
(二)相差显微镜和微分干涉显微镜 微分干涉显微镜以平面偏 振光为光源,使样品中厚 度上的微小区别转化成明 暗区别 一分辨率比普通光镜提高了一 个数量级 -录像增差显微镜可以用来直 (B) 10um 接观察颗粒物质沿着微管运 输的动态过程 Figure 9-9 Molecular Biology of the Cell (Garland Science 2008)
(二)相差显微镜和微分干涉显微镜 • 微分干涉显微镜以平面偏 振光为光源,使样品中厚 度上的微小区别转化成明 暗区别 – 分辨率比普通光镜提高了一 个数量级 – 录像增差显微镜可以用来直 接观察颗粒物质沿着微管运 输的动态过程 Figure 9-9 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008)
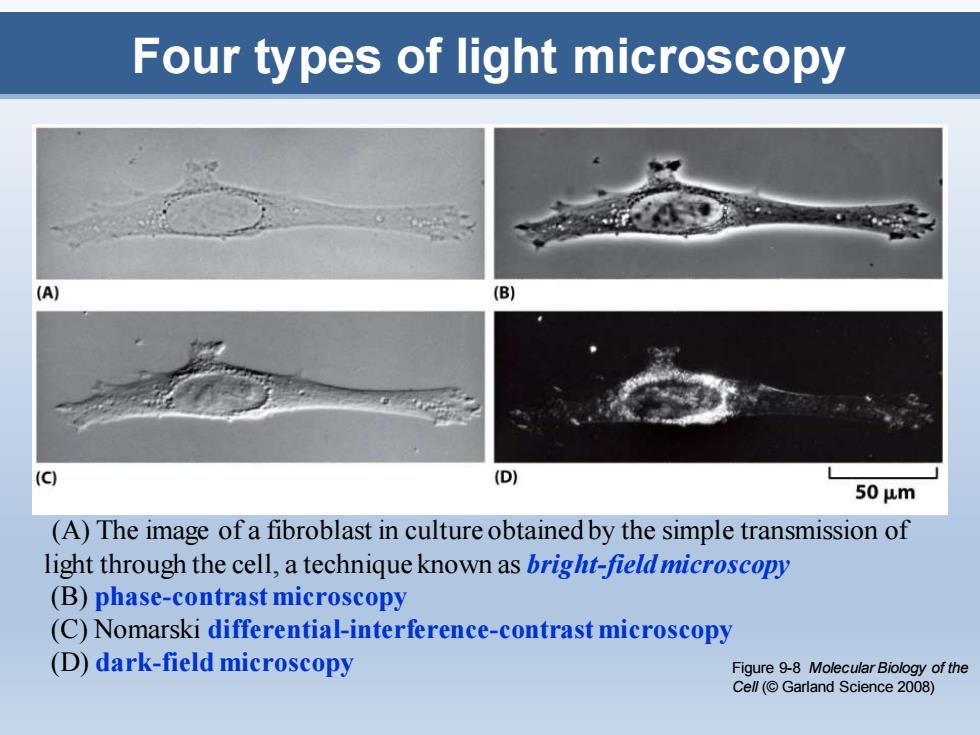
Four types of light microscopy (A) (B) (C) (D) 50μm (A)The image of a fibroblast in culture obtained by the simple transmission of light through the cell,a technique known as bright-field microscopy (B)phase-contrast microscopy (C)Nomarski differential-interference-contrast microscopy (D)dark-field microscopy Figure 9-8 Molecular Biology of the Cell(Garland Science 2008)
