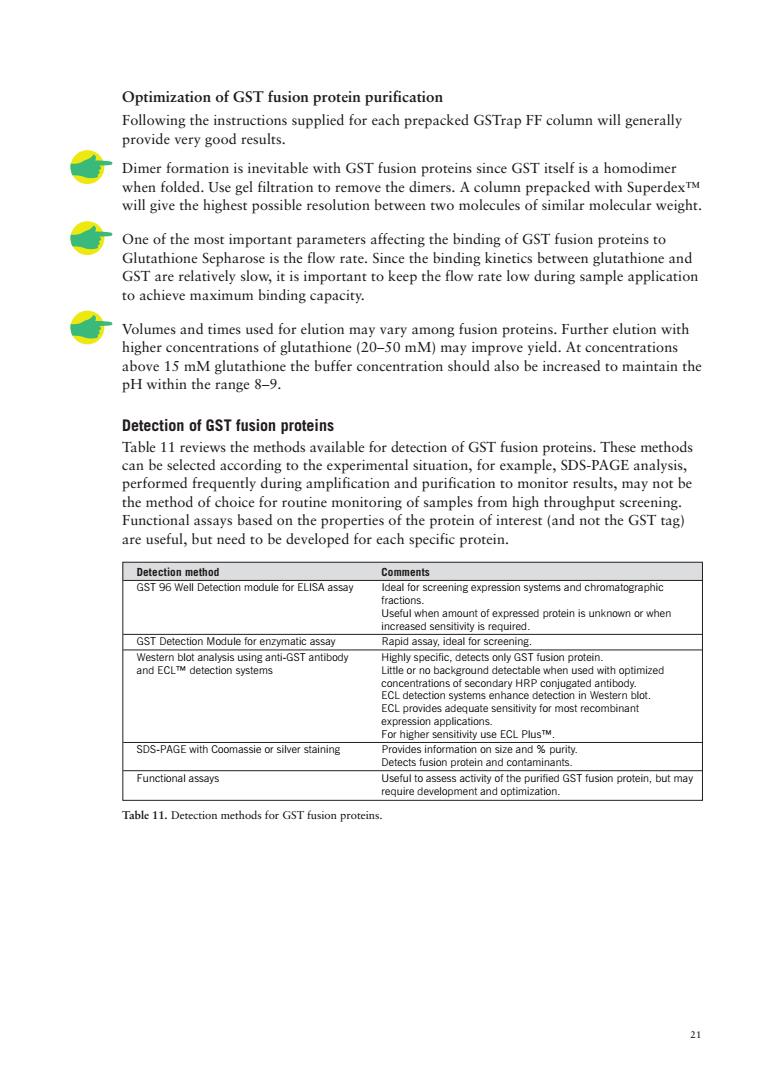
Optimization of GSTfusion protein purification Following the instructions supplied for each prepacked GSTrap FF column will generally provide very good results. Dimer formation is inevitable with GST fusion proteins since GST itself is a homodimer when folded.Use gel filtration to remove the dimers.A column prepacked with Superdex will give the highest possible resolution between two molecules of similar molecular weight. One of the most important parameters affecting the binding of GST fusion proteins to Glutathione Sepharose is the flow rate.Since the binding kinetics between glutathione and GST are relatively slow,it is important to keep the flow rate low during sample application to achieve maximum binding capacity. s used for elutio sof guathione (2050 mM) g fusion proteins.Further elution with vield.At 15 mM glutathion H within the range 8-9. Detection of GST fusion proteins Table 11 reviews the methods available for detection of GST fusion proteins.These methods can be selected according to the experimental situation,for example,SDS-PAGE analysis, performed frequently during amplification and purification to monitor results,may not be the method of choice for routine monitoring of samples from high throughput screening. Functional assays based on the properties of the protein of interest(and not the GST tag) are useful,but need to be developed for each specific protein. ion module for ELISA assay ion5到ys s and chro matographic en amount of expressed protein is GST Detection Module for enzymatic assay Rapid assay.ideal for screening. SDS-PAGE with Coomassie or silver staining Functional assays ,but may Table 11.Detection methods for GST fusion proteins. 2
21 Optimization of GST fusion protein purification Following the instructions supplied for each prepacked GSTrap FF column will generally provide very good results. Dimer formation is inevitable with GST fusion proteins since GST itself is a homodimer when folded. Use gel filtration to remove the dimers. A column prepacked with Superdex™ will give the highest possible resolution between two molecules of similar molecular weight. One of the most important parameters affecting the binding of GST fusion proteins to Glutathione Sepharose is the flow rate. Since the binding kinetics between glutathione and GST are relatively slow, it is important to keep the flow rate low during sample application to achieve maximum binding capacity. Volumes and times used for elution may vary among fusion proteins. Further elution with higher concentrations of glutathione (20–50 mM) may improve yield. At concentrations above 15 mM glutathione the buffer concentration should also be increased to maintain the pH within the range 8–9. Detection of GST fusion proteins Table 11 reviews the methods available for detection of GST fusion proteins. These methods can be selected according to the experimental situation, for example, SDS-PAGE analysis, performed frequently during amplification and purification to monitor results, may not be the method of choice for routine monitoring of samples from high throughput screening. Functional assays based on the properties of the protein of interest (and not the GST tag) are useful, but need to be developed for each specific protein. Detection method Comments