效绵鼎 Conventions ■ a,b,..are input symbols. ...,X,Y,Z are tape symbols ...w,X,y,z are strings of input symbols. ,阝,.are strings of tape symbols. .6
Conventions ◼ a, b, … are input symbols. ◼ …, X, Y, Z are tape symbols. ◼ …, w, x, y, z are strings of input symbols. ◼ , ,… are strings of tape symbols. 6
效绵鼎 The Transition Function Takes two arguments: 1.A state,in Q. 2.A tape symbol in r. 6(q,Z)is either undefined or a triple of the form (P,Y,D): p is a state. Y is the new tape symbol. D is a direction,L or R. 7
The Transition Function ◼ Takes two arguments: 1. A state, in Q. 2. A tape symbol in Γ. ◼ δ(q, Z) is either undefined or a triple of the form (p, Y, D). p is a state. Y is the new tape symbol. D is a direction, L or R. 7

效绵鼎 Example:Turing Machine This TM scans its input right,looking for a 1. If it finds one,it changes it to a 0,goes to final state f,and halts. ■ If it reaches a blank,it changes it to a 1 and moves left. 8
Example: Turing Machine ◼ This TM scans its input right, looking for a 1. ◼ If it finds one, it changes it to a 0, goes to final state f, and halts. ◼ If it reaches a blank, it changes it to a 1 and moves left. 8
效绵鼎 Example:Turing Machine-(2) States ={q (start),f(final)}. Input symbols =(0,1). Tape symbols ={0,1,B). ■6(q,0)=(q,0,R) δ(q,1)=(E,0,R) ■δ(q,B)=(q,1,L) 9
Example: Turing Machine – (2) ◼ States = {q (start), f (final)}. ◼ Input symbols = {0, 1}. ◼ Tape symbols = {0, 1, B}. ◼ δ(q, 0) = (q, 0, R). ◼ δ(q, 1) = (f, 0, R). ◼ δ(q, B) = (q, 1, L). 9
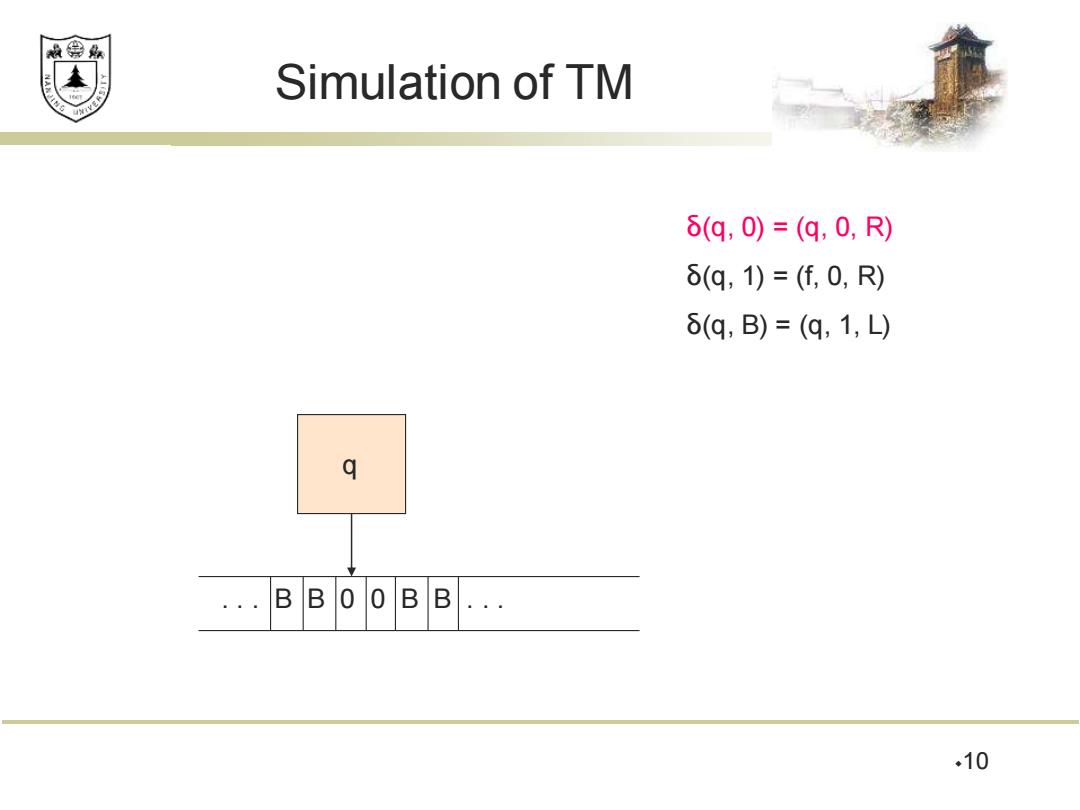
效绵鼎 Simulation of TM 6(q,0)=(q,0,R) δ(q,1)=(f,0,R) δ(q,B)=(q,1,L) q ..BB .. .10
Simulation of TM 10 δ(q, 0) = (q, 0, R) δ(q, 1) = (f, 0, R) δ(q, B) = (q, 1, L) . . . B B 0 0 B B . . . q