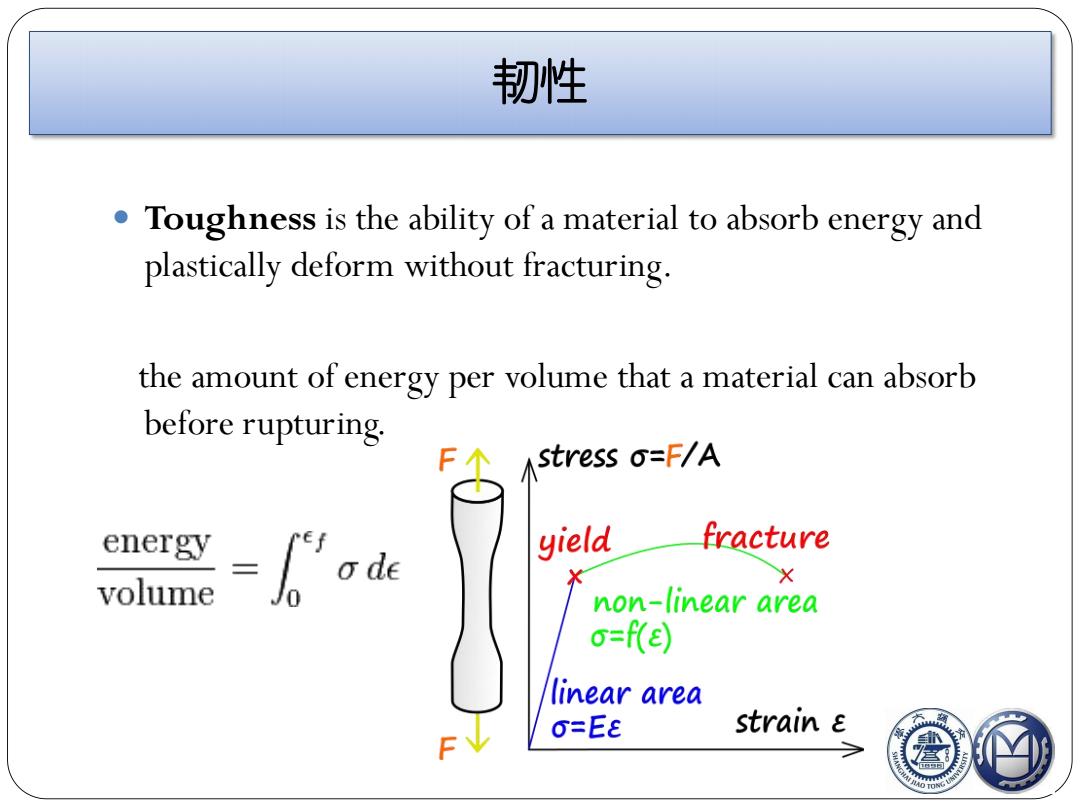
韧性 Toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing. the amount of energy per volume that a material can absorb before rupturing. Astress O=F/A energy "ef fracture 'o de yield X volume non-linear area o=f(E) linear area O=EE strain E
韧性 Toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing. the amount of energy per volume that a material can absorb before rupturing

金属材料 300 250 “The future of 200 Steels Metals” Lu Ke 150- 'ssauybnoy ainpeid 2010 Science 100- Ni alloys Ti alloys Cu 50- alloys Engineering polymeric composites AL alfoys 0 Polymers Mg alloys Carbon fibers Ceramics 1D0 2D0 300 400 1000 2000 Strength-to-weight ratio (MPa cm3g-1)
金属材料 “The future of Metals ” Lu Ke 2010 Science

材料选择 为何钢铁: 钢铁是什么?Fe一C合金? 钢铁成分组织性能关系 钢铁的问题? 复杂的成分,多种晶体结构,多 种相及相结构,多层次相结构, 大范围可调节的组织
材料选择 复杂的成分,多种晶体结构,多 种相及相结构,多层次相结构, 大范围可调节的组织。 为何钢铁:
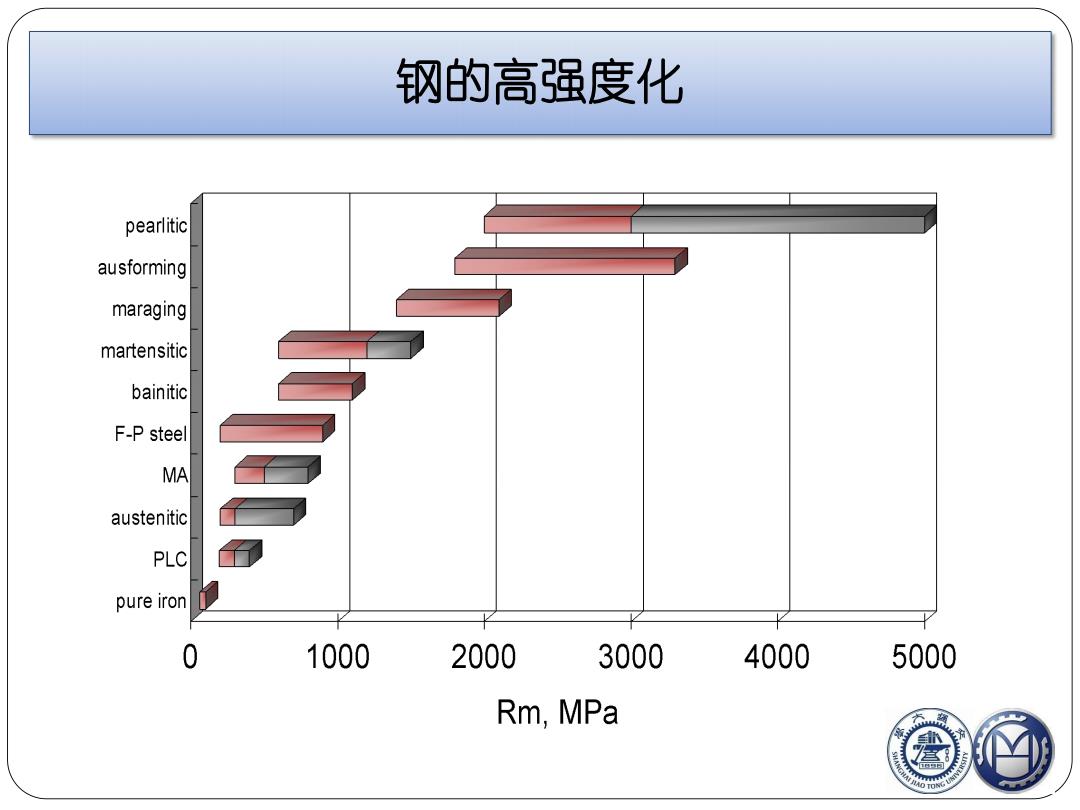
钢的高强度化 pearlitic ausforming maraging martensitic bainitic F-P steel MA austenitic PLC pure iron 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Rm,MPa
钢的高强度化

钢铁依然是现在和可见将来的主要结构材料 来源丰富: faster 价格低廉: higher 制备技术成熟: 应用技术完善: 性能大幅可调: 寿命设计可靠: 循环使用可行: stronger 材料技术来源: 发展空间广阔:
钢铁依然是现在和可见将来的主要结构材料