Four types of light microscopy (A) The image of a fibroblast in culture obtained by the simple transmission of light through the cell, a technique known as bright-field microscopy (B) phase-contrast microscopy (C) Nomarski differential-interference-contrast microscopy (D) dark-field microscopy Figure 9-8 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008)
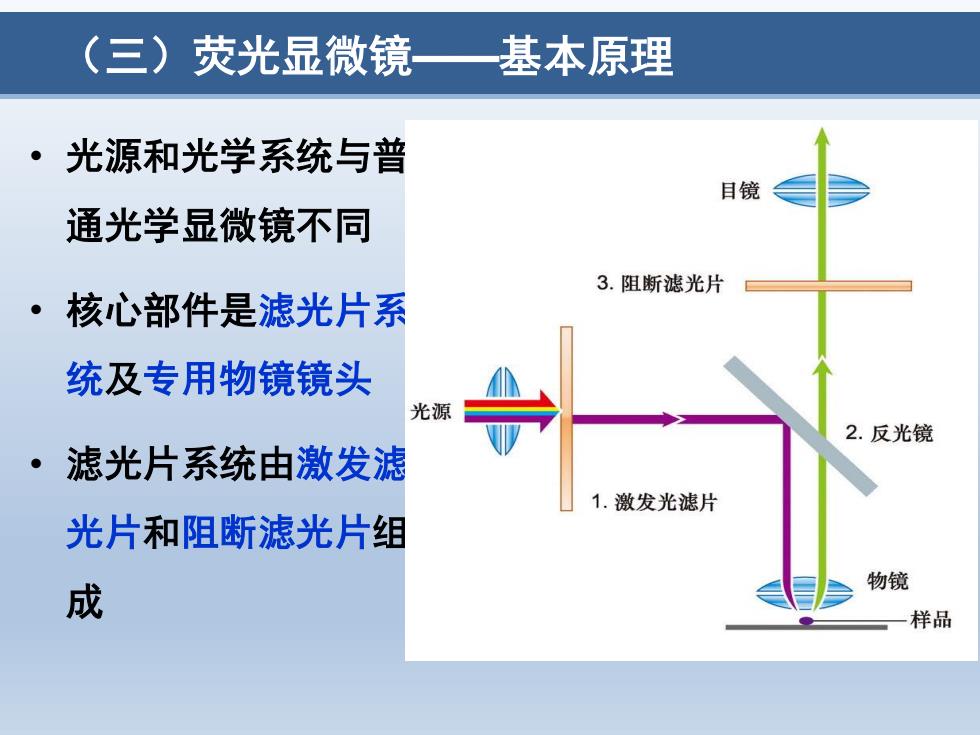
(三)荧光显微镜 基本原理 。 光源和光学系统与普 目镜 通光学显微镜不同 3.阻断滤光片 ·核心部件是滤光片系 统及专用物镜镜头 光源 2.反光镜 ·滤光片系统由激发滤 1.激发光滤片 光片和阻断滤光片组 成 物镜 一样品
(三)荧光显微镜——基本原理 • 光源和光学系统与普 通光学显微镜不同 • 核心部件是滤光片系 统及专用物镜镜头 • 滤光片系统由激发滤 光片和阻断滤光片组 成
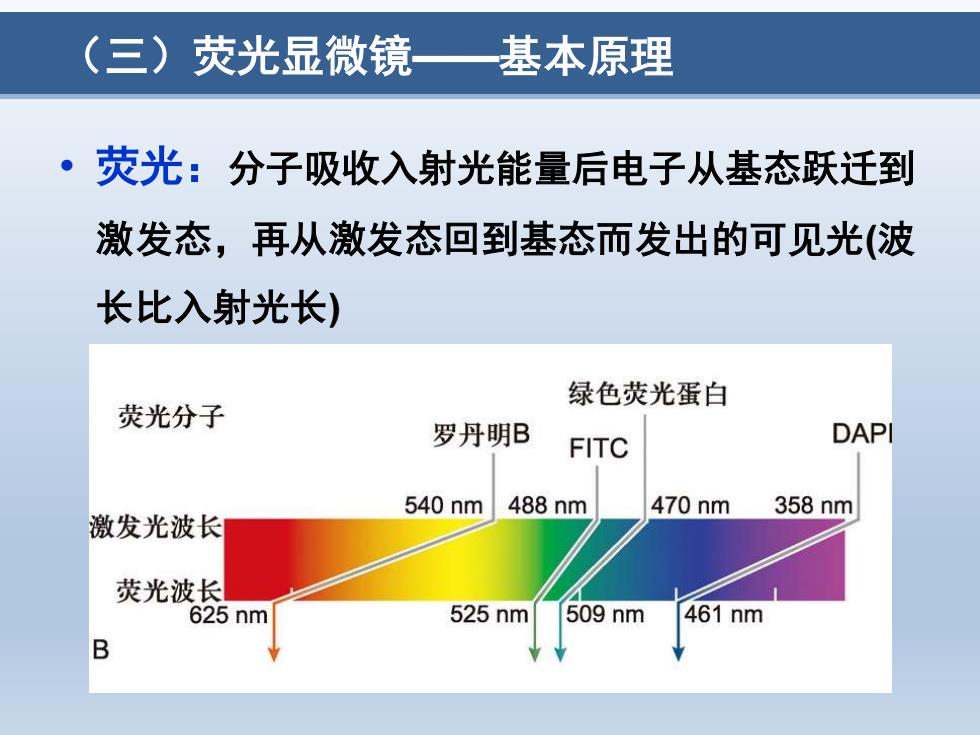
(三)荧光显微镜 基本原理 ·荧光:分子吸收入射光能量后电子从基态跃迁到 激发态,再从激发态回到基态而发出的可见光(波 长比入射光长) 绿色荧光蛋白 荧光分子 罗丹明B FITC DAPI 540nm 488nm 470nm 358nm 激发光波长 荧光波长 25nm 525nm 509nm 461nm B
(三)荧光显微镜——基本原理 • 荧光:分子吸收入射光能量后电子从基态跃迁到 激发态,再从激发态回到基态而发出的可见光(波 长比入射光长)
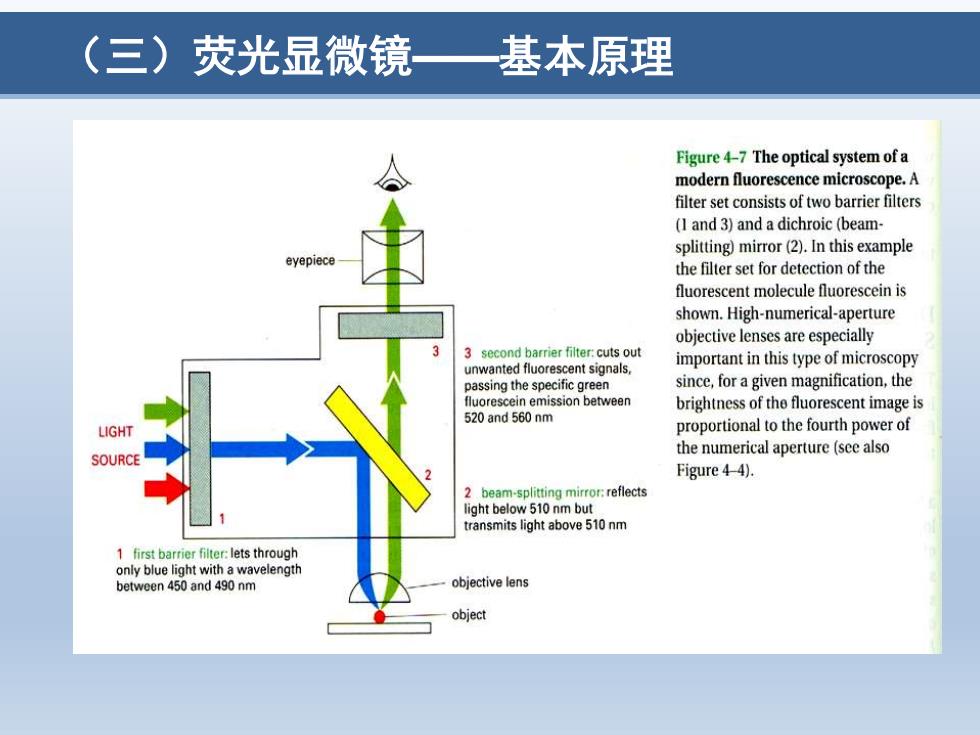
(三)荧光显微镜 基本原理 Figure 4-7 The optical system of a modern fluorescence microscope.A filter set consists of two barrier filters (I and 3)and a dichroic(beam- splitting)mirror(2).In this example eyepiece the filter set for detection of the fluorescent molecule fluorescein is shown.High-numerical-aperture objective lenses are especially 3 second barrier filter:cuts out unwanted fluorescent signals. important in this type of microscopy passing the specific green since,for a given magnification,the luorescein emission between brightness of the fluorescent image is 520 and 560 nm LIGHT proportional to the fourth power of SOURCE the numerical aperture(see also Figure 4-4). 2 beam-splitting mirror:reflects light below 510 nm but transmits light above 510 nm 1 first barrier filter:lets through only blue light with a wavelength between 450 and 490 nm objective lens object
(三)荧光显微镜——基本原理 (三)荧光显微镜——基本原理