
高级加密标准AES要点 15 AES是一种分组密码,用以取代DES的商业应用。 其分组长度为128位,密钥长度为128位、192位 或256位。 ·AES没有使用Feistel结构,每轮由四个独立的运 算组成:字节代换、置换、有限域上的算术运算, 以及与密钥的异或运算。 平四 2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 2/29
2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 2/29 高级加密标准AES要点 ⚫ AES是一种分组密码,用以取代DES的商业应用。 其分组长度为128位,密钥长度为128位、192位 或256位。 ⚫ AES没有使用Feistel结构,每轮由四个独立的运 算组成:字节代换、置换、有限域上的算术运算, 以及与密钥的异或运算

AES的评估准则 15 ●AES的起源 因为DES的不安全,建议用3DES,: 密钥168位 抵御密码分析攻击。但是3DES用软件实现速度较 慢,分组短,仅64位。 美国国家标准技术协会NIST在1997年征集新标准, 要求分组128位,密钥128、192或256位。 15种候选算法在1998年6月通过了第一轮评估,仅 有5个候选算法在1999年8月通过了第二轮评估。 ● 2000年10月,NIST选择Riindael作为AES算法, Rijndael的作者是比利时的密码学家Joan Daemen 博士和Vincent Rijment博士。 2001年11月,NIST完成评估并发布了最终标准 FIPS PUB197。 nn量 2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 3/29
2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 3/29 AES的评估准则 ⚫ AES的起源 ⚫ 因为DES的不安全,建议用3DES,密钥168位, 抵御密码分析攻击。但是3DES用软件实现速度较 慢,分组短,仅64位。 ⚫ 美国国家标准技术协会NIST在1997年征集新标准, 要求分组128位,密钥128、192或256位。 ⚫ 15种候选算法在1998年6月通过了第一轮评估,仅 有5个候选算法在1999年8月通过了第二轮评估。 ⚫ 2000年10月,NIST选择Rijndael作为AES算法, Rijndael的作者是比利时的密码学家Joan Daemen 博士和Vincent Rijmen博士。 ⚫ 2001年11月,NIST完成评估并发布了最终标准 FIPS PUB 197

车太 AES的评估 1950 ·AES评估准则的三大类别 。安全性:指密码分析方法分析一个算法所需的代价 ● 成本:期望AES能够广泛应用于各种实际应用,计 算效率要高 算法和执行特征:算法灵活性、适合于多种硬件和 软件方式的实现、简洁性,便于分析安全性 平N里 2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 4/29
2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 4/29 AES的评估 ⚫ AES评估准则的三大类别 ⚫ 安全性:指密码分析方法分析一个算法所需的代价 ⚫ 成本:期望AES能够广泛应用于各种实际应用,计 算效率要高 ⚫ 算法和执行特征:算法灵活性、适合于多种硬件和 软件方式的实现、简洁性,便于分析安全性

