
2 Chapter 1 3.Van't Hoff and Le Bel proposed that the 4 atoms to which carbon forms bonds sit 4.ofa regula tetrahedron. nd pointing B.Covalent bonds 1.Atoms bond together because the resulting compound is more stable than the ind A tion of th rest noble to form ionic con c.Atoms in the middle of the periodic table share electrons by forming covalent 2.The mber of covalent bonds formed by nds electrons it has and on the number it needs to achieve an octet. on the number of 3.Covalent bonds can be represented two ways. res,bo nds are represented as pairs of dots s drawn between two 4.Valence electrons not used for bonding are called lone-pair electrons. Lone-pair elec c ons are represented as dots. ed b the overlan of two atomic orbitals each of which contains one electron.The two electrons have posite spins. 2.Each of the bo s sha by both atoms 3. overlapping orbital symmetrical and are called a bonds Bond strength is the measure of the amount of energy needed to break a bond. Bond leng is the optimum distance erween nucle n (ond length and bond strength a. n ca mms 4 bond ith le orbita orbital b. rahedrally oriented. c.Because these orbitals are unsymmetrical,they can form stronger bonds than orbitals can geometry and a bond angle of 109.5 2. re of etha ne has the same type of hybridization as occurs C bond is forn ed rlap of two sp orbitals. angles are very close to those of methane. 1R engths and I.If one carbon 2s orbital combines with two carbon 2p orbitals,three hybrid sp nd one p orbital remains oar to 3.Two different types of bonds form between two carbons. a.A o bond forms from the overlap of two sp2orbitals. b.A n bond forms by sideways overla c