GST 96 Well Detection module for ELISA assay Ideal for screening expression systems and chromatographic fractions. Useful when amount of expressed protein is unknown or when increased sensitivity is required. GST Detection Module for enzymatic assay Rapid assay, ideal for screening. Western blot analysis using anti-GST antibody Highly specific, detects only GST fusion protein. and ECL™ detection systems Little or no background detectable when used with optimized concentrations of secondary HRP conjugated antibody. ECL detection systems enhance detection in Western blot. ECL provides adequate sensitivity for most recombinant expression applications. For higher sensitivity use ECL Plus™. SDS-PAGE with Coomassie or silver staining Provides information on size and % purity. Detects fusion protein and contaminants. Functional assays Useful to assess activity of the purified GST fusion protein, but may require development and optimization. Table 11. Detection methods for GST fusion proteins
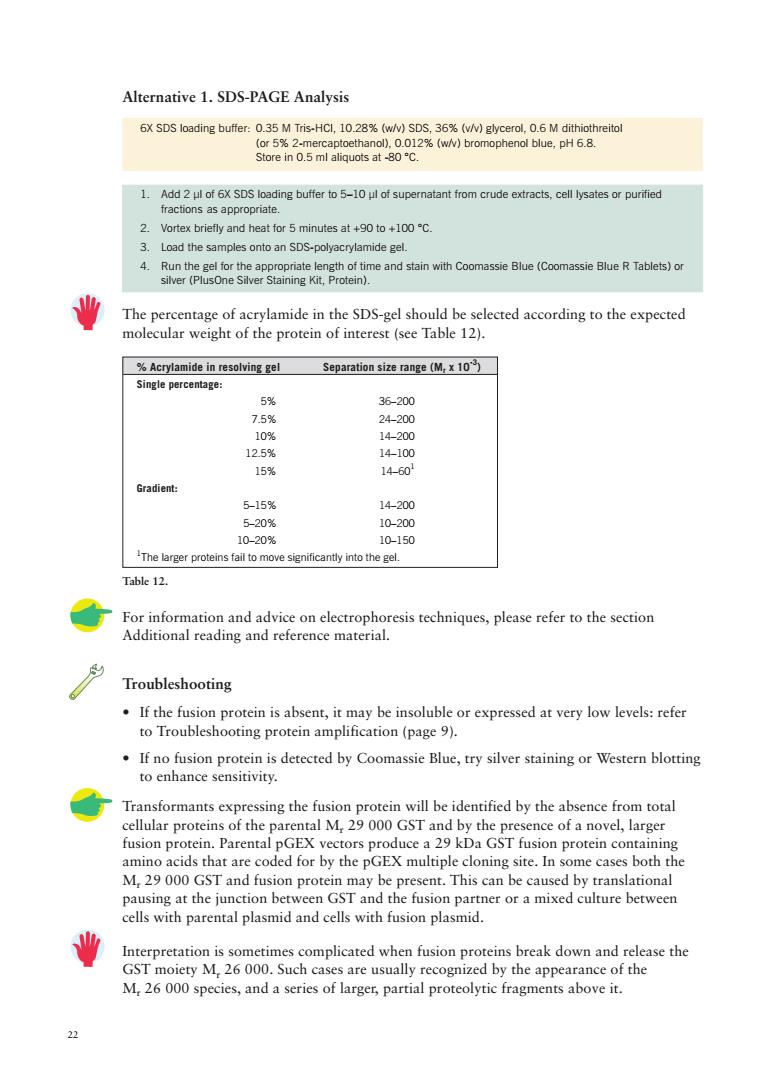
Alternative 1.SDS-PAGE Analysis 6X SDS loading buffer:0.35 M Tris-HCI,108%(w/v)SDS.36%(v/)glycerol,.6M dithiothreitol 8g82a5inesa80g2wbomopeabueH6a 1.Add loading buffer to5-10f superatant from crude extracts,cell lysatesr purified fractions as appropriate 2.Vortex briefly and heat for 5 minutes at 90 to +100C. 3 Load the samples onto an SDS-polvacrvlamide gel 4 The percentage of acrylamide in the SDS-gel should eeled according to the expected %Acrylamide in resolving gel Separation size range (M,x 10) Single percentage: 5 36-209 7.59 125 15% 5-15% 14-200 5-20% 10-200 10-20% 10-150 The the gel. Table 12. For information and advice on electrophoresis techniques,please refer to the section Additional reading and reference material. Troubleshooting h robmay be insolble or expresed ar very low level:rfer oting protein amplification (page 9). .If no fusion protein is detected by Coomassie Blue,try silver staining or Western blotting to enhance sensitivity. will be identified by the absence from total pare A ence of a novel,larg ent Is p n protein co 。 M.29000GsT d fusio site. s both can t caus wh他pth P tner or a mi e between Interpretation is sometimes complicated when fusion proteins break down and release the GST moiety M.26 000.Such cases are usually recognized by the appearance of the M,26 000 species,and a series of larger,partial proteolytic fragments above it
22 Alternative 1. SDS-PAGE Analysis For information and advice on electrophoresis techniques, please refer to the section Additional reading and reference material. Troubleshooting • If the fusion protein is absent, it may be insoluble or expressed at very low levels: refer to Troubleshooting protein amplification (page 9). • If no fusion protein is detected by Coomassie Blue, try silver staining or Western blotting to enhance sensitivity. Transformants expressing the fusion protein will be identified by the absence from total cellular proteins of the parental Mr 29 000 GST and by the presence of a novel, larger fusion protein. Parental pGEX vectors produce a 29 kDa GST fusion protein containing amino acids that are coded for by the pGEX multiple cloning site. In some cases both the Mr 29 000 GST and fusion protein may be present. This can be caused by translational pausing at the junction