
Level of Significance,a Defines the unlikely values of the sample statistic if the null hypothesis is true Defines region of rejection of the sampling distribution Is designated by a,(level of significance) Typical values are.01,.05,or.10 Is selected by the researcher at the beginning Provides the critical value(s)of the test Statistics for Mar agers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-11
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-11 Level of Significance, Defines the unlikely values of the sample statistic if the null hypothesis is true Defines region of rejection of the sampling distribution Is designated by , (level of significance) Typical values are .01, .05, or .10 Is selected by the researcher at the beginning Provides the critical value(s) of the test

Regions of Rejection and Non-rejection Region of Critical Region of Critical Region of Rejection Value Nonrejection Value Rejection Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-12
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-12 Regions of Rejection and Non-rejection X Critical Value Critical Value μ Region of Rejection Region of Rejection Region of Nonrejection
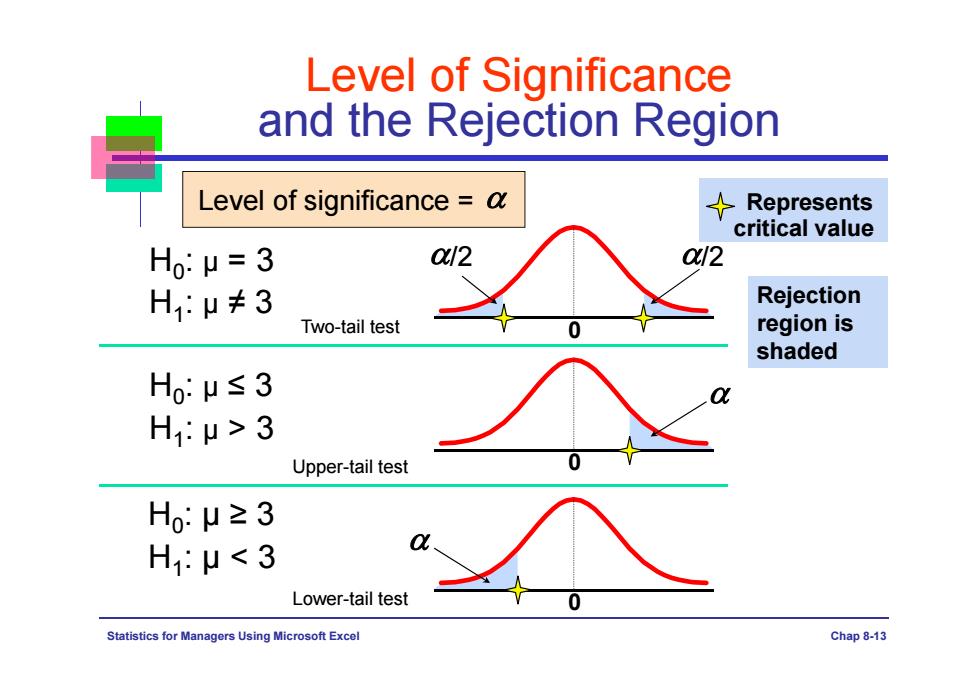
Level of Significance and the Rejection Region Level of significance =a Represents critical value H0μ=3 a12 02 H1:μ≠3 Rejection Two-tail test region is shaded Ho:μ≤3 H1:μ>3 Upper-tail test Ho:μ≥3 H:μ<3 Lower-tail test Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-13
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-13 Level of Significance and the Rejection Region H0: μ ≥ 3 H1: μ < 3 0 H0: μ ≤ 3 H1: μ > 3 Represents critical value Lower-tail test Level of significance = Upper-tail test 0 Two-tail test Rejection region is shaded /2 0 H /2 0: μ = 3 H1: μ ≠ 3

Errors in Making Decisions Type I Error:occurs if the null hypothesis is rejected when in fact it is true and should not be rejected. Reject a true null hypothesis -Considered a serious type of error The probability of Type I Error is a -Called level of significance of the test Set by researcher in advance Statistics for Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-14
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-14 Errors in Making Decisions Type I Error: occurs if the null hypothesis is rejected when in fact it is true and should not be rejected. Reject a true null hypothesis Considered a serious type of error The probability of Type I Error is Called level of significance of the test Set by researcher in advance

Errors in Making Decisions ontinued) Type ll Error:occurs if the null hypothesis is not rejected when in fact it is false and should be rejected. Fail to reject a false null hypothesis The probability of Type ll Error is B Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-15
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel Chap 8-15 Errors in Making Decisions(continued) Type II Error: occurs if the null hypothesis is not rejected when in fact it is false and should be rejected. Fail to reject a false null hypothesis The probability of Type II Error is β