Structure and Bonding 3 obiato arbon double bond a onds for f bitals of hy en The double bond of ethylene is both shorter and stronger than the C-C bond of ethane. C.sp Orbitals (Sec 1.10 eiormcaandwbpasaiewntnangcartbon2porbital,twohybnidsporbitals 2.The two sp orbitals are 180 apart,and the two p orbitals are perpendicular to them and to other 3. wo dil type s of bonds form of two orhitals o中w,u0 qaeo e se um00ys!u0eao少 ide n of four norhitale 4.Acetylene is composed of a carbon-carbon triple bond and two o bonds formed between th g two sp orbit als of carbon and the Is orbi f hydrogen 00g.10 arbon-carbon .od td byusin hybrid prbitals 2.Both the nitrogen atom in ammonia and the oxygen atom in water form sphybrid 3.The bond angles between hydrogen and the central atom is often less than 109 because the lone-pair electrons take up more room than the o bond. 4.Beca e of their positions s in the e thir typic phosphorus and sun form more valent bond IV.Molecular hita A.Molecular orbitals arise from a mathematical combination of atomic orbitals and belong to the entire molecule. r in energy than the two b.The subtractive combination is an antibonding MO and is higher in energy than orbitals. 2.A nod the two hydrogen Is atomic rs ben nu onsaenfIedehot 3.The number of MOs in a molecule is the same as the number of ato orbitals combined V.Che structu on 112) Condensed structures don't show C-H bonds and don't show the bonds between 2. CH3,CH2 and CH units. ures are still aren't usually shown c.Other atoms are shown