Table 5.1 NIST Evaluation Criteria for AES(September 12,1997)(page 1 of 2) SECURITY .Actual security:compared to other submitted algorithms(at the same key and block size). .Randomness:The extent to which the algorithm output is indistinguishable from a random permutation on the input block. .Soundness:of the mathematical basis for the algorithm's security. .Other security factors:raised by the public during the evaluation process,including any attacks which demonstrate that the actual security of the algorithm is less than the strength claimed by the submitter. COST .Licensing requirements:NIST intends that when the AES is issued,the algorithm(s) specified in the AES shall be available on a worldwide,non-exclusive,royalty-free basis. .Computational efficiency:The evaluation of computational efficiency will be applicable to both hardware and software implementations.Round 1 analysis by NIST will focus primarily on software implementations and specifically on one key-block size combination (128-128);more attention will be paid to hardware implementations and other supported key-block size combinations during Round 2 analysis.Computational efficiency essentially refers to the speed of the algorithm.Public comments on each algorithm's efficiency (particularly for various platforms and applications)will also be taken into consideration by NIST. .Memory requirements:The memory required to implement a candidate algorithm--for both hardware and software implementations of the algorithm--will also be considered during the evaluation process.Round 1 analysis by NIST will focus primarily on software implementations;more attention will be paid to hardware implementations during Round 2. 2022/10/1 Memory requirements will include such factors as gate counts for hardware implementations,and code size and RAM requirements for software implementations. 5/29
2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 5/29
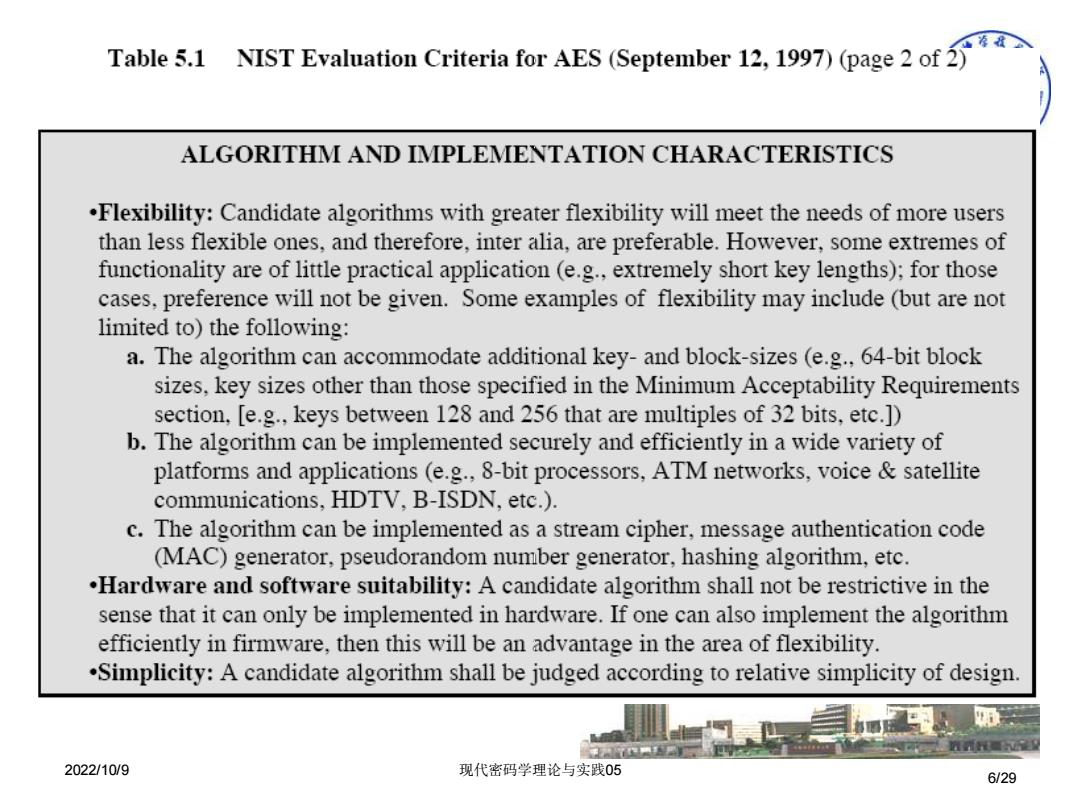
Table 5.1 NIST Evaluation Criteria for AES(September 12,1997)(page 2of ALGORITHM AND IMPLEMENTATION CHARACTERISTICS .Flexibility:Candidate algorithms with greater flexibility will meet the needs of more users than less flexible ones,and therefore,inter alia,are preferable.However,some extremes of functionality are of little practical application(e.g.,extremely short key lengths);for those cases,preference will not be given.Some examples of flexibility may include (but are not limited to)the following: a.The algorithm can accommodate additional key-and block-sizes (e.g.,64-bit block sizes,key sizes other than those specified in the Minimum Acceptability Requirements section,[e.g.,keys between 128 and 256 that are multiples of 32 bits,etc.] b.The algorithm can be implemented securely and efficiently in a wide variety of platforms and applications (e.g.,8-bit processors,ATM networks,voice satellite communications,HDTV,B-ISDN,etc.). c.The algorithm can be implemented as a stream cipher,message authentication code (MAC)generator,pseudorandom number generator,hashing algorithm,etc. .Hardware and software suitability:A candidate algorithm shall not be restrictive in the sense that it can only be implemented in hardware.If one can also implement the algorithm efficiently in firmware,then this will be an advantage in the area of flexibility. .Simplicity:A candidate algorithm shall be judged according to relative simplicity of design 2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 6/29
2022/10/9 现代密码学理论与实践05 6/29