
电子科技女学 Software Architecture Design Pattern Univers的aEe中onic Science and Technolopy时C■ Lecture 4 Concurrent Computing Concurrency vs.Parallism ·Threading Model Thread Synchronization ·案例:高并发网站架构解决方案 Software Architecture and Design Pattern
Software Architecture & Design Pattern Software Architecture and Design Pattern 1 Lecture 4 Concurrent Computing • Concurrency vs. Parallism • Threading Model • Thread Synchronization • 案例:高并发网站架构解决方案
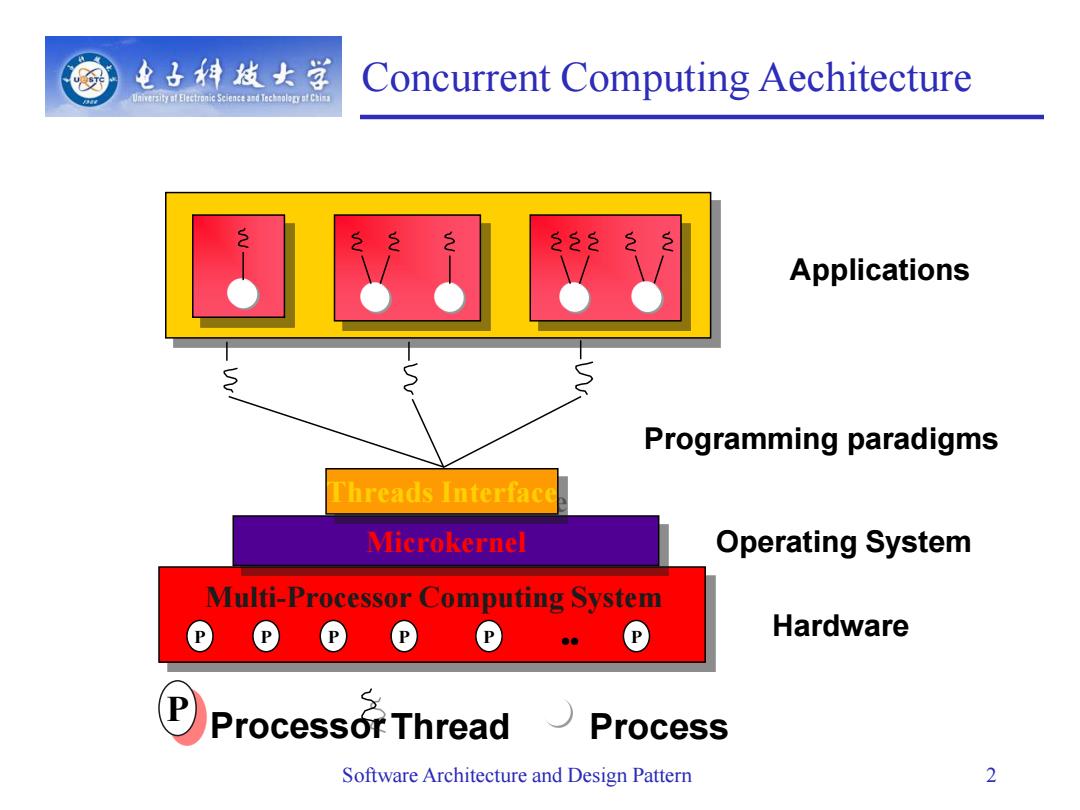
电子特技女学 Concurrent Computing Aechitecture University af Electronic Science and Technoloryf Chim 222 Applications ● Programming paradigms Threads Interface Microkernel Operating System Multi-Processor Computing System Hardware P Processor Thread Process Software Architecture and Design Pattern 2
Concurrent Computing Aechitecture Software Architecture and Design Pattern 2 P P P P P .. P Microkernel Multi-Processor Computing System Threads Interface Hardware Operating System ProcessorThread Process P Applications Programming paradigms

电子科技女学 Software Architecture Design Pattern University Eectronic Scienceand ecol Parallel computing:using multiple processors in parallel to solve problems more quickly than with a single processor 。 Examples of parallel machines: -A cluster computer that contains multiple PCs combined together with a high speed network -A shared memory multiprocessor (SMP*)by connecting multiple processors to a single memory system -A Chip Multi-Processor (CMP)contains multiple processors(called cores)on a single chip Concurrent execution comes from desire for performance; unlike the inherent concurrency in a multi-user distributed system Technically,SMP stands for "Symmetric Multi-Processor" Software Architecture and Design Pattern 3
Software Architecture & Design Pattern Software Architecture and Design Pattern 3 • Parallel computing: using multiple processors in parallel to solve problems more quickly than with a single processor • Examples of parallel machines: – A cluster computer that contains multiple PCs combined together with a high speed network – A shared memory multiprocessor (SMP*) by connecting multiple processors to a single memory system – A Chip Multi-Processor (CMP) contains multiple processors (called cores) on a single chip • Concurrent execution comes from desire for performance; unlike the inherent concurrency in a multi-user distributed system * Technically, SMP stands for “Symmetric Multi-Processor

电子科技女学 Software Architecture Design Pattern University af Electronic Science and Technoloryf Chim Motivation for Concurrency Leverage hardware/software advances,e.g. multi-processors and OS thread support Increase performance,e.g.,overlap computation and communication Improve response-time,e.g.,GUIs and network servers Simplify program structure,e.g.,synchronous vs.asynchronous network IPC Software Architecture and Design Pattern 4
Software Architecture & Design Pattern Software Architecture and Design Pattern 4 Motivation for Concurrency • Leverage hardware/software advances, e.g. multi-processors and OS thread support • Increase performance, e.g., overlap computation and communication • Improve response-time, e.g., GUIs and network servers • Simplify program structure, e.g., synchronous vs. asynchronous network IPC
电子科技女学 Software Architecture Design Pattern University af Electronic Science and Technoloryf Chim Definitions 。Concurrency -"Logically"simultaneous processing Does not imply multiple processing elements ·Parallelism -"Physically"simultaneous processing Involves multiple processing elements and/or independent device operations Both concurrency and parallelism require controlled access to shared resources,e.g.I/O devices,files,database records,in-core data structures,consoles,etc. Software Architecture and Design Pattern 5
Software Architecture & Design Pattern Software Architecture and Design Pattern 5 Definitions • Concurrency - “Logically" simultaneous processing - Does not imply multiple processing elements • Parallelism - “Physically" simultaneous processing - Involves multiple processing elements and/or independent device operations Both concurrency and parallelism require controlled access to shared resources, e.g. I/O devices, files, database records, in-core data structures, consoles, etc