between GST and the fusion partner or a mixed culture between cells with parental plasmid and cells with fusion plasmid. Interpretation is sometimes complicated when fusion proteins break down and release the GST moiety Mr 26 000. Such cases are usually recognized by the appearance of the Mr 26 000 species, and a series of larger, partial proteolytic fragments above it. % Acrylamide in resolving gel Separation size range (Mr x 10-3) Single percentage: 5% 36–200 7.5% 24–200 10% 14–200 12.5% 14–100 15% 14–601 Gradient: 5–15% 14–200 5–20% 10–200 10–20% 10–150 1 The larger proteins fail to move significantly into the gel. 6X SDS loading buffer: 0.35 M Tris-HCl, 10.28% (w/v) SDS, 36% (v/v) glycerol, 0.6 M dithiothreitol (or 5% 2-mercaptoethanol), 0.012% (w/v) bromophenol blue, pH 6.8. Store in 0.5 ml aliquots at -80 °C. 1. Add 2 µl of 6X SDS loading buffer to 5–10 µl of supernatant from crude extracts, cell lysates or purified fractions as appropriate. 2. Vortex briefly and heat for 5 minutes at +90 to +100 °C. 3. Load the samples onto an SDS-polyacrylamide gel. 4. Run the gel for the appropriate length of time and stain with Coomassie Blue (Coomassie Blue R Tablets) or silver (PlusOne Silver Staining Kit, Protein). The percentage of acrylamide in the SDS-gel should be selected according to the expected molecular weight of the protein of interest (see Table 12). Table 12
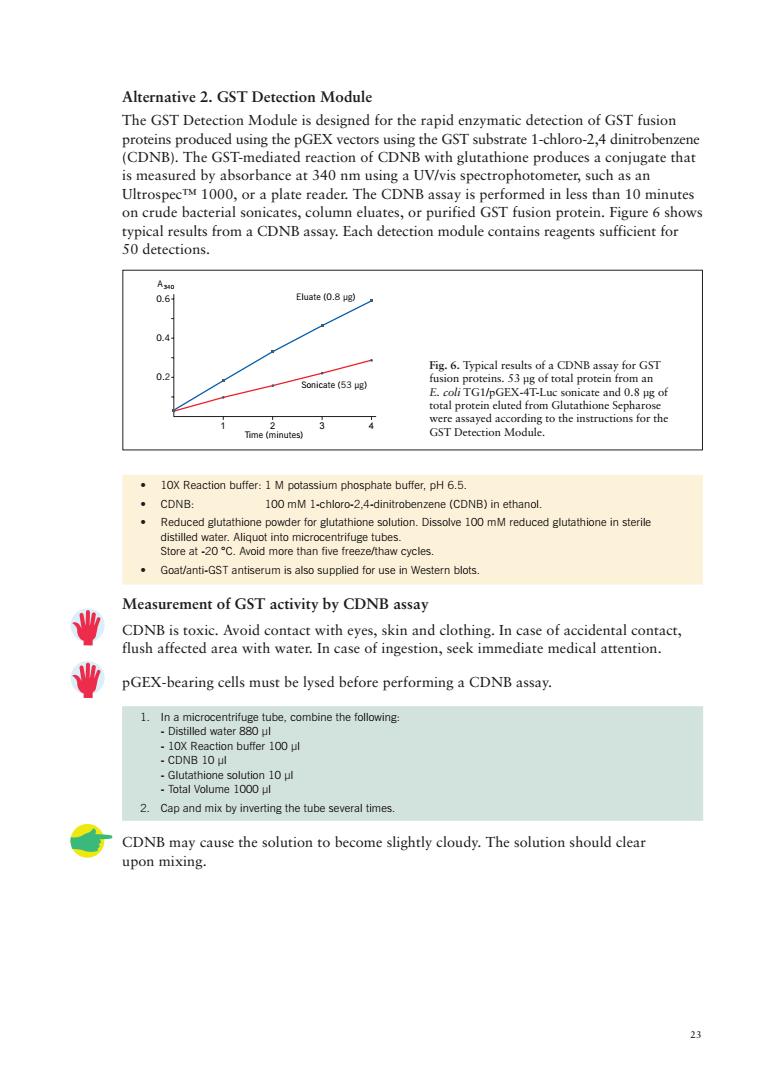
Alternative 2.GST Detection Module The GST Detection Module is designed for the rapid enzymatic detection of GST fusion proteins produced using the pGEX vectors using the GST substrate 1-chloro-2,4 dinitrobenzene (CDNB).The GST-mediated reaction of CDNB with glutathione produces a conjugate that is measured by absorbance at 340 nm using a UV/vis spectrophotometer,such as an UltrospecTM 1000,or a plate reader.The CDNB assay is performed in less than 10 minutes on crude bacterial sonicates,column eluates,or purified GST fusion protein.Figure 6 shows typical results from a CDNB assay.Each detection module contains reagents sufficient for 50detections. Eluate (0.8 ug) 0.d Sonicate (53) otalprotcncote Tamenue 10X Reaction buffer:1 M potassium phosphate buffer.pH 6.5. 100 mM 1-chloro-2.4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB)in ethanol Reduced glutathione powder for glutathioneoioDissolve 100mM reduced glutathone insterile i-STntisermisupplie for se in Wester blot Measurement of GST activity by CDNB assay 业 CDNB is toxic.Avoid contact with eyes,skin and clothing.In case of accidental contact, flush affected area with water.In case of ingestion,seek immediate medical attention. 业 pGEX-bearing cells must be lysed before performing a CDNB assay. 1.In a microcentrifuee tube.combine the following er 100 ul 2.Cap and mix by inverting the tube several times CDNB may cause the solution to become slightly cloudy.The solution should clear upon mixing. 2