4 Chapter1 Solutions to Problems tothe proper energy levelsn with the lowest leve ore assigning electron s to a higher energy level 2p朴牛+ Oxygen 2s+ 1s+ Remember that only two electrons can occupy the same orbital,and that they must be of nd-state electror dowAecep2YoniSeaiatenageaRiHeoS example,the elctron confiuration for oxyen is 3p↓— 3s什 Silicon 2p什+H 2s Is way to represent groud-state clctron coin ori: C)122s22p53s23p4 3p什十+ 3什 Sulfur 2p什什 2什 什
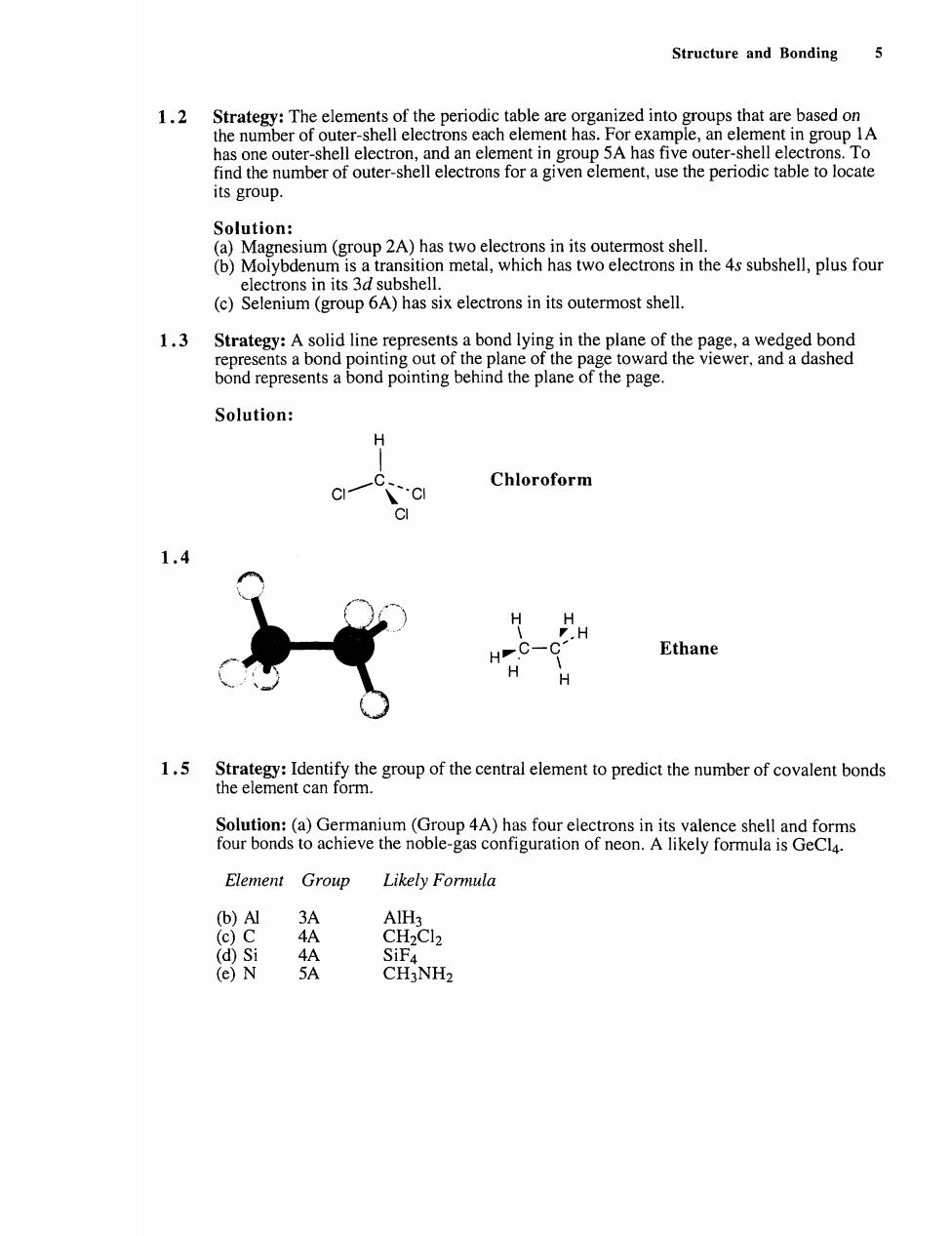
Structure and Bonding 5 1.2 he me o n h ent in group IA Solution: ons in its 3d subshell. (c)Selenium(group 6A)has six electrons in its outermost shell. 1.3 Strategy:bond A solid li ts a bond lyi bndbond pontingnd the pofpage. Solution: H CI- Chloroform 1.d H PH Ethane H 1.5 Identify the group of the central element to predict the number of covalent bonds Element Group Likely Formula (b)Al (d)Si SiF (e)N 5A CH3NH2
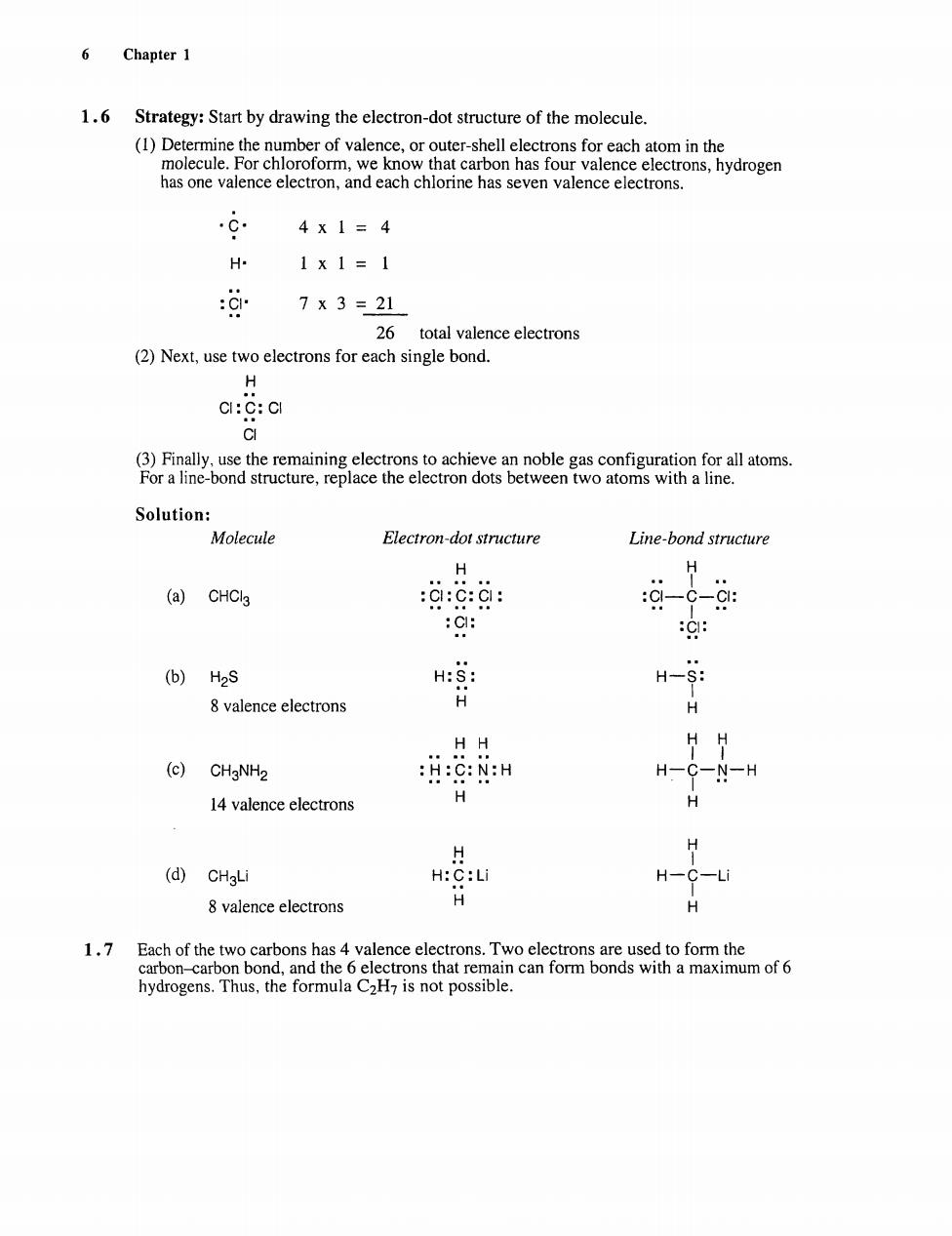
6 Chapter 1 1.6 Strategy:Start by drawing the electron-dot structure of the molecule. has onc valer nce elect ectrons,hydrogen a 4x1=4 H 1x1=1 :CI 7X3=21 26 total valence electrons (2)Next,use two electrons for each single bond. H CI:C:CI Solution: Molecule Electron-dot structure Line-bond structure H H (a)CHCIl3 :0:0g :c-c-: :C: 9: (b)H2S 8 valence electrons 磨 H-S: HH (c)CHaNH2 N:H 14 valence electrons H (d)CHaLi H:C:Li H--U 8 valence electrons H ons has 4 vale ce electrons Two elec hydrogens.Thus,the formula C2H is not possible