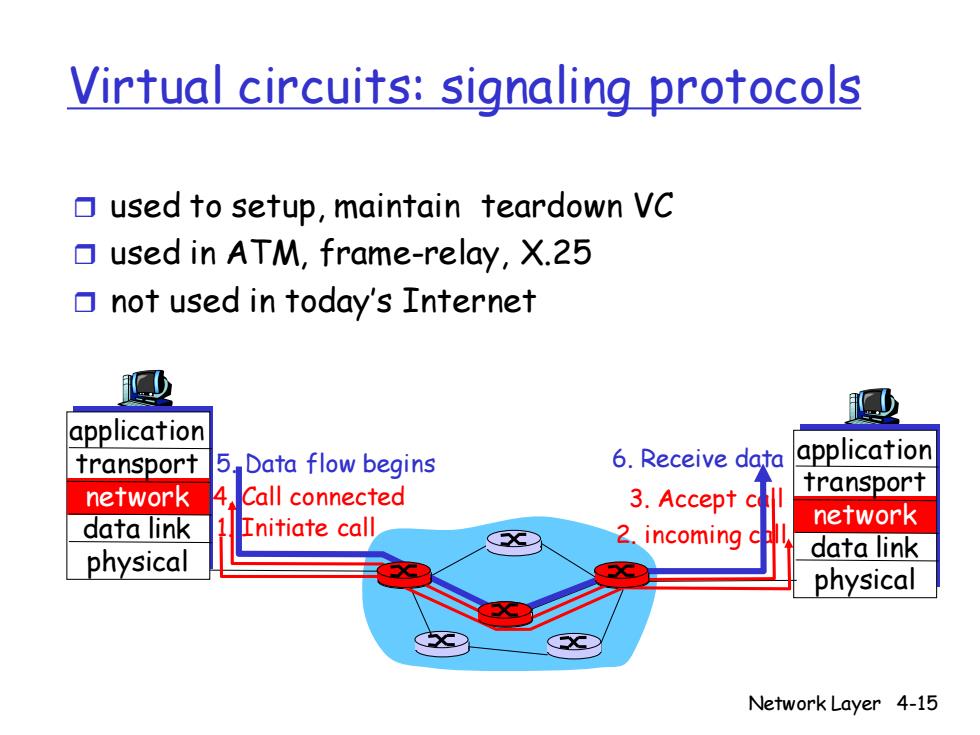
Virtual circuits:signaling protocols used to setup,maintain teardown VC used in ATM,frame-relay,X.25 not used in today's Internet application transport 5.Data flow begins 6.Receive data application network Call connected 3.Accept c transport data link Initiate call network 2.incoming physical data link physical Network Layer 4-15
Network Layer 4-15 Virtual circuits: signaling protocols used to setup, maintain teardown VC used in ATM, frame-relay, X.25 not used in today’s Internet application transport network data link physical application transport network data link physical 1. Initiate call 2. incoming call 4. Call connected 3. Accept call 5. Data flow begins 6. Receive data