23 • 10X Reaction buffer: 1 M potassium phosphate buffer, pH 6.5. • CDNB: 100 mM 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB) in ethanol. • Reduced glutathione powder for glutathione solution. Dissolve 100 mM reduced glutathione in sterile distilled water. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes. Store at -20 °C. Avoid more than five freeze/thaw cycles. • Goat/anti-GST antiserum is also supplied for use in Western blots. Measurement of GST activity by CDNB assay CDNB is toxic. Avoid contact with eyes, skin and clothing. In case of accidental contact, flush affected area with water. In case of ingestion, seek immediate medical attention. pGEX-bearing cells must be lysed before performing a CDNB assay. 1. In a microcentrifuge tube, combine the following: - Distilled water 880 µl - 10X Reaction buffer 100 µl - CDNB 10 µl - Glutathione solution 10 µl - Total Volume 1000 µl 2. Cap and mix by inverting the tube several times. CDNB may cause the solution to become slightly cloudy. The solution should clear upon mixing. Alternative 2. GST Detection Module The GST Detection Module is designed for the rapid enzymatic detection of GST fusion proteins produced using the pGEX vectors using the GST substrate 1-chloro-2,4 dinitrobenzene (CDNB). The GST-mediated reaction of CDNB with glutathione produces a conjugate that is measured by absorbance at 340 nm using a UV/vis spectrophotometer, such as an Ultrospec™ 1000, or a plate reader. The CDNB assay is performed in less than 10 minutes on crude bacterial sonicates, column eluates, or purified GST fusion protein. Figure 6 shows typical results from a CDNB assay. Each detection module contains reagents sufficient for 50 detections. Fig. 6. Typical results of a CDNB assay for GST fusion proteins. 53 µg of total protein from an E. coli TG1/pGEX-4T-Luc sonicate and 0.8 µg of total protein eluted from Glutathione Sepharose were assayed according to the instructions for the GST Detection Module. 1234 Time (minutes) 0.2 0.4 0.6 Sonicate (53 µg) Eluate (0.8 µg) A340

volume in the sample cuvet Cover each cuvette with wax film and invert to mix 340nm 7.Calculate the A/min/ml sample Calculations Where:A(=absorbance at 340 nm at time t in minutes A(t)=absorbance at 340 nm at time t:in minutes 业 The activity of the GST moiety can be affected by the folding of the fusion partner. Absorbance readings obtained for a given fusion protein may not reflect the actual amount of fusion protein present. Troubleshooting rate is linear provided that an nute Plo ate i rse.Adjust th of protein expressior nder standard assay conditions at +22C and in the absence of GST,glutathion /min of ety tha oximately 0.003 (or 0.015 in 5 m nutes).Correct for baseline drift b blanking the with the blank cuvette before ach reading of the sample cuve Alternative 3:GST96 Well Detection Module The GST 96 Well Detection Module provides ●德●●●● a highly sensitive ELISA assay for testing clarified lysates and intermediate purification fractions.Each detection module contains reagents sufficient for 96 detections: ●● 《C● ●●●
24 Alternative 3: GST 96 Well Detection Module The GST 96 Well Detection Module provides a highly sensitive ELISA assay for testing clarified lysates and intermediate purification fractions. Each detection module contains reagents sufficient for 96 detections: 3. Transfer 500 µl volumes of the above solution into two UV-transparent cuvettes. Add sample (5–50 µl) to the "sample cuvette". To the "blank cuvette", add a volume of 1X reaction buffer equal to the sample volume in the sample cuvette. 4. Cover each cuvette with wax film and invert to mix. 5. Place the blank cuvette in the spectrophotometer and blank at 340 nm. Measure the absorbance of the sample cuvette at 340 nm and simultaneously start a stopwatch or other timer. 6. Record absorbance readings at 340 nm at one-minute intervals for 5 minutes by first blanking the spectrophotometer with the blank cuvette and then measuring the absorbance of the sample cuvette. 7. Calculate the A340 /min/ml sample Calculations DA340 /min/ml = Where: A340 (t2) = absorbance at 340 nm at time t2 in minutes A340 (t1) = absorbance at 340 nm at time t1 in minutes DA340 /min/ml values can be used as a relative comparison of GST fusion protein content between samples of a given fusion protein. Adapt the assay to give absolute fusion protein concentrations by constructing a standard curve of DA340/min versus fusion protein amount. The activity of the GST moiety can be affected by the folding of the fusion partner. Absorbance readings obtained for a given fusion protein may not reflect the actual amount of fusion protein present. Troubleshooting • The reaction rate is linear provided that an A340 of approximately 0.8 is not exceeded during the five-minute time course. Plot initial results to verify that the reaction rate is linear over the time course. Adjust the amount of sample containing the GST fusion protein to maintain a linear reaction rate. • If a low absorbance is obtained using the CDNB assay, a Western blot using the Anti-GST Antibody may reveal high levels of protein expression. • Under standard assay conditions at +22 °C and in the absence of GST, glutathione and CDNB react spontaneously to form a chemical moiety that produces a baseline drift at DA340/min of approximately 0.003 (or 0.015 in 5 minutes). Correct for baseline drift by blanking the spectrophotometer with the blank cuvette before each reading of the sample cuvette. A340 (t2) - A340 (t1) (t2 - t1)(ml sample added)

.GSTWell detection plates in which each well is coated with anti-GST antibody,blocked and dried Horse-radish peroxidase conjugated to goat polyclonal anti-GST antibody. .Purified recombinant glutathione S-transferase test protein Additional reagents to be prepared PBS 140 mM NaCl,2.7 mM KCI,10 mM Na,HPO.1.8 mM.PH 7.4 Wash buffer: (mi/well plate). Blocking buffer:1 non-t ny in ilk in PBS with 005%Tw Prepare fresh buffers daily. Aseach fusion protein is captured uniquely,prepare standards of rGST protein and the et fusio dilutio lin1X blocking pro every assay Screening of GST expression clones or chromatographic fractions 1.Bring each test sample to a final volume of 50 ul with 1X PBS. 2.Mix with 50 ul of 2X blocking buffer. 3 For sereening.dilute GSt nrotein standard to 1 ne/10o ul in 1X hlockine budfer 4 For qu and for the target fusion protein 5. dessicant provided 6.Pipette 100 ul of sample into each well 7.Incubate for 1 hour at room temperature in a humidified container or incubator. 8.Empty contentsof the well by flicking the inverted plate. Biohazardous material shoud be pipettedor aspirated into a suable container.) 9.Blot the inverted well or strips on to a paper towel to remove excess liquid. 10.Wash each well 5 times with wash butfer (inverting and ficking out the contents each time). 11.Blot the inverted well or strips on to a paper towel to remove excess wash buffer. 12HPanSTcoe:(1m)nXbkinbuffer.One well plate wll qr 14.Empty well contents and wash twice with wash buffer as previously described. 15.Add soluble horseradish peroxidase substrate*to each well and incubate according to supplier's instructions. *3,3,5,5'-tetramethyl benzidine(A4so)or 2',2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid)diammonium salt(ABTSTM)(A)have been used successfully. 16.Read plate absorbance in a microplate readeror spectrophotometer. Troubleshooting See also Purification and Detection Troubleshooting page 28 25
25 • GST 96 Well detection plates in which each well is coated with anti-GST antibody, blocked and dried. • Horse-radish peroxidase conjugated to goat polyclonal anti-GST antibody. • Purified recombinant glutathione S-transferase test protein. Additional reagents to be prepared: PBS: 140 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4, pH 7.4. Wash buffer: 0.05% Tween™ 20 in PBS (500 ml/96 well plate). Store at room temperature until needed. Blocking buffer: 1 x conc. 3% non-fat dry milk in PBS with 0.05% Tween 20 (10 ml/96 well plate). 2 x conc. 6% non-fat dry milk in PBS with 0.1% Tween 20 (5 ml/96 well plate). Prepare fresh buffers daily. As each fusion protein is captured uniquely, prepare standards of rGST protein and the target fusion protein using a dilution series from 100 ng/100 µl to 10 pg/µl in 1X blocking buffer if quantification is required. Run recombinant GST (rGST) protein as a standard control in every assay. Screening of GST expression clones or chromatographic fractions 1. Bring each test sample to a final volume of 50 µl with 1X PBS. 2. Mix with 50 µl of 2X blocking buffer. 3. For screening: dilute rGST protein standard to 1 ng/100 µl in 1X blocking buffer. 4. For quantification: use dilution series from 100 ng/100 µl to 10 pg/µl in 1X blocking buffer for rGST protein and for the target fusion protein. 5. Remove one 96-well plate from the foil pouch. If using less than 96 wells, carefully remove the well strips from the holder by pushing up on the wells from below. Store unused swell strips in the pouch with the dessicant provided. 6. Pipette 100 µl of sample into each well. 7. Incubate for 1 hour at room temperature in a humidified container or incubator. 8. Empty contents of the well by flicking the inverted plate. (Biohazardous material should be pipetted or aspirated into a suitable container.) 9. Blot the inverted well or strips on to a paper towel to remove excess liquid. 10. Wash each well 5 times with wash buffer (inverting and flicking out the contents each time). 11. Blot the inverted well or strips on to a paper towel to remove excess wash buffer. 12. Dilute HRP/anti-GST conjugate 1:10 000 (1 µl:10 ml) in 1X blocking buffer. One 96 well plate will require 10 ml of the diluted solution. 13. Add 100 µl of diluted HRP/anti-GST conjugate to each well and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature in a humidified container or incubator. 14. Empty well contents and wash twice with wash buffer as previously described. 15. Add soluble horseradish peroxidase substrate* to each well and incubate according to supplier's instructions. *3,3',5,5'-tetramethyl benzidine (A450) or 2',2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS™) (A410) have been used successfully. 16. Read plate absorbance in a microplate reader or spectrophotometer. Troubleshooting See also Purification and Detection Troubleshooting page 28