Responses to Environmental Changes -2 2.Physiological responses involve a change in the internal state of an organism. Physiological responses take longer than behavioral responses. ·Example:Human sweat(出汗)in response to hot temperatures.Evaporation of perspiration cools the body -warm-blooded animals(恒温动物)maintain a constant body temperature. Fever(发烧)for infection
Responses to Environmental Changes Responses to Environmental Changes – 2 2. Physiological responses involve a change in the internal state of an organism. • Physiological responses take longer than behavioral responses. • Example: Human sweat (出汗) in response to hot temperatures. Evaporation of perspiration cools the body. – warm-blooded animals (恒温动物)maintain a constant body temperature. – Fever (发烧) for infection

Responses to Environmental Changes -3 3.Morphological responses involve a change in the development or growth of an organism. Morphological responses take longer than physiological responses. Example:A tree in a high wind area will grow so as to bend with the 6UR3331 Difference in morphology of "sun leaves"and "shade leaves"in response to different light exposure can occur within the same individlor the same spein thiscase prevailing direction of the wind. white oak (Quercus alba)
Responses to Environmental Changes Responses to Environmental Changes – 3 3. Morphological responses involve a change in the development or growth of an organism. • Morphological responses take longer than physiological responses. • Example: A tree in a high wind area will grow so as to bend with the prevailing direction of the wind

The grasshopper蝗虫can change its color to match its surroundings 。 WHY?To avoid detection by predators ·HOW? -epidermal pigments表皮色素laid down at the time of molting respond to hormones produced in the brain at the time of molting in response to quality and intensity of light et the time of molaing
The grasshopper The grasshopper 蝗虫 can change its color its color to match its surroundings its surroundings • WHY? To avoid detection by predators • HOW? – epidermal pigments 表皮色素 laid down at the time of molting – respond to hormones produced in the brain at the time of molting – in response to quality and intensity of light at the time of molting
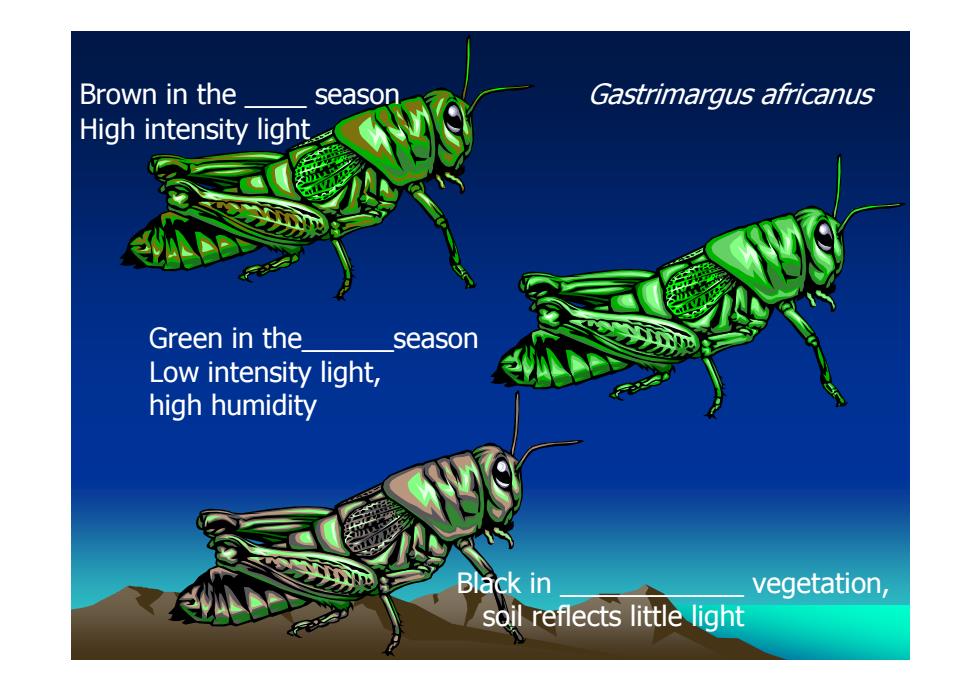
Brown in the season Gastrimargus africanus High intensity light. Green in the season Low intensity light, high humidity Black in vegetation, soil reflects little light
Brown in the _ season Green in the_season Low intensity light, high humidity Black in _ vegetation, soil reflects little light High intensity light Gastrimargus africanus

Responses to Environmental Changes-4 4.Evolutionary responses involve adaptation of a population over a long period of time. Evolutionary responses require many generations Example:sugar maples which grow in Canada are more resistant to winter injury than populations in the southern United States.This difference has a genetic basis
Responses to Environmental Changes Responses to Environmental Changes – 4 4. Evolutionary responses involve adaptation of a population over a long period of time. • Evolutionary responses require many generations. • Example: sugar maples which grow in Canada are more resistant to winter injury than populations in the southern United States. This difference has a genetic basis