
目录 /956 一、 视觉系统的形态学 二、经典感受野与非经典感受野 三、视网膜的组成与信息处理 四、外膝体的组成与信息处理 ·五、视皮层细胞的反应特性和视觉功能 ■六、 视觉系统中的串行与平行处理机制 七、选择性注意机制与模型 ■八、立体视觉模型 ·九、神经信息整合作用
目 录 一、视觉系统的形态学 二、经典感受野与非经典感受野 三、视网膜的组成与信息处理 四、外膝体的组成与信息处理 五、视皮层细胞的反应特性和视觉功能 六、视觉系统中的串行与平行处理机制 七、选择性注意机制与模型 八、立体视觉模型 九、神经信息整合作用

Background /956 We perceive the world as three-dimensional. The inputs to our visual system,however,are only a pair of two-dimensional projections on the two retinal surfaces. EBUR EBURY Image in left eye Image in right eye depth
We perceive the world as three-dimensional. The inputs to our visual system, however, are only a pair of two-dimensional projections on the two retinal surfaces. Image in left eye Image in right eye depth Background

鸟类、家禽:双眼朝向两边,双眼(共同)视觉功能一般 /966 Pigeon ☐Binocular vision 捕食者与 被捕食者
鸟类、家禽: 双眼朝向两边,双眼(共同)视觉功能一般 捕食者与 被捕食者

昆虫主要依靠复眼提供距离、速度、方向信息 /966 IC
昆虫主要依靠复眼提供距离、速度、方向信息
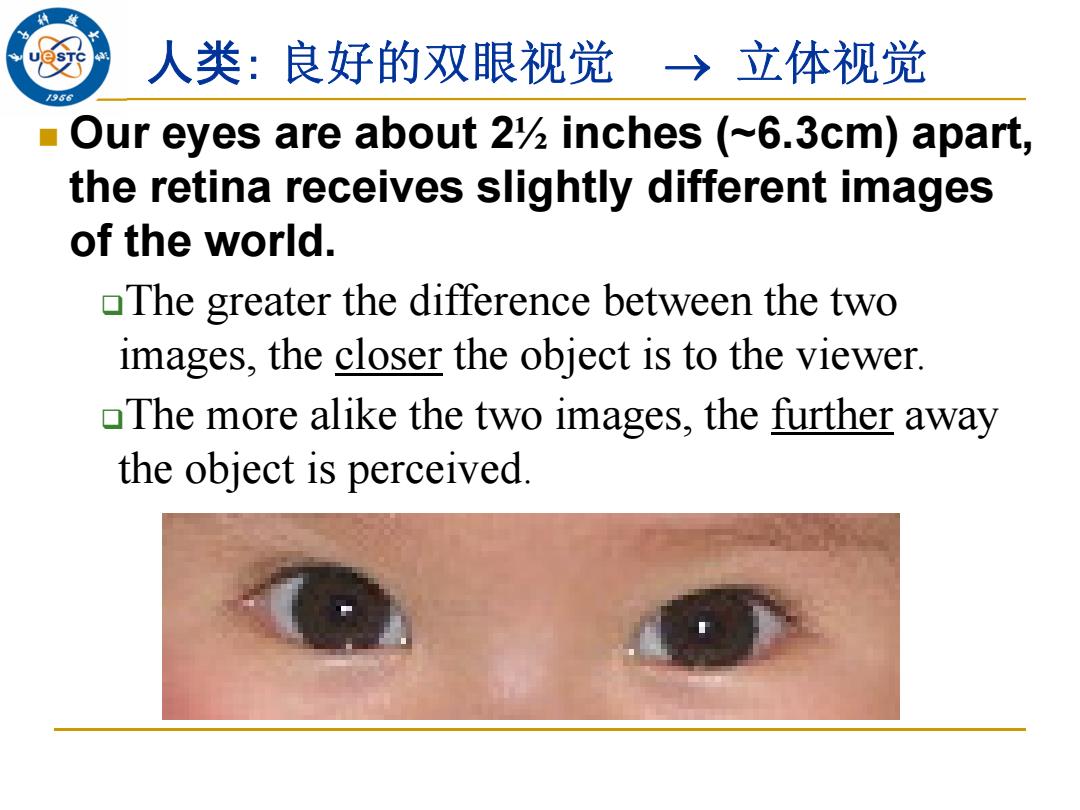
人类:良好的双眼视觉→立体视觉 Our eyes are about 2%inches (~6.3cm)apart, the retina receives slightly different images of the world. The greater the difference between the two images,the closer the object is to the viewer. The more alike the two images,the further away the object is perceived
Our eyes are about 2½ inches (~6.3cm) apart, the retina receives slightly different images of the world. The greater the difference between the two images, the closer the object is to the viewer. The more alike the two images, the further away the object is perceived. 人类: 良好的双眼视觉 立